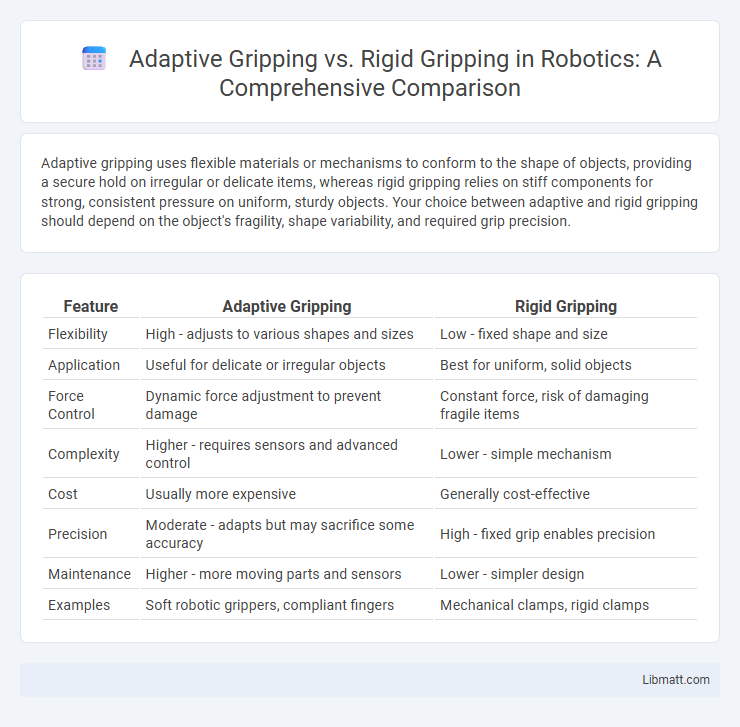
Adaptive gripping uses flexible materials or mechanisms to conform to the shape of objects, providing a secure hold on irregular or delicate items, whereas rigid gripping relies on stiff components for strong, consistent pressure on uniform, sturdy objects. Your choice between adaptive and rigid gripping should depend on the object's fragility, shape variability, and required grip precision.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Adaptive Gripping | Rigid Gripping |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High - adjusts to various shapes and sizes | Low - fixed shape and size |
| Application | Useful for delicate or irregular objects | Best for uniform, solid objects |
| Force Control | Dynamic force adjustment to prevent damage | Constant force, risk of damaging fragile items |
| Complexity | Higher - requires sensors and advanced control | Lower - simple mechanism |
| Cost | Usually more expensive | Generally cost-effective |
| Precision | Moderate - adapts but may sacrifice some accuracy | High - fixed grip enables precision |
| Maintenance | Higher - more moving parts and sensors | Lower - simpler design |
| Examples | Soft robotic grippers, compliant fingers | Mechanical clamps, rigid clamps |
Understanding Gripping Technologies: Adaptive vs. Rigid
Adaptive gripping technology uses flexible materials and sensors to conform to various shapes, enhancing precision and reducing part damage during handling. Rigid gripping relies on fixed, sturdy structures designed for consistent, repeatable grasping of uniform objects, ensuring stability in high-force applications. Your choice between adaptive and rigid gripping depends on the complexity and variability of the items in your automation process.
Core Principles of Adaptive Gripping
Adaptive gripping relies on flexible materials and sensors to conform to the shape and texture of objects, enabling secure handling of irregular or delicate items. This method enhances precision and reduces damage by dynamically adjusting grip force based on real-time feedback. Your automation process benefits from improved versatility and efficiency compared to rigid gripping, which uses fixed structures suited for uniform objects.
Fundamentals of Rigid Gripping Mechanisms
Rigid gripping mechanisms rely on fixed structures such as clamps, chucks, or jaws to hold objects securely, ensuring precise positioning and minimal movement during machining or assembly. These systems depend on mechanical rigidity and high clamping force to prevent slippage, making them ideal for consistent, repeatable tasks with uniform workpieces. Understanding the fundamentals of rigid gripping helps you select the appropriate tooling for applications requiring stability and accuracy.
Key Advantages of Adaptive Grippers
Adaptive grippers offer superior flexibility by conforming to a variety of object shapes and sizes, enhancing precision in handling delicate or irregular items. Their compliant design reduces the risk of damage during gripping, making them ideal for applications requiring gentle yet secure hold. You benefit from increased efficiency and reduced downtime, as adaptive grippers can adapt to diverse tasks without frequent tool changes.
Limitations of Rigid Gripping Systems
Rigid gripping systems face limitations such as reduced flexibility when handling objects with varying shapes, sizes, or delicate surfaces, leading to potential damage or slippage during operation. These systems often require precise object positioning and lack the adaptability to compensate for inconsistencies in the workpiece, which can decrease process efficiency and increase cycle times. Your choice of gripping solution should consider how adaptive gripping systems offer enhanced compliance and versatility to overcome these challenges.
Application Scenarios: Adaptive vs. Rigid Gripping
Adaptive gripping excels in handling delicate or irregularly shaped objects, making it ideal for applications in electronics assembly, food packaging, and medical devices where precision and object variability are critical. Rigid gripping suits environments requiring strong, repeatable holding force on uniform parts, commonly found in automotive manufacturing, heavy machinery, and metal fabrication. Your choice between adaptive and rigid gripping should align with the complexity and fragility of the items being manipulated to optimize performance and reduce damage.
Precision and Flexibility in Gripping Tasks
Adaptive gripping offers superior flexibility by adjusting to varying object shapes and sizes, ensuring secure handling without damage. Rigid gripping excels in precision tasks requiring consistent positioning and firm hold, ideal for uniform objects. Combining both techniques enhances automation efficiency, balancing adaptability with exact control in complex gripping operations.
Cost, Maintenance, and Deployment Considerations
Adaptive gripping systems typically involve higher upfront costs due to advanced sensors and flexible materials, but they reduce long-term expenses through lower maintenance needs and fewer part replacements. Rigid gripping solutions are generally more affordable initially but may incur increased maintenance costs and downtime from wear and misalignment issues. Your choice should consider deployment environments where adaptive gripping enhances efficiency with minimal adjustments, while rigid gripping suits stable, repetitive tasks requiring less frequent recalibration.
Safety and Reliability in Industrial Settings
Adaptive gripping offers enhanced safety and reliability in industrial settings by automatically adjusting to varying shapes and sizes, reducing the risk of product damage and workplace accidents. Rigid gripping provides consistent pressure and high precision for uniform objects, ensuring stable hold but may increase the likelihood of slippage or breakage with unpredictable loads. Your choice between adaptive and rigid gripping systems will impact operational safety, product integrity, and overall process reliability.
Future Trends in Gripping Technology
Future trends in gripping technology emphasize the rise of adaptive gripping systems that utilize soft robotics and sensor integration to enhance flexibility and precision in handling diverse objects. Rigid gripping solutions continue to evolve with advancements in materials science, offering improved strength and durability for heavy-duty applications. Your production efficiency can significantly benefit from hybrid gripping systems combining adaptive sensitivity with rigid stability to meet the demands of complex manufacturing environments.
Adaptive gripping vs Rigid gripping Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com