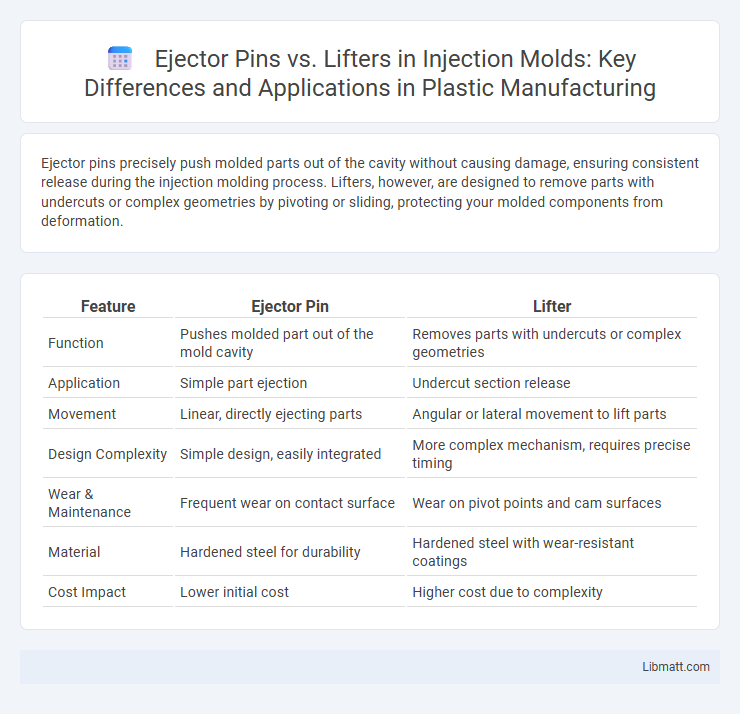
Ejector pins precisely push molded parts out of the cavity without causing damage, ensuring consistent release during the injection molding process. Lifters, however, are designed to remove parts with undercuts or complex geometries by pivoting or sliding, protecting your molded components from deformation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ejector Pin | Lifter |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Pushes molded part out of the mold cavity | Removes parts with undercuts or complex geometries |
| Application | Simple part ejection | Undercut section release |
| Movement | Linear, directly ejecting parts | Angular or lateral movement to lift parts |
| Design Complexity | Simple design, easily integrated | More complex mechanism, requires precise timing |
| Wear & Maintenance | Frequent wear on contact surface | Wear on pivot points and cam surfaces |
| Material | Hardened steel for durability | Hardened steel with wear-resistant coatings |
| Cost Impact | Lower initial cost | Higher cost due to complexity |
Introduction to Ejector Pins and Lifters
Ejector pins and lifters are essential components in injection molding used to remove molded parts from cavities. Ejector pins provide direct, linear force to push parts out, while lifters apply angled force to release undercuts or complex geometries. Proper selection between ejector pins and lifters ensures efficient ejection, minimizes part deformation, and maintains mold integrity.
The Function of Ejector Pins in Injection Molds
Ejector pins in injection molds are critical components designed to push the molded part out of the mold cavity once the plastic has solidified, ensuring smooth and efficient part release. These pins apply uniform ejecting force without damaging the part, maintaining the integrity and precision required in high-volume manufacturing. Their precise placement and durability are essential for preventing defects such as distortion or incomplete ejection during the injection molding cycle.
The Role of Lifters in Mold Ejection
Lifters in injection molds play a critical role in ejecting undercut or side-hole features that cannot be released by conventional ejector pins alone. Unlike ejector pins that push the part vertically out of the cavity, lifters move at an angle to release molded parts with complex geometries, preventing damage and ensuring smooth demolding. This combination enables efficient ejection of intricate components, improving mold functionality and part quality.
Key Differences Between Ejector Pins and Lifters
Ejector pins and lifters serve distinct roles in injection molds, with ejector pins primarily used to push the molded part out of the mold cavity, ensuring quick and precise ejection. Lifters, however, are designed to release undercut features or complex geometries by lifting the part away from the mold, preventing damage to delicate sections during ejection. Understanding these key differences helps you optimize mold design and improve part quality.
Advantages of Using Ejector Pins
Ejector pins in injection molds provide precise and consistent part ejection, reducing the risk of product damage and ensuring high-quality finishes. Their straightforward design allows for easier maintenance and cost-effective manufacturing compared to lifters, which involve more complex mechanisms. By using ejector pins, your mold cycle times improve, ultimately increasing production efficiency and output.
Benefits of Employing Lifters in Mold Design
Lifters in injection molds enhance part ejection by enabling the release of undercuts and complex geometries that ejector pins alone cannot handle. Employing lifters improves mold longevity by reducing wear on ejector pins and decreasing cycle time, leading to higher production efficiency. Your mold design benefits from increased flexibility and precision in part removal, ensuring consistent quality and less post-processing.
Common Applications for Ejector Pins vs Lifters
Ejector pins are commonly used in injection molds to push plastic parts out of the mold cavity during the ejection phase, especially for simple geometries and flat surfaces. Lifters are applied in molds with undercuts or side actions, enabling the release of complex shapes or features that cannot be ejected straight out. Your choice between ejector pins and lifters depends heavily on the part design complexity and the mold's mechanical requirements.
Design Considerations for Ejector Pins and Lifters
Design considerations for ejector pins and lifters in injection molds revolve around material selection, placement, and stroke length to ensure efficient part ejection without damage. Ejector pins typically require precise alignment and hard surface coatings to withstand repetitive impact, while lifters demand angled placement and smooth acting mechanisms to remove undercuts or side cores effectively. Your mold's complexity and part geometry dictate optimal pin diameter and lifter arm design to balance durability and minimize cycle time.
Troubleshooting Ejection Issues: Pins vs Lifters
Ejector pins and lifters serve distinct roles in injection molds, where pins directly push the part out while lifters angle or slide to release complex geometries. Troubleshooting ejection issues often involves inspecting pins for bending or wear and checking lifter mechanisms for proper movement or binding. Your mold's ejection system performance improves by diagnosing whether sticking or damage stems from pin misalignment or lifter malfunction.
Choosing the Right Ejection Method for Your Mold
Choosing the right ejection method for your mold directly impacts product quality and cycle time efficiency. Ejector pins provide precise and controlled ejection ideal for flat or simple geometries, while lifters excel in releasing undercut or complex parts without damaging the molded component. Evaluate your mold design and part complexity to determine whether ejector pins or lifters best support your production needs and ensure smooth mold operation.
Ejector pin vs lifter (in injection molds) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com