Point cloud data represents spatial information as a collection of individual points in 3D space, capturing surface geometry without connectivity, while mesh data consists of vertices, edges, and faces that create a continuous polygonal surface, making it ideal for detailed visualization and analysis. Understanding the differences helps you choose the appropriate format for applications like 3D modeling, simulation, or augmented reality.
Table of Comparison
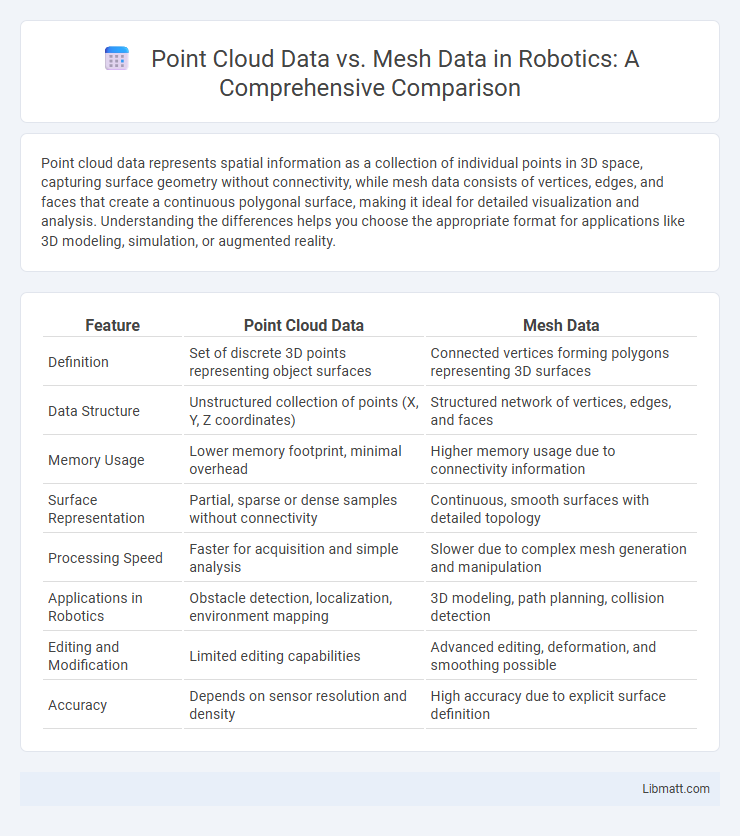
| Feature | Point Cloud Data | Mesh Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Set of discrete 3D points representing object surfaces | Connected vertices forming polygons representing 3D surfaces |
| Data Structure | Unstructured collection of points (X, Y, Z coordinates) | Structured network of vertices, edges, and faces |
| Memory Usage | Lower memory footprint, minimal overhead | Higher memory usage due to connectivity information |
| Surface Representation | Partial, sparse or dense samples without connectivity | Continuous, smooth surfaces with detailed topology |
| Processing Speed | Faster for acquisition and simple analysis | Slower due to complex mesh generation and manipulation |
| Applications in Robotics | Obstacle detection, localization, environment mapping | 3D modeling, path planning, collision detection |
| Editing and Modification | Limited editing capabilities | Advanced editing, deformation, and smoothing possible |
| Accuracy | Depends on sensor resolution and density | High accuracy due to explicit surface definition |
Introduction to Point Cloud and Mesh Data
Point cloud data consists of a collection of spatial points representing the external surface of objects or scenes, acquired through 3D scanning technologies like LiDAR or photogrammetry. Mesh data is a structured representation of 3D geometry that connects points via vertices, edges, and faces to form polygons, typically triangles or quads, creating a continuous surface model. Both point cloud and mesh data are fundamental in applications such as 3D modeling, virtual reality, and computer-aided design, with point clouds providing raw spatial information and meshes enabling detailed surface reconstruction.
