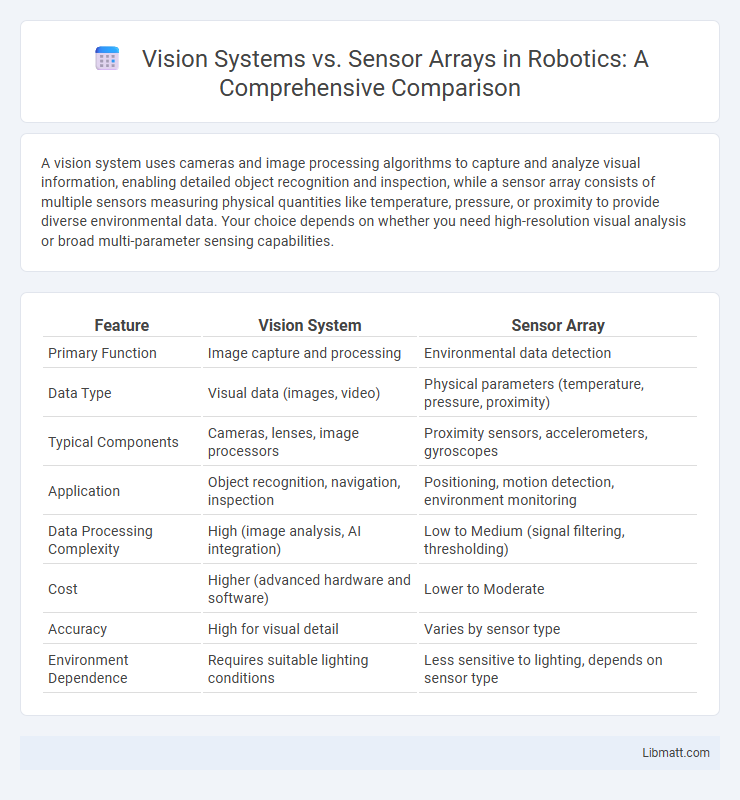
A vision system uses cameras and image processing algorithms to capture and analyze visual information, enabling detailed object recognition and inspection, while a sensor array consists of multiple sensors measuring physical quantities like temperature