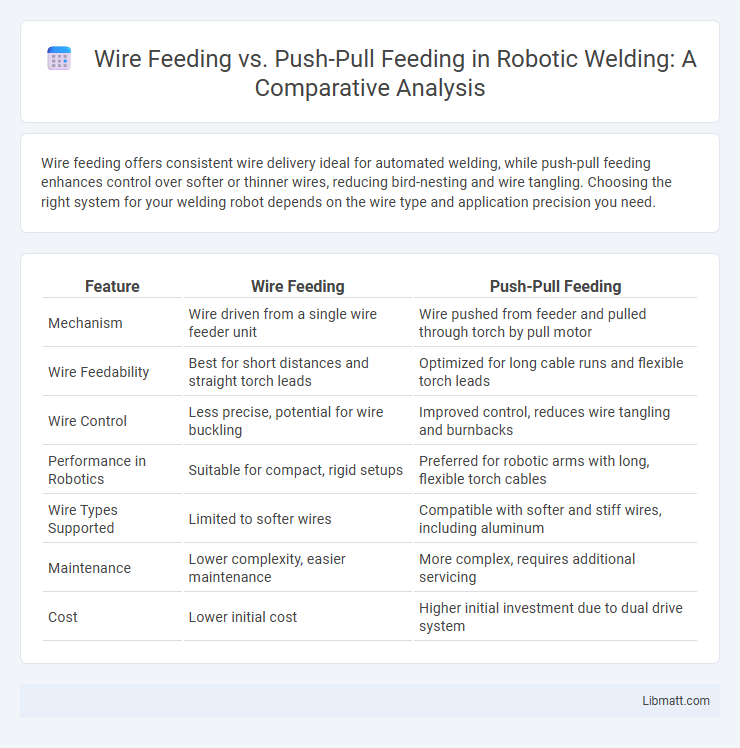
Wire feeding offers consistent wire delivery ideal for automated welding, while push-pull feeding enhances control over softer or thinner wires, reducing bird-nesting and wire tangling. Choosing the right system for your welding robot depends on the wire type and application precision you need.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wire Feeding | Push-Pull Feeding |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Wire driven from a single wire feeder unit | Wire pushed from feeder and pulled through torch by pull motor |
| Wire Feedability | Best for short distances and straight torch leads | Optimized for long cable runs and flexible torch leads |
| Wire Control | Less precise, potential for wire buckling | Improved control, reduces wire tangling and burnbacks |
| Performance in Robotics | Suitable for compact, rigid setups | Preferred for robotic arms with long, flexible torch cables |
| Wire Types Supported | Limited to softer wires | Compatible with softer and stiff wires, including aluminum |
| Maintenance | Lower complexity, easier maintenance | More complex, requires additional servicing |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial investment due to dual drive system |
Introduction to Wire Feeding and Push-Pull Feeding
Wire feeding in welding robots involves the continuous supply of welding wire from a spool directly into the welding torch, providing a consistent arc and efficient metal deposition. Push-pull feeding systems use two synchronized motors--one pushing the wire from the spool and another pulling it through the torch--to better control wire feeding over longer distances or through complex torch configurations. This dual-motor setup reduces wire feeding issues such as birdnesting and improves overall weld quality in robotic welding applications.
How Wire Feeding Works in Welding Robots
Wire feeding in welding robots involves a mechanism that continuously supplies welding wire to the welding gun at a controlled speed, ensuring a consistent arc and weld quality. Push-pull feeding uses separate motors to push the wire from the feeder and pull it near the welding torch, reducing wire deformation and improving feed reliability, especially for softer wires. In contrast, conventional wire feeding relies solely on pushing the wire, which can cause feeding issues over longer distances or with softer wire types.
Push-Pull Feeding: Principles and Mechanisms
Push-pull feeding in welding robots utilizes two synchronized motors--one pushing the wire from the spool and the other pulling it toward the welding torch--ensuring consistent wire delivery and reducing feed issues with softer wires. This system enhances wire control and minimizes wire deformation or bird-nesting, which is common in long cable runs or flexible setups. Your welding process benefits from improved precision and smoother operation, especially when working with delicate or low-alloy wires.
Key Differences Between Wire Feeding and Push-Pull Feeding
Wire feeding in welding robots uses a single motor to push the wire through the torch, suitable for short, flexible cables but can struggle with softer wires prone to deformation. Push-pull feeding employs two synchronized motors--one pushes the wire from the feeder while the other pulls it through the torch--providing superior control and consistent feeding performance, especially with long cable lengths and softer wire types. Your selection between these systems affects welding precision, wire feed reliability, and suitability for different wire materials and cable configurations.
Advantages of Standard Wire Feeding Systems
Standard wire feeding systems in welding robots offer precise control of wire speed and consistent wire delivery, resulting in higher-quality welds with fewer defects. These systems are typically more durable and require less maintenance compared to push-pull feeders, enhancing production efficiency. Your welding process benefits from reduced wire tangling and smoother feeding, especially when working with softer or thinner wire materials.
Benefits of Push-Pull Feeding in Robotic Welding
Push-pull feeding in robotic welding offers enhanced control over wire feed speed and reduces the risk of wire stubbing and bird-nesting, resulting in consistent weld quality. This method supports the use of softer or larger diameter wires that are prone to deformation, increasing your welding versatility. Improved wire handling minimizes downtime and maintenance, boosting overall productivity in automated welding operations.
Applications Suited for Wire Feeding vs Push-Pull Feeding
Wire feeding systems excel in robotic welding applications involving short to medium-length cable runs and lightweight wire types, offering precise wire control for automotive and general fabrication industries. Push-pull feeding mechanisms are better suited for long cable distances and softer wires, such as aluminum, commonly used in shipbuilding and aerospace sectors requiring flexible handling and consistent wire feed. Understanding your specific project demands helps determine whether wire feeding or push-pull feeding enhances efficiency and weld quality.
Common Challenges and Limitations
Wire feeding systems in welding robots face challenges such as inconsistent wire feeding, wire tangling, and feed motor wear, which can lead to weld defects and reduced productivity. Push feeding struggles with long cable lengths and rigid wire types, causing feeding resistance and potential wire deformation, while push-pull feeding mitigates these issues but introduces higher complexity and maintenance requirements. Understanding these limitations helps you select the optimal system for reliable wire delivery and sustained welding performance.
Choosing the Right Feeding Method for Your Robotic Setup
Choosing the right feeding method for your welding robot depends on factors like wire type, distance to the weld, and application precision. Wire feeding systems excel in short distances with minimal wire flex, ensuring consistent feed rates, while push-pull feeding offers better control for softer or larger diameter wires over longer cable lengths. Understanding these differences optimizes your robotic welding performance and reduces downtime caused by wire feeding issues.
Future Trends in Welding Wire Feed Technologies
Welding robots are increasingly adopting advanced wire feeding technologies, with future trends emphasizing the integration of high-precision push-pull feeding systems that minimize wire deformation and improve feed consistency, crucial for robotic automation in complex welding tasks. Innovations include smart sensors and adaptive control algorithms that optimize wire feed speed and tension in real-time, enhancing overall weld quality and reducing downtime. The convergence of IoT connectivity and AI-driven analytics is transforming wire feeding into a predictive maintenance tool, signaling a shift toward more intelligent and autonomous welding operations.
Wire Feeding vs Push-Pull Feeding (in welding robots) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com