Telemanipulation enables you to control robotic systems remotely with precision, allowing physical interaction in hazardous or inaccessible environments. Telepresence focuses on immersive communication, providing real-time audio-visual feedback to simulate being physically present at a distant location.
Table of Comparison
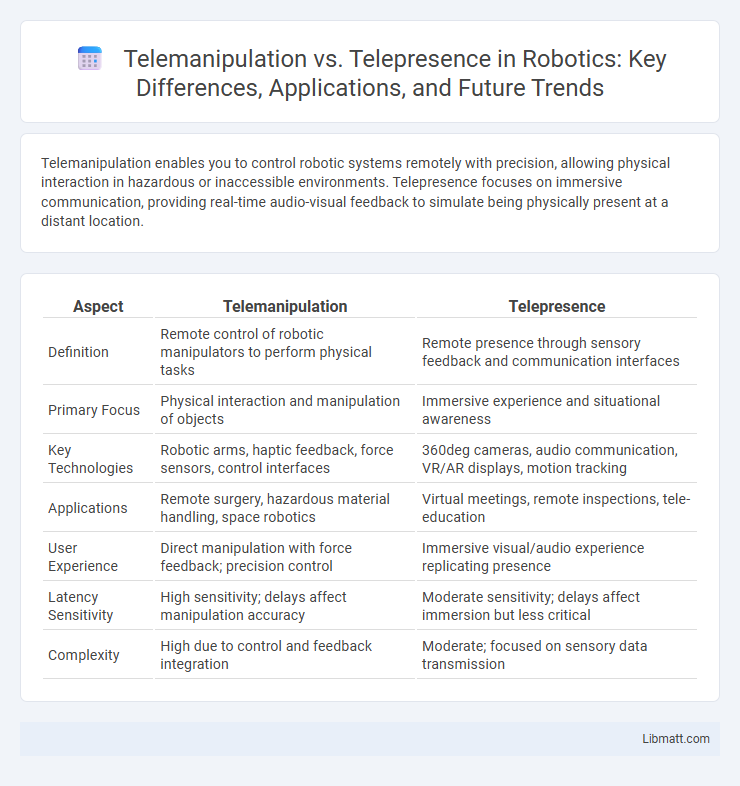
| Aspect | Telemanipulation | Telepresence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Remote control of robotic manipulators to perform physical tasks | Remote presence through sensory feedback and communication interfaces |
| Primary Focus | Physical interaction and manipulation of objects | Immersive experience and situational awareness |
| Key Technologies | Robotic arms, haptic feedback, force sensors, control interfaces | 360deg cameras, audio communication, VR/AR displays, motion tracking |
| Applications | Remote surgery, hazardous material handling, space robotics | Virtual meetings, remote inspections, tele-education |
| User Experience | Direct manipulation with force feedback; precision control | Immersive visual/audio experience replicating presence |
| Latency Sensitivity | High sensitivity; delays affect manipulation accuracy | Moderate sensitivity; delays affect immersion but less critical |
| Complexity | High due to control and feedback integration | Moderate; focused on sensory data transmission |
Introduction to Telemanipulation and Telepresence
Telemanipulation involves remotely controlling robotic arms or devices to physically interact with objects, enabling precise tasks in hazardous or inaccessible environments. Telepresence allows users to experience a remote location through immersive audiovisual feedback, creating a sense of being physically present without direct physical interaction. Both technologies enhance remote operation capabilities but differ fundamentally in their interaction modes--telemanipulation emphasizes physical manipulation, while telepresence focuses on sensory immersion.
Defining Telemanipulation: Concepts and Technologies
Telemanipulation involves remotely controlling robotic devices to perform precise physical tasks, often using haptic feedback and robotic arms for enhanced accuracy. This technology integrates sensors, actuators, and real-time data transmission to replicate human movements and enable interaction with distant environments. Understanding Telemanipulation helps you leverage advanced robotics for applications such as surgical procedures, hazardous material handling, and remote maintenance.
Understanding Telepresence: Core Principles
Telepresence enables users to experience and interact with a remote environment as if physically present through real-time audiovisual feedback and sensory input. Core principles include immersive communication, precise control of remote devices, and seamless integration of sensory data to create a convincing sense of presence. Understanding these elements helps optimize your remote interaction experience by enhancing situational awareness and responsiveness.
Key Differences Between Telemanipulation and Telepresence
Telemanipulation involves remotely controlling robotic systems to physically interact with environments, prioritizing precise manipulation and tactile feedback, whereas telepresence emphasizes immersive remote presence through audio-visual communication, enabling users to experience and navigate distant locations in real-time. Telemanipulation is critical in applications requiring fine motor control, such as robotic surgery or hazardous material handling, while telepresence is ideal for virtual meetings, remote inspections, and social interactions. Understanding these distinctions allows you to select the appropriate technology based on whether physical interaction or immersive presence is your primary objective.
Applications of Telemanipulation in Industry
Telemanipulation technologies enable precise remote control of robotic arms and machinery in hazardous or inaccessible industrial environments, enhancing safety and efficiency. Applications include nuclear facility maintenance, underwater equipment handling, and assembly line automation where human presence is limited or risky. Your operations can benefit significantly from telemanipulation by reducing downtime and increasing operational precision in high-risk settings.
Real-world Uses of Telepresence Technology
Telepresence technology enables remote interaction with environments across various sectors such as healthcare, where surgeons perform minimally invasive operations using robotic systems, and in industrial settings for remote inspection and maintenance of hazardous facilities. It enhances collaboration by providing immersive audiovisual experiences, allowing teams to participate in meetings or training sessions as if physically present. Furthermore, telepresence supports social connectivity for individuals with mobility limitations, reducing isolation through real-time virtual presence.
Advantages and Limitations of Telemanipulation
Telemanipulation enables precise remote control of robotic systems, offering distinct advantages such as enhanced safety in hazardous environments and improved accuracy in delicate tasks like surgery or industrial automation. Limitations include latency issues, restricted sensory feedback, and the high cost of advanced robotic equipment, which can impact operational efficiency and accessibility. Your ability to perform complex tasks remotely depends on overcoming these challenges to fully leverage telemanipulation's potential.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Telepresence
Telepresence offers immersive remote presence through high-definition video and audio, enabling real-time interaction and enhanced situational awareness, which strengthens communication and collaboration across distances. Its weaknesses include reliance on stable internet connectivity for seamless operation and limited physical control or tactile feedback, making it less suitable for tasks requiring fine motor skills or direct manipulation. Despite these limitations, telepresence excels in applications like remote meetings, virtual tours, and surveillance where visual and auditory immersion are critical.
Future Trends in Teleoperation: Merging Telemanipulation and Telepresence
Future trends in teleoperation emphasize the integration of telemanipulation and telepresence to enhance remote interaction capabilities. Advances in robotics, haptic feedback, and virtual reality are creating immersive environments where users can both control robotic actions precisely and experience real-time sensory input. This convergence fosters more intuitive and efficient remote work in fields such as surgery, hazardous environment maintenance, and space exploration.
Choosing the Right Technology: Telemanipulation vs Telepresence
Choosing the right technology between telemanipulation and telepresence depends on your specific needs for remote interaction and control. Telemanipulation enables precise, real-time control of robotic devices in hazardous or inaccessible environments, ideal for surgeries or industrial tasks requiring fine motor skills. Telepresence focuses on immersive communication and situational awareness, allowing you to virtually experience and interact with distant locations in real time.
Telemanipulation vs Telepresence Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com