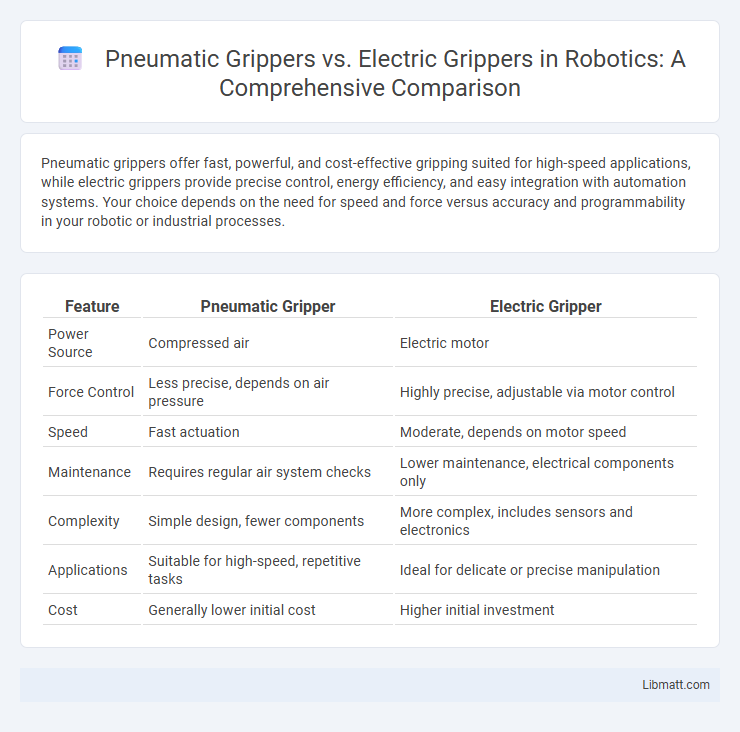
Pneumatic grippers offer fast, powerful, and cost-effective gripping suited for high-speed applications, while electric grippers provide precise control, energy efficiency, and easy integration with automation systems. Your choice depends on the need for speed and force versus accuracy and programmability in your robotic or industrial processes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pneumatic Gripper | Electric Gripper |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Compressed air | Electric motor |
| Force Control | Less precise, depends on air pressure | Highly precise, adjustable via motor control |
| Speed | Fast actuation | Moderate, depends on motor speed |
| Maintenance | Requires regular air system checks | Lower maintenance, electrical components only |
| Complexity | Simple design, fewer components | More complex, includes sensors and electronics |
| Applications | Suitable for high-speed, repetitive tasks | Ideal for delicate or precise manipulation |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial investment |
Introduction to Grippers: Pneumatic vs Electric
Pneumatic grippers utilize compressed air to generate gripping force, offering rapid response times and high gripping strength ideal for handling heavy or irregular objects. Electric grippers rely on electric motors and precise control systems to provide adjustable gripping force and improved energy efficiency, making them suitable for delicate or precision tasks. Both gripper types serve critical roles in automation, with selection depending on application requirements such as speed, force, control, and maintenance considerations.
How Pneumatic Grippers Work
Pneumatic grippers operate using compressed air to generate linear or rotary motion, allowing precise gripping and releasing of objects in automated systems. These grippers rely on air pressure to move pistons within cylinders, which then actuate the gripping fingers for reliable handling of diverse materials. Understanding how pneumatic grippers work can help you choose the ideal tool for applications requiring quick response times and high force output.
How Electric Grippers Operate
Electric grippers operate using electric motors that drive the gripping mechanism, providing precise control over force and position. These grippers use feedback systems such as encoders or sensors to adjust grip strength and ensure accurate object handling, enhancing repeatability in automated tasks. Compared to pneumatic grippers, electric versions offer quieter operation and greater energy efficiency in industrial automation applications.
Key Differences Between Pneumatic and Electric Grippers
Pneumatic grippers use compressed air to generate force, providing rapid cycle times and high gripping strength ideal for heavy-duty applications, while electric grippers operate via electric motors offering precise control, adjustable force, and easier integration with automated systems. Pneumatic grippers require an air supply system, making them less energy-efficient and noisier, whereas electric grippers are quieter, more energy-efficient, and simplify maintenance due to fewer moving parts. Your choice between the two depends on factors like load capacity, speed requirements, and the complexity of control needed for your specific automation tasks.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Precision
Pneumatic grippers offer high-speed operation with rapid cycle times suitable for simple pick-and-place tasks, while electric grippers excel in precision and fine control, delivering consistent gripping force and accurate positioning for delicate or complex components. The speed of pneumatic systems can reach up to several hundred cycles per minute, but their precision is limited by air compressibility and mechanical backlash. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize quick actuation for high-throughput applications or precise handling for sensitive parts in automated processes.
Energy Efficiency: Analyzing Power Consumption
Pneumatic grippers typically consume compressed air, which can lead to higher energy costs due to the inefficiencies in air compression and leakage. Electric grippers, powered by electric motors, offer improved energy efficiency by using only the necessary power for gripping actions and minimizing waste. Your choice between these options should consider the specific application's power consumption patterns and the potential for energy savings over time.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Maintenance
Pneumatic grippers generally involve lower initial investment costs due to simpler design and widespread availability of compressed air systems in industrial settings, making them cost-effective for high-volume, repetitive tasks. Electric grippers have higher upfront costs driven by sophisticated electronics and integrated control systems but tend to incur lower maintenance expenses due to reduced wear and fewer mechanical components, offering long-term savings in precision applications. Evaluating total cost of ownership requires considering factors like energy consumption, system complexity, and downtime, where pneumatic units may demand more frequent part replacements and line maintenance compared to the more durable electric alternatives.
Applications in Various Industries
Pneumatic grippers excel in industries requiring rapid, repetitive gripping with high force, such as automotive assembly and packaging, due to their simple design and reliability in harsh environments. Electric grippers offer precise control and adaptability, making them ideal for delicate tasks in electronics manufacturing and medical device assembly. Choosing the right gripper enhances your automation efficiency by aligning grip strength and control with specific industrial application needs.
Pros and Cons of Pneumatic and Electric Grippers
Pneumatic grippers excel in high-speed, high-force applications with simple control systems and lower initial costs but require compressed air systems, leading to higher energy consumption and maintenance. Electric grippers offer precise control, programmability, and energy efficiency with quieter operation, yet they typically have higher upfront costs and may exhibit slower response times under heavy loads. Choosing between them depends on factors such as operational environment, control requirements, and total cost of ownership.
Choosing the Right Gripper for Your Automation Needs
Pneumatic grippers offer reliable, high-speed operation with simple maintenance, making them ideal for applications requiring fast, repetitive motions and cost-effective solutions. Electric grippers provide precise control, adjustable force, and programmability, which suit complex tasks needing delicate handling and adaptability. Understanding your automation needs, including speed, precision, and control requirements, will help you select the optimal gripper type for improved operational efficiency.
Pneumatic Gripper vs Electric Gripper Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com