Vector graphics use mathematical equations to create sharp, scalable images ideal for logos and designs requiring precision, while raster images consist of pixels, making them better suited for rich, detailed photos but lose quality when resized. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize scalability and clarity or detailed color and texture in your project.
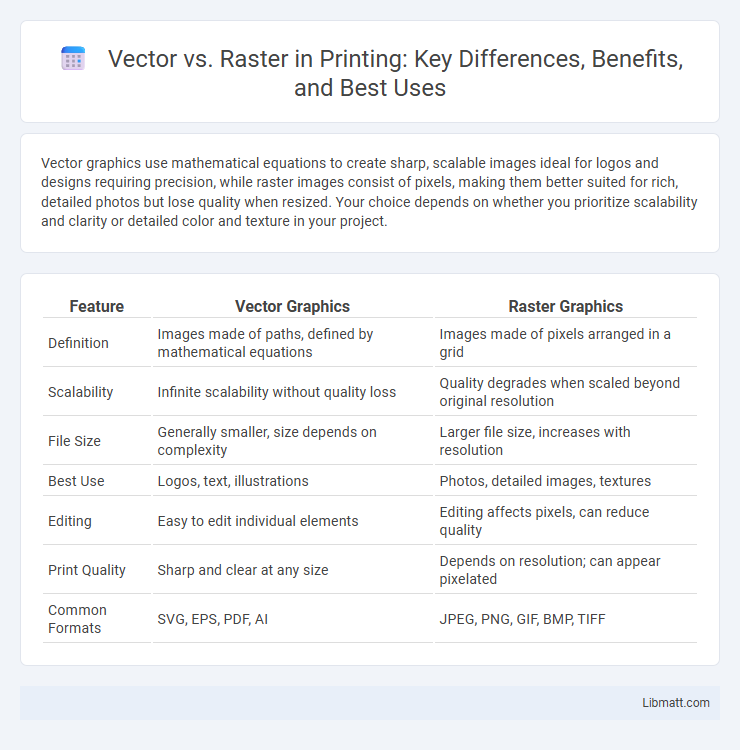
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vector Graphics | Raster Graphics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Images made of paths, defined by mathematical equations | Images made of pixels arranged in a grid |
| Scalability | Infinite scalability without quality loss | Quality degrades when scaled beyond original resolution |
| File Size | Generally smaller, size depends on complexity | Larger file size, increases with resolution |
| Best Use | Logos, text, illustrations | Photos, detailed images, textures |
| Editing | Easy to edit individual elements | Editing affects pixels, can reduce quality |
| Print Quality | Sharp and clear at any size | Depends on resolution; can appear pixelated |
| Common Formats | SVG, EPS, PDF, AI | JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, TIFF |
Introduction to Vector and Raster Graphics
Vector graphics use mathematical equations to create shapes, allowing for infinite scalability without loss of quality, making them ideal for logos and detailed illustrations. Raster graphics are composed of pixels arranged in a grid, offering rich detail and complex color variations but losing clarity when resized beyond their resolution. Understanding the differences between vector and raster graphics helps you choose the right format for your design needs, ensuring optimal quality and performance.
Key Differences Between Vector and Raster
Vector graphics use mathematical equations to represent images through points, lines, and shapes, allowing for infinite scalability without quality loss. Raster graphics consist of a fixed grid of pixels, each holding color information, which can result in pixelation when resized beyond their original resolution. Key differences include scalability, file size, and ideal uses: vectors excel in logos and illustrations, while rasters are preferred for detailed photographs and complex color variations.
Pros and Cons of Vector Graphics
Vector graphics offer scalability without loss of quality, making them ideal for logos, icons, and designs requiring precision and flexibility. Their smaller file sizes enhance performance and ease of editing, but they struggle with complex color gradients and photorealistic images compared to raster graphics. Vector files such as SVG and AI excel in print and digital projects that demand clean, sharp lines but may require conversion for detailed photographic content.
Pros and Cons of Raster Graphics
Raster graphics excel in detailed and complex images with rich color variations, making them ideal for photographs and digital paintings. However, their resolution dependency means image quality deteriorates when scaled up, leading to pixelation and loss of sharpness. You must consider larger file sizes and limited scalability when working with raster graphics for high-resolution displays or print media.
Common Uses of Vector Graphics
Vector graphics are commonly used in logo design, typography, and scalable illustrations due to their ability to maintain crisp lines and quality at any size. They are essential for CAD drawings, technical diagrams, and map creation where precision and scalability are crucial. Digital print media, web graphics, and animation also rely heavily on vector formats like SVG and AI for clear and flexible visual assets.
Typical Applications of Raster Graphics
Raster graphics are predominantly used in digital photography, web images, and detailed artwork where complex color gradients and intricate details matter. They excel in applications such as photo editing, textures in video games, and digital painting due to their pixel-based nature. Common file formats include JPEG, PNG, GIF, and BMP, which support a wide range of color depths and transparency options.
File Formats: Vector vs Raster
Vector file formats such as SVG, AI, and EPS store images using mathematical paths, allowing infinite scalability without loss of quality. Raster file formats like JPEG, PNG, and GIF consist of pixels, making them ideal for detailed photographs but prone to quality degradation when resized. Choosing the right format depends on whether Your project requires crisp lines and scalability (vector) or rich detail and color depth (raster).
Scalability and Resolution Explained
Vector graphics use mathematical formulas to define shapes, allowing infinite scalability without loss of resolution, making them ideal for logos and illustrations that require crisp lines at any size. Raster graphics consist of pixels, so their resolution depends on pixel density; scaling up a raster image can cause pixelation and a loss of quality. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right format for projects where clarity and detail at various sizes are essential.
Editing and Flexibility Comparison
Vector graphics offer superior editing and flexibility due to their use of mathematical paths, allowing you to scale and modify elements without loss of quality. Raster images, composed of pixels, lose clarity when resized and require more effort to edit individual components precisely. For projects demanding frequent adjustments and scalability, vector formats like SVG or AI are more adaptable than raster formats such as JPEG or PNG.
Choosing the Right Format for Your Project
Choosing between vector and raster formats depends on your project's needs for scalability and detail. Vector graphics use mathematical paths for clean, scalable images ideal for logos and illustrations, while raster graphics rely on pixels, offering rich detail best suited for photos and complex images. Understanding these differences ensures you select the optimal format to maintain quality and efficiency in your design work.
vector vs raster Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com