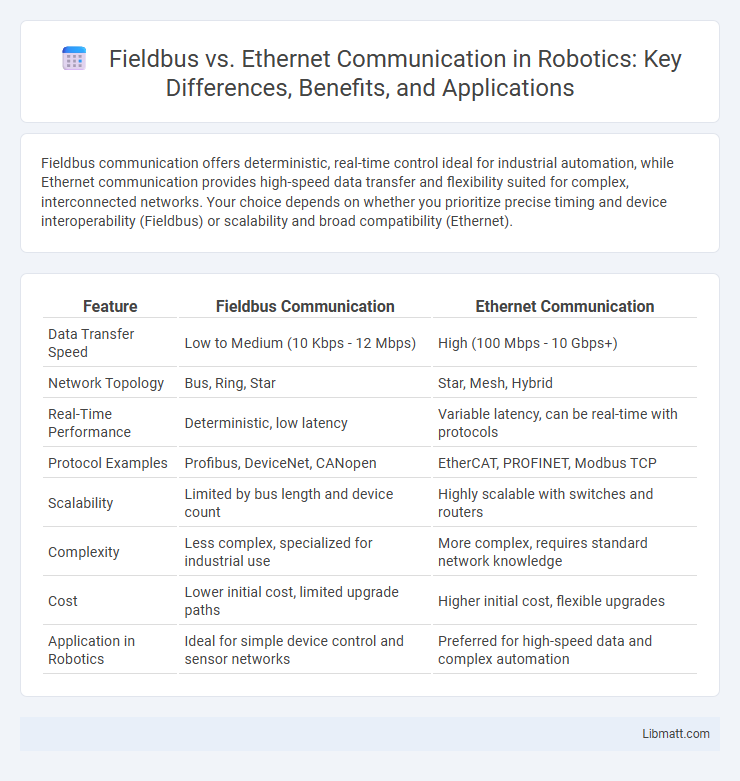
Fieldbus communication offers deterministic, real-time control ideal for industrial automation, while Ethernet communication provides high-speed data transfer and flexibility suited for complex, interconnected networks. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize precise timing and device interoperability (Fieldbus) or scalability and broad compatibility (Ethernet).
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fieldbus Communication | Ethernet Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transfer Speed | Low to Medium (10 Kbps - 12 Mbps) | High (100 Mbps - 10 Gbps+) |
| Network Topology | Bus, Ring, Star | Star, Mesh, Hybrid |
| Real-Time Performance | Deterministic, low latency | Variable latency, can be real-time with protocols |
| Protocol Examples | Profibus, DeviceNet, CANopen | EtherCAT, PROFINET, Modbus TCP |
| Scalability | Limited by bus length and device count | Highly scalable with switches and routers |
| Complexity | Less complex, specialized for industrial use | More complex, requires standard network knowledge |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, limited upgrade paths | Higher initial cost, flexible upgrades |
| Application in Robotics | Ideal for simple device control and sensor networks | Preferred for high-speed data and complex automation |
Introduction to Industrial Communication Protocols
Industrial communication protocols enable seamless data exchange between devices in manufacturing environments, with Fieldbus and Ethernet as two prevalent options. Fieldbus protocols, such as Profibus and Foundation Fieldbus, offer deterministic real-time control optimized for sensors and actuators on the factory floor. Ethernet-based protocols like EtherNet/IP and PROFINET leverage standard networking infrastructure to provide high-speed, flexible, and scalable communication for complex automation systems.
Overview of Fieldbus Technology
Fieldbus technology is a widely used digital communication system in industrial automation, designed for real-time, reliable data exchange between field devices such as sensors, actuators, and controllers. It operates through a deterministic network protocol that ensures timely data transfer, essential for process control and monitoring. Your choice of Fieldbus can enhance system efficiency with its robust noise immunity and simplified wiring compared to traditional analog signals.
