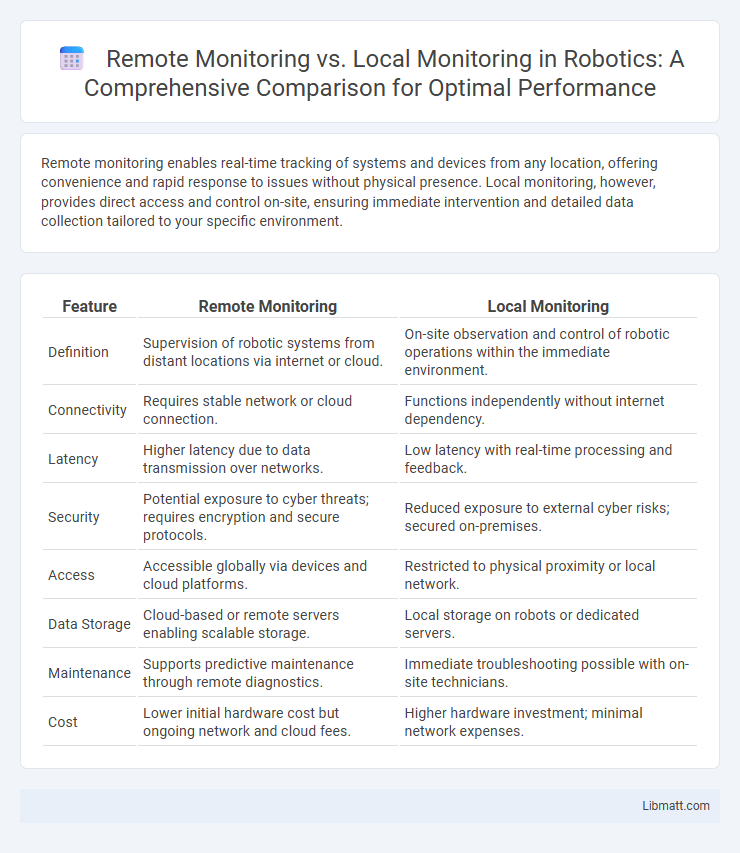
Remote monitoring enables real-time tracking of systems and devices from any location, offering convenience and rapid response to issues without physical presence. Local monitoring, however, provides direct access and control on-site, ensuring immediate intervention and detailed data collection tailored to your specific environment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Remote Monitoring | Local Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supervision of robotic systems from distant locations via internet or cloud. | On-site observation and control of robotic operations within the immediate environment. |
| Connectivity | Requires stable network or cloud connection. | Functions independently without internet dependency. |
| Latency | Higher latency due to data transmission over networks. | Low latency with real-time processing and feedback. |
| Security | Potential exposure to cyber threats; requires encryption and secure protocols. | Reduced exposure to external cyber risks; secured on-premises. |
| Access | Accessible globally via devices and cloud platforms. | Restricted to physical proximity or local network. |
| Data Storage | Cloud-based or remote servers enabling scalable storage. | Local storage on robots or dedicated servers. |
| Maintenance | Supports predictive maintenance through remote diagnostics. | Immediate troubleshooting possible with on-site technicians. |
| Cost | Lower initial hardware cost but ongoing network and cloud fees. | Higher hardware investment; minimal network expenses. |
Introduction to Remote and Local Monitoring
Remote monitoring enables you to continuously track systems, devices, or environments from a distant location using internet-connected sensors and software, providing real-time data and alerts. Local monitoring involves on-site observation and data collection through physical presence or localized hardware, allowing immediate intervention and control. Each method offers distinct advantages depending on the need for accessibility, immediacy, and scope of data management.
Key Differences Between Remote and Local Monitoring
Remote monitoring enables real-time data collection and analysis from multiple locations via internet-connected devices, while local monitoring involves on-site data acquisition and processing limited to a specific physical area. Remote systems offer greater scalability and flexibility, allowing centralized control and faster response times, whereas local monitoring provides higher security and lower latency due to direct access and reduced dependency on network connectivity. Key differences include connectivity requirements, data accessibility, and the scope of monitoring, impacting overall system efficiency and management.
Benefits of Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring offers real-time access to critical data from anywhere, improving operational efficiency and reducing the need for on-site visits. It enables proactive maintenance by detecting issues early, minimizing downtime and repair costs. Your business can leverage enhanced security and scalability, adapting quickly to changing needs without significant infrastructure investments.
Advantages of Local Monitoring
Local monitoring offers immediate access to data and real-time system control without relying on internet connectivity, ensuring higher reliability and security for sensitive operations. It allows for faster response times to critical events by minimizing latency and eliminating dependence on external networks. Your on-site team benefits from direct oversight, reducing potential downtime and enhancing operational efficiency.
Challenges of Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring faces challenges such as limited real-time data accuracy due to network latency and potential connectivity issues, impacting timely decision-making in critical systems. Security vulnerabilities pose significant risks as transmitted data can be intercepted or hacked without robust encryption protocols. Furthermore, remote monitoring demands high infrastructure costs and skilled personnel to manage complex systems, especially in industries requiring constant oversight like healthcare or manufacturing.
Limitations of Local Monitoring
Local monitoring faces limitations such as restricted data accessibility, as it requires physical presence or direct network connection for real-time observation and troubleshooting. It often lacks scalability, making it unsuitable for managing multiple remote sites or large industrial environments. Furthermore, local monitoring systems may suffer from delays in data processing and response time, impacting timely decision-making and maintenance actions.
Use Cases for Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring is essential in industries such as healthcare, where continuous patient vital sign tracking can prevent emergencies, and in environmental management, enabling real-time data collection from sensor networks in remote locations. In manufacturing, remote monitoring facilitates predictive maintenance by analyzing equipment performance data to reduce downtime and optimize production efficiency. Energy utilities use remote monitoring systems to oversee grid performance and detect faults quickly, improving reliability and reducing operational costs.
Use Cases for Local Monitoring
Local monitoring is essential in environments where immediate data processing and real-time response are critical, such as manufacturing plants, healthcare facilities, and security systems. It ensures continuous operation and swift detection of anomalies without reliance on internet connectivity, reducing latency and increasing reliability. Industries prioritize local monitoring to maintain operational control, enhance data privacy, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Security Considerations in Monitoring Systems
Remote monitoring systems face significant security challenges such as data interception, unauthorized access, and cyberattacks due to their dependence on internet connectivity, requiring robust encryption protocols and multi-factor authentication to safeguard sensitive information. Local monitoring systems offer enhanced security by limiting network exposure and maintaining data within controlled environments, reducing vulnerabilities associated with external threats. Implementing comprehensive security measures, including firewalls, regular software updates, and access controls, is critical for both remote and local monitoring to ensure data integrity and system reliability.
Choosing the Right Monitoring Solution
Selecting the appropriate monitoring solution depends on factors such as network size, security requirements, and budget constraints. Remote monitoring offers centralized control and real-time updates ideal for distributed environments, while local monitoring provides enhanced security and faster response times for on-site operations. Evaluating the scale of infrastructure, data sensitivity, and resource availability ensures the choice aligns with organizational goals and operational efficiency.
Remote Monitoring vs Local Monitoring Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com