Defining Point Cloud Data
Point cloud data consists of millions of individual points in 3D space, each representing precise spatial coordinates captured by LiDAR sensors or photogrammetry. Unlike mesh data, which connects points to form surfaces and polygons, point clouds provide raw, unstructured geometric information ideal for detailed spatial analysis. Your choice depends on whether you need exact spatial measurements from point clouds or visually continuous surfaces from mesh data.
Understanding Mesh Data Structures
Mesh data structures consist of vertices, edges, and faces that define the shape of a 3D object with connected polygons, typically triangles or quads, enabling smooth surface representation and efficient rendering. Unlike point cloud data, which captures discrete spatial points without explicit connectivity, mesh data provides detailed topological information essential for simulations, animations, and texture mapping. Understanding mesh structures involves analyzing vertex connectivity and face orientation to optimize geometric accuracy and computational performance in 3D modeling applications.
Data Acquisition Methods
Point cloud data is commonly acquired using LiDAR scanners, photogrammetry, or structured light sensors, which capture millions of discrete points representing the surface geometry of objects or environments. Mesh data is often generated by processing point clouds through algorithms like Poisson surface reconstruction or Delaunay triangulation to create continuous polygonal surfaces. Understanding the differences in data acquisition methods helps you select the appropriate technique for applications in 3D modeling, mapping, or virtual reality.
Accuracy and Precision Comparison
Point cloud data captures individual points in 3D space, offering high accuracy in representing raw surfaces but often lacks the precision of connected geometry. Mesh data provides structured, triangulated surfaces that improve precision through interpolation, enabling smoother and more detailed models. Your choice depends on whether accurate raw spatial data or precise, continuous surfaces are critical for your 3D applications.
File Formats and Storage Requirements
Point cloud data is commonly stored in formats like LAS, PLY, and XYZ, which efficiently capture spatial coordinates but often demand large storage due to unstructured point information. Mesh data utilizes formats such as OBJ, STL, and FBX, providing compact representations by encoding vertices, edges, and faces to model surfaces, resulting in typically smaller file sizes. Understanding these differences in your file format choice impacts storage efficiency and data processing workflows in 3D modeling applications.
Visualization Techniques
Point cloud data visualization relies on rendering millions of individual points representing 3D object surfaces, often using color coding or intensity to convey additional information. Mesh data visualization creates continuous surfaces by connecting vertices with polygons, enabling more detailed and smooth representations suitable for realistic shading and texture mapping. Your choice between point clouds and meshes affects the visualization techniques available, with point clouds offering raw spatial detail and meshes providing structured geometric clarity.
Applications in Different Industries
Point cloud data excels in industries like construction and surveying, enabling precise 3D mapping and spatial analysis for site planning and infrastructure inspection. Mesh data is widely used in entertainment, gaming, and medical fields, providing detailed, textured 3D models suitable for animations, simulations, and surgical planning. Your choice depends on whether you need raw spatial measurements or fully rendered, interactive 3D models tailored to industry-specific applications.
Advantages and Limitations
Point cloud data offers high precision in representing real-world objects by capturing millions of individual spatial points, making it ideal for detailed analysis and measurement. Mesh data provides a more manageable and visually coherent representation by connecting points with polygons, enabling smoother surfaces and efficient rendering for simulations and visualizations. Your choice depends on the need for raw spatial accuracy with point clouds or optimized, continuous surface models with meshes, each having limitations in data size and complexity versus visual realism.
Choosing Between Point Cloud and Mesh Data
When choosing between point cloud data and mesh data, consider that point clouds represent raw spatial coordinates ideal for capturing detailed 3D scans, while mesh data provides a structured, connected surface useful for visualizations and simulations. Your decision depends on the application's need for precision or visual realism, as point clouds excel in accuracy without surface information, whereas meshes offer seamless surfaces for rendering and analysis. Evaluating the data format compatibility with your software and the project's end goals ensures the most efficient use of 3D models.
Point Cloud Data vs Mesh Data Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com