Fundamentals of Ethernet Communication
Ethernet communication operates on a protocol suite called TCP/IP, enabling devices to exchange data over local area networks (LANs) using standard hardware like switches and routers. It relies on a layered model, primarily the Media Access Control (MAC) and Physical layers, to manage data framing, addressing, and error detection, ensuring efficient and reliable packet transmission. Your industrial network benefits from Ethernet's high-speed data transfer, scalability, and compatibility with modern automation systems, making it a robust choice over traditional Fieldbus methods.
Key Differences: Fieldbus vs Ethernet
Fieldbus communication uses a serial data protocol designed specifically for real-time industrial control applications with deterministic timing, while Ethernet offers faster data transfer rates and broader compatibility with standard networking devices. Fieldbus networks typically support fewer devices with specialized communication layers, whereas Ethernet supports larger, flexible networks leveraging TCP/IP protocols for interoperability. Key differences include Fieldbus's robustness in noisy industrial environments and Ethernet's scalability and integration with IT infrastructure.
Data Transmission Speed and Bandwidth Comparison
Fieldbus systems typically offer data transmission speeds ranging from 31.25 kbps to 12 Mbps, which suits simple sensor and actuator communication but limits bandwidth for large data volumes. Ethernet communication supports significantly higher speeds, commonly 100 Mbps to 10 Gbps, enabling faster and broader bandwidth suitable for complex industrial automation and real-time data transfer. The enhanced capacity of Ethernet allows integration of multiple high-speed devices and supports advanced protocols like Profinet and EtherNet/IP for greater efficiency in industrial environments.
Network Topology and Scalability
Fieldbus networks typically use a linear or bus topology, limiting scalability and making large-scale expansions complex. Ethernet communication supports star or mesh topologies, offering flexible scalability and easier integration of multiple devices. Your industrial network will benefit from Ethernet's ability to handle extensive nodes and higher data demands with minimal performance loss.
Reliability and Real-Time Performance
Fieldbus communication systems provide high reliability and deterministic real-time performance due to their dedicated network architecture and time-triggered protocol, ensuring consistent data delivery in industrial automation environments. Ethernet communication, particularly with Industrial Ethernet standards like PROFINET or EtherCAT, offers increased bandwidth and scalability but requires advanced protocols and synchronization mechanisms to achieve comparable real-time performance and reliability. Reliability in Fieldbus is inherent through collision-free data transmission, while Ethernet depends on network design and protocol enhancements to minimize latency and jitter in time-critical applications.
Integration with Industrial Automation Systems
Fieldbus communication integrates seamlessly with legacy industrial automation systems, providing robust real-time control through protocols like Profibus and DeviceNet. Ethernet communication leverages higher bandwidth and standard TCP/IP protocols, enabling easy integration with modern industrial networks and supporting advanced applications such as Industry 4.0 and IIoT. Hybrid solutions combining Fieldbus and Ethernet optimize system performance by ensuring compatibility and scalability across diverse automation architectures.
Cost and Implementation Considerations
Fieldbus communication systems generally offer lower initial costs and simpler implementation for small to medium industrial networks due to their limited cable requirements and dedicated protocols. Ethernet communication, while often involving higher upfront investment for hardware and network design, provides greater scalability, faster data transmission, and easier integration with existing IT infrastructure. Your choice between Fieldbus and Ethernet should balance budget constraints against long-term flexibility and network performance needs.
Future Trends in Industrial Networking
Industrial networking is increasingly shifting towards Ethernet communication due to its higher bandwidth, scalability, and compatibility with modern IIoT applications. Fieldbus systems, while still reliable for specific real-time control tasks, face limitations in data speed and flexibility compared to Ethernet-based protocols like PROFINET and EtherNet/IP. Future trends emphasize the integration of Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) standards and enhanced cybersecurity within Ethernet frameworks to support seamless, deterministic communication in smart factories and Industry 4.0 environments.
Fieldbus vs Ethernet Communication Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com