Force sensors measure linear force or load applied along a single axis, while torque sensors detect rotational force or twisting motion around an axis. Choosing the right sensor depends on whether your application requires monitoring straight-line pressure or rotational power.
Table of Comparison
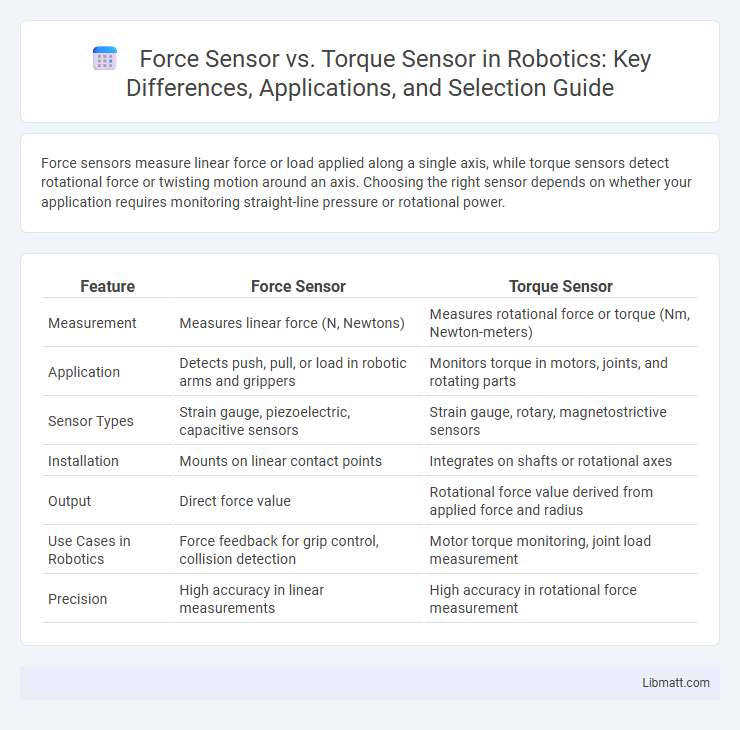
| Feature | Force Sensor | Torque Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement | Measures linear force (N, Newtons) | Measures rotational force or torque (Nm, Newton-meters) |
| Application | Detects push, pull, or load in robotic arms and grippers | Monitors torque in motors, joints, and rotating parts |
| Sensor Types | Strain gauge, piezoelectric, capacitive sensors | Strain gauge, rotary, magnetostrictive sensors |
| Installation | Mounts on linear contact points | Integrates on shafts or rotational axes |
| Output | Direct force value | Rotational force value derived from applied force and radius |
| Use Cases in Robotics | Force feedback for grip control, collision detection | Motor torque monitoring, joint load measurement |
| Precision | High accuracy in linear measurements | High accuracy in rotational force measurement |
Introduction to Force Sensors and Torque Sensors
Force sensors measure the magnitude of force applied to an object, providing precise data in applications like industrial automation, robotics, and medical devices. Torque sensors quantify rotational force or torque on a rotating system, essential for monitoring motor performance, drivetrain efficiency, and mechanical testing. Both sensors convert physical stimuli into electrical signals, enabling real-time monitoring and control in various engineering and manufacturing processes.
Key Differences Between Force and Torque Sensors
Force sensors measure linear force applied in a specific direction, typically expressed in newtons (N), while torque sensors detect rotational force or moment, measured in newton-meters (Nm). Your choice depends on whether the application requires sensing straight-line push/pull forces or rotational twisting forces. Key differences include their design, output type, and the physical phenomena they measure, with force sensors converting mechanical force into electrical signals and torque sensors capturing torque through strain gauges or magnetoelastic effects.
How Force Sensors Work
Force sensors operate by detecting the amount of force applied to an object, converting mechanical pressure into an electrical signal using piezoelectric, capacitive, or strain gauge elements. These sensors measure linear force and are widely used in applications like robotics, industrial automation, and healthcare to monitor pressure levels accurately. Understanding how your force sensor works allows for precise force measurement, ensuring optimal performance and safety in various systems.
How Torque Sensors Operate
Torque sensors operate by measuring the twisting force applied to an object, typically through strain gauges that detect deformation in a rotating shaft. These sensors convert mechanical torque into electrical signals, allowing for precise monitoring of rotational forces in applications like automotive testing and industrial machinery. Understanding how torque sensors work can enhance your ability to select the right sensor for accurate torque measurement and performance optimization.
Applications of Force Sensors
Force sensors are widely used in industries such as automotive, robotics, and healthcare for applications including weight measurement, impact detection, and material testing. These sensors enable precision control in robotic grippers, monitor patient movement in rehabilitation devices, and ensure safety by detecting force thresholds in automotive crash systems. Their ability to convert mechanical force into readable electrical signals makes them essential in quality control and process automation.
Applications of Torque Sensors
Torque sensors are widely used in automotive industries to monitor engine performance and ensure efficient transmission systems. In robotics, they enable precise control of joint movements by measuring the rotational force applied. Industrial machinery relies on torque sensors for real-time feedback during assembly processes and to prevent mechanical overloads.
Sensor Accuracy and Performance Comparison
Force sensors provide precise measurements of linear forces with high accuracy, typically achieving resolution in the milli-Newton range, making them ideal for applications requiring sensitive load detection. Torque sensors measure rotational forces with accuracy often expressed as a percentage of full-scale output, typically ranging from +-0.1% to +-0.5%, ensuring reliable performance in dynamic rotational environments. Your choice between force and torque sensors should consider these performance metrics to ensure optimal measurement accuracy for specific application needs.
Selection Criteria: Choosing Between Force and Torque Sensors
Selecting between force sensors and torque sensors depends on the specific measurement needs of your application, such as detecting linear force magnitude or rotational force (torque). Consider factors like accuracy, range, environmental conditions, and mounting constraints to ensure appropriate sensor integration. Your choice directly impacts system performance, reliability, and precision in monitoring mechanical loads.
Latest Innovations in Force and Torque Sensing Technology
Recent innovations in force sensors include the integration of nanomaterial-based piezoresistive elements, enhancing sensitivity and durability for precise industrial and biomedical applications. Torque sensors have advanced with wireless telemetry and magnetoelastic sensing, enabling real-time monitoring in automotive and aerospace systems with improved accuracy and reduced maintenance. Both sensor types benefit from AI-driven signal processing algorithms that optimize measurement reliability and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Conclusion: Which Sensor Fits Your Needs?
Force sensors measure linear force applied to an object, ideal for applications requiring direct force quantification such as weighing or tension measurement. Torque sensors detect rotational force or twisting moment, making them essential for monitoring motors, shafts, or rotary systems. Evaluating your specific application requirements, including force type and measurement direction, helps determine whether a force sensor or torque sensor best fits your needs.
Force Sensor vs Torque Sensor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com