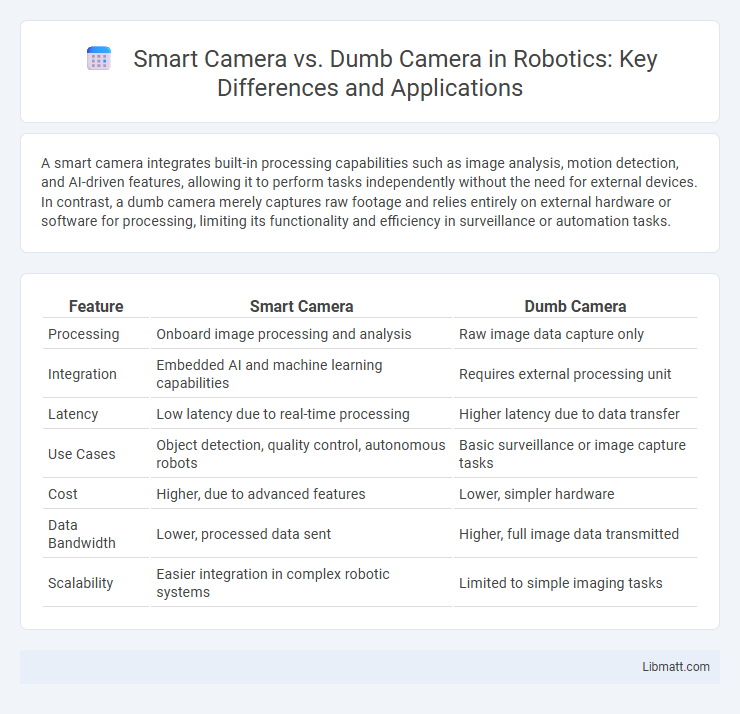
A smart camera integrates built-in processing capabilities such as image analysis, motion detection, and AI-driven features, allowing it to perform tasks independently without the need for external devices. In contrast, a dumb camera merely captures raw footage and relies entirely on external hardware or software for processing, limiting its functionality and efficiency in surveillance or automation tasks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Camera | Dumb Camera |
|---|---|---|
| Processing | Onboard image processing and analysis | Raw image data capture only |
| Integration | Embedded AI and machine learning capabilities | Requires external processing unit |
| Latency | Low latency due to real-time processing | Higher latency due to data transfer |
| Use Cases | Object detection, quality control, autonomous robots | Basic surveillance or image capture tasks |
| Cost | Higher, due to advanced features | Lower, simpler hardware |
| Data Bandwidth | Lower, processed data sent | Higher, full image data transmitted |
| Scalability | Easier integration in complex robotic systems | Limited to simple imaging tasks |
Introduction to Smart and Dumb Cameras
Smart cameras integrate advanced processing capabilities such as artificial intelligence, enabling real-time image analysis and decision-making directly within the device, unlike dumb cameras that solely capture and transmit raw footage for external processing. These intelligent devices offer features like motion detection, facial recognition, and automated alerts, enhancing security and operational efficiency. Your choice between a smart or dumb camera depends on the need for on-device analytics versus basic video recording.
Key Features of Smart Cameras
Smart cameras possess advanced features like AI-powered motion detection, facial recognition, and real-time video analytics that distinguish them from traditional dumb cameras. These devices offer cloud storage, remote access via mobile apps, and automated alerts, enhancing security and convenience significantly. Your surveillance system benefits from a smart camera's ability to intelligently process data and adapt to different environments, providing superior monitoring capabilities.
Key Features of Dumb Cameras
Dumb cameras, also known as traditional or analog cameras, primarily capture and record video without advanced processing or connectivity features. They lack built-in intelligence such as motion detection, facial recognition, and remote access, making them reliant on external devices for video storage and analysis. These cameras typically offer basic image quality and require manual adjustments for focus and exposure.
Image Quality Comparison
Smart cameras deliver superior image quality by integrating advanced processing capabilities such as AI-based noise reduction, HDR, and real-time image enhancement algorithms. Dumb cameras rely solely on hardware specifications like sensor size and lens quality, lacking software optimization that boosts clarity, color accuracy, and detail in varied lighting conditions. The combination of intelligent software and high-performance hardware in smart cameras ensures consistently sharper and more vibrant images compared to traditional dumb cameras.
Connectivity and Integration
Smart cameras offer advanced connectivity options such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cloud integration, enabling seamless real-time data transfer and remote monitoring. Dumb cameras lack these features, relying solely on local storage and manual retrieval, which restricts your ability to access footage instantly or integrate with other smart home systems. The integration capabilities of smart cameras allow for automation and enhanced security workflows that dumb cameras cannot provide.
Ease of Use and User Experience
Smart cameras offer enhanced ease of use with features like automatic adjustments, real-time analytics, and intuitive mobile app controls that simplify monitoring and management. Dumb cameras require manual configuration and lack advanced functionality, often resulting in a less seamless user experience due to limited automation and remote access. Your interaction with smart cameras becomes more efficient and user-friendly, making surveillance more accessible and responsive.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Smart cameras offer advanced security features like real-time alerts and AI-powered motion detection, enhancing your ability to monitor environments effectively. However, they often collect and transmit data to cloud servers, raising privacy concerns about potential unauthorized access or data breaches. Dumb cameras, lacking connectivity features, provide basic surveillance with minimal risk of digital privacy violations but offer limited functionality compared to their smart counterparts.
Cost and Value Analysis
Smart cameras typically have higher upfront costs due to integrated AI capabilities, advanced sensors, and on-device processing power, offering enhanced features such as real-time analytics and motion detection. Dumb cameras are more affordable initially but require additional infrastructure like external servers and software to analyze footage, which can increase long-term operational expenses. Evaluating cost and value depends on specific use cases; smart cameras provide significant ROI through reduced labor and faster response times, while dumb cameras may be suitable for low-budget or basic surveillance needs.
Common Use Cases for Each Type
Smart cameras excel in surveillance, facial recognition, and automated quality control due to their onboard processing and AI capabilities. Dumb cameras are typically used for basic video recording and live streaming, relying on external systems for analysis and storage. Industries like retail and manufacturing often deploy smart cameras for real-time analytics, while security setups favor dumb cameras for cost-effective monitoring.
Choosing the Right Camera for Your Needs
Smart cameras offer advanced features like AI-powered motion detection, facial recognition, and cloud storage, making them ideal for those seeking enhanced security and automation. Dumb cameras provide basic video recording without intelligent processing, suitable for straightforward surveillance tasks or budget-conscious users. Determine your priorities for features, integration capabilities, and budget to select the camera that best aligns with your specific security and monitoring needs.
Smart Camera vs Dumb Camera Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com