Heat stabilizers protect materials by preventing degradation during high-temperature processing, while UV stabilizers shield your products from damage caused by ultraviolet radiation exposure. Choosing the right stabilizer ensures improved durability and longevity of plastics or coatings under specific environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
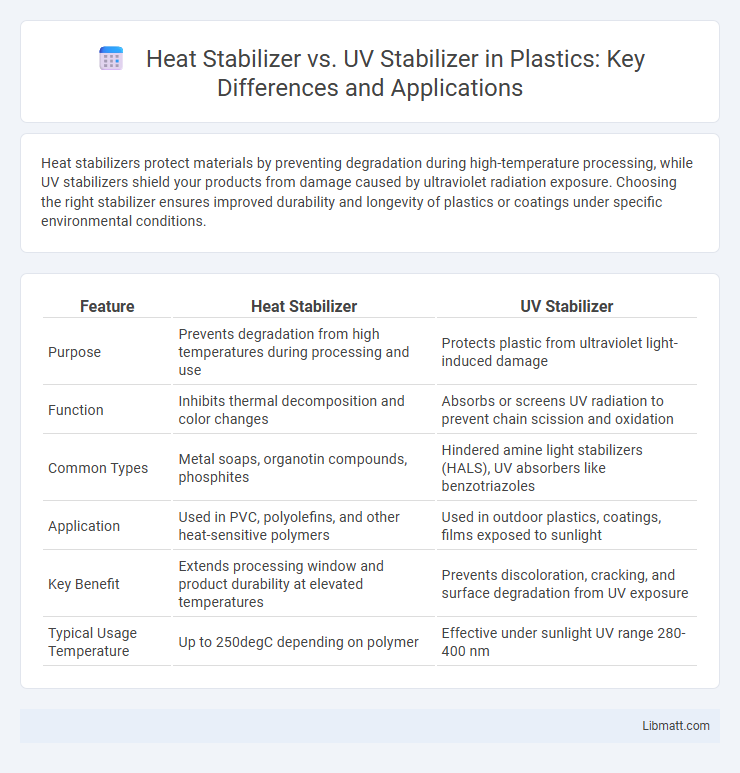
| Feature | Heat Stabilizer | UV Stabilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents degradation from high temperatures during processing and use | Protects plastic from ultraviolet light-induced damage |
| Function | Inhibits thermal decomposition and color changes | Absorbs or screens UV radiation to prevent chain scission and oxidation |
| Common Types | Metal soaps, organotin compounds, phosphites | Hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS), UV absorbers like benzotriazoles |
| Application | Used in PVC, polyolefins, and other heat-sensitive polymers | Used in outdoor plastics, coatings, films exposed to sunlight |
| Key Benefit | Extends processing window and product durability at elevated temperatures | Prevents discoloration, cracking, and surface degradation from UV exposure |
| Typical Usage Temperature | Up to 250degC depending on polymer | Effective under sunlight UV range 280-400 nm |
Introduction to Polymer Stabilizers
Polymer stabilizers enhance the durability and longevity of materials by protecting them from environmental degradation. Heat stabilizers prevent thermal decomposition during processing and usage, maintaining your polymer's mechanical properties under high temperatures. UV stabilizers absorb or block ultraviolet radiation, preventing photodegradation and discoloration caused by sunlight exposure.
Understanding Heat Stabilizers
Heat stabilizers are essential additives in plastics and polymers, preventing degradation caused by high processing temperatures by maintaining material integrity and mechanical properties. They function by neutralizing free radicals and decomposing peroxides formed during thermal exposure, thereby extending the lifespan of your products. Unlike UV stabilizers, which protect against ultraviolet radiation, heat stabilizers specifically target thermal decomposition to enhance durability during manufacturing and use.
Role and Types of UV Stabilizers
UV stabilizers play a crucial role in protecting polymers from degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation, extending the lifespan and maintaining the physical properties of materials exposed to sunlight. Common types of UV stabilizers include UV absorbers, which absorb harmful UV radiation; hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS), which neutralize free radicals formed during UV exposure; and quenchers, which dissipate the energy absorbed by the polymer. These stabilizers are essential in industries like plastics, coatings, and automotive manufacturing to enhance durability and prevent discoloration or cracking.
Mechanisms of Action: Heat vs. UV Stabilizers
Heat stabilizers work by neutralizing free radicals and decomposing harmful metal ions generated during the thermal degradation of polymers, effectively preventing discoloration and loss of mechanical properties at elevated temperatures. UV stabilizers absorb or screen harmful ultraviolet radiation, converting it into harmless heat or dissipating it, which protects your materials from photodegradation and surface cracking caused by prolonged sunlight exposure. Understanding the specific mechanisms of action helps in selecting the right stabilizer to enhance the durability and lifespan of polymers under thermal or UV stress conditions.
Common Applications of Heat Stabilizers
Heat stabilizers are primarily used in the manufacturing of PVC products, such as window profiles, pipes, and electrical cables, to prevent degradation caused by high processing temperatures. These stabilizers enhance the thermal resistance and durability of polymers during extrusion and molding processes. Your choice of heat stabilizer ensures improved product longevity and performance in heat-exposed applications.
Key Uses for UV Stabilizers
UV stabilizers are essential for protecting materials, especially plastics and coatings, from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation by preventing degradation, discoloration, and loss of mechanical properties. They are widely used in outdoor applications such as automotive parts, outdoor furniture, packaging, and construction materials to enhance durability and extend the lifespan of products exposed to sunlight. Your choice of UV stabilizer ensures optimum resistance to fading and brittleness, maintaining the material's integrity under prolonged UV exposure.
Performance Comparison: Heat vs. UV Stabilization
Heat stabilizers excel in maintaining material integrity by preventing thermal degradation during processing and high-temperature applications, ensuring long-term durability and mechanical performance. UV stabilizers primarily protect polymers from photodegradation caused by ultraviolet radiation, preserving color, flexibility, and surface properties under prolonged sunlight exposure. Your choice depends on the environmental stressors; heat stabilizers are ideal for high-heat conditions, while UV stabilizers are essential for outdoor products exposed to sunlight.
Selection Criteria for Stabilizer Choice
Selecting between heat stabilizers and UV stabilizers depends on the polymer's exposure conditions and degradation mechanisms. Heat stabilizers are essential for materials subjected to high processing temperatures or prolonged thermal exposure, preventing thermal degradation by scavenging radicals or decomposing peroxides. UV stabilizers are critical for applications exposed to sunlight or artificial UV sources, protecting polymers from photodegradation by absorbing UV radiation or neutralizing excited states.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Heat stabilizers and UV stabilizers both enhance polymer durability but differ significantly in environmental and safety impacts. Heat stabilizers, especially those containing heavy metals like lead or cadmium, pose toxicity risks and require careful handling and disposal to prevent environmental contamination. UV stabilizers, often based on organic compounds such as benzotriazoles or hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS), tend to be less hazardous and more environmentally friendly, contributing to the safer long-term use of your plastic products.
Future Trends in Stabilizer Technology
Heat stabilizers and UV stabilizers are evolving with advancements in nanotechnology and bio-based materials, enhancing durability and environmental compatibility. Emerging trends focus on multi-functional stabilizers that provide combined heat and UV protection, extending the lifespan of polymers in outdoor applications. Innovations in sustainable and non-toxic stabilizer formulations are driving the future of stabilizer technology toward greener and more efficient solutions.
Heat Stabilizer vs UV Stabilizer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com