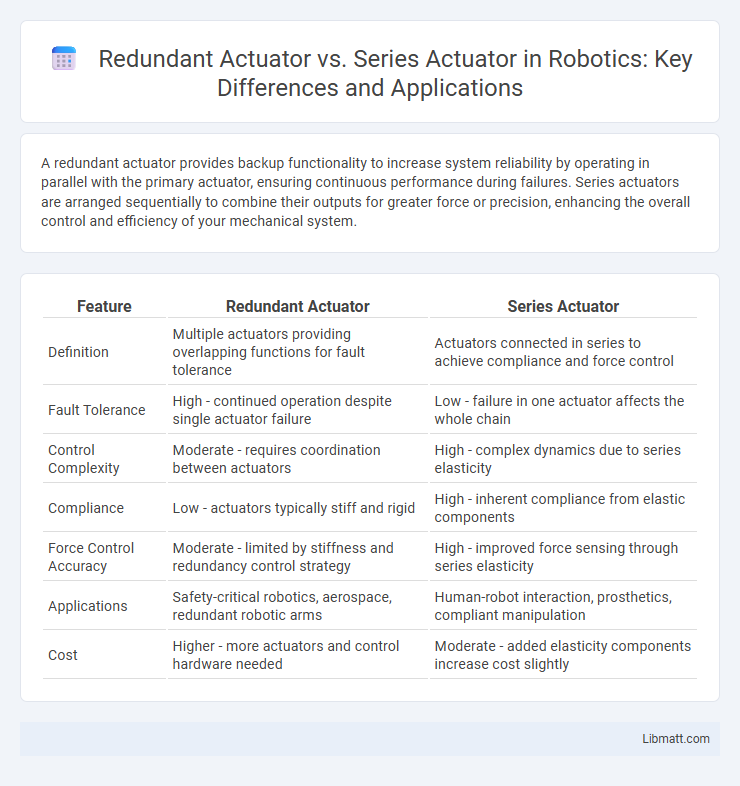
A redundant actuator provides backup functionality to increase system reliability by operating in parallel with the primary actuator, ensuring continuous performance during failures. Series actuators are arranged sequentially to combine their outputs for greater force or precision, enhancing the overall control and efficiency of your mechanical system.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Redundant Actuator | Series Actuator |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple actuators providing overlapping functions for fault tolerance | Actuators connected in series to achieve compliance and force control |
| Fault Tolerance | High - continued operation despite single actuator failure | Low - failure in one actuator affects the whole chain |
| Control Complexity | Moderate - requires coordination between actuators | High - complex dynamics due to series elasticity |
| Compliance | Low - actuators typically stiff and rigid | High - inherent compliance from elastic components |
| Force Control Accuracy | Moderate - limited by stiffness and redundancy control strategy | High - improved force sensing through series elasticity |
| Applications | Safety-critical robotics, aerospace, redundant robotic arms | Human-robot interaction, prosthetics, compliant manipulation |
| Cost | Higher - more actuators and control hardware needed | Moderate - added elasticity components increase cost slightly |
Introduction: Understanding Actuator Technologies
Redundant actuators are designed with multiple independent drive mechanisms to ensure continuous operation in critical systems, enhancing reliability and safety. Series actuators utilize a sequential configuration where actuators work in tandem, optimizing force output and precision for complex motion control tasks. These technologies impact system design choices based on requirements for fault tolerance, response time, and operational complexity.
What Is a Redundant Actuator?
A redundant actuator consists of multiple actuators working in parallel to ensure system reliability and continuous operation if one actuator fails. It enhances safety and fault tolerance in critical applications such as aerospace or industrial automation by providing backup functionality. Series actuators, in contrast, connect actuators in sequence to amplify motion or force rather than improve redundancy or reliability.
What Is a Series Actuator?
A series actuator consists of multiple actuator elements connected in sequence, enabling precise control by distributing loads and enhancing reliability through redundancy. It operates by sequentially activating each element, allowing for smoother motion and improved fault tolerance compared to single actuators. This design is particularly effective in applications requiring high accuracy and safety, such as robotics and aerospace systems.
Key Design Differences
Redundant actuators feature multiple independent actuating units working simultaneously to ensure system reliability and fault tolerance. Series actuators consist of actuators arranged sequentially, where the output of one influences the input of the next, enhancing precision and control. The key design difference lies in redundancy for fault management versus sequential linkage for improved motion accuracy.
Performance Comparison: Redundant vs Series
Redundant actuators provide enhanced reliability by including multiple actuator elements that can take over in case of failure, ensuring continuous operation and minimizing downtime. Series actuators, in contrast, focus on precise control and increased force output by connecting actuators sequentially, but may have single points of failure impacting overall system performance. Your choice between redundant and series actuators should consider the criticality of reliability versus the need for enhanced force and precision in your application.
Reliability and Safety Considerations
Redundant actuators enhance reliability by providing backup operation when one actuator fails, ensuring system safety through fail-safe mechanisms critical in high-stakes environments like aerospace and nuclear plants. Series actuators prioritize precise control and force amplification but rely on the integrity of each element in the chain, making them less tolerant to individual actuator failure. Your choice depends on whether fault tolerance or control accuracy is paramount in your safety-critical application.
Cost Implications and Efficiency
Redundant actuators generally incur higher upfront costs due to the need for duplicate components and more complex control systems, but they offer increased reliability and reduced downtime in critical applications. Series actuators tend to be more cost-effective initially, with simpler designs and maintenance processes, yet may sacrifice some efficiency and resilience under heavy or variable loads. Your decision should weigh the balance between long-term operational efficiency and initial investment based on the specific application's demands.
Application Scenarios and Industry Use Cases
Redundant actuators are essential in safety-critical applications such as aerospace, nuclear power plants, and medical devices where failure is not an option, providing backup operation to ensure continuous functionality. Series actuators excel in precision control tasks found in robotics and manufacturing automation by enabling smooth, incremental movement through sequential activation. Understanding Your specific industry requirements will help determine whether redundancy or series configuration best optimizes reliability and performance.
Pros and Cons of Each Actuator Type
Redundant actuators offer enhanced reliability and safety by incorporating multiple actuators working simultaneously to prevent system failure, but they increase complexity, weight, and cost. Series actuators provide smoother force control and energy efficiency by linking actuators mechanically in series, yet they may suffer from reduced overall responsiveness and are more challenging to maintain. Your choice depends on whether system safety or operational efficiency is the primary priority.
Choosing the Right Actuator for Your Needs
Selecting the right actuator depends on your system's requirements for reliability and precision. Redundant actuators provide increased safety by incorporating backup components to ensure continuous operation in critical applications. Series actuators offer smoother motion control and reduced backlash, ideal for tasks demanding high accuracy and responsiveness.
Redundant actuator vs Series actuator Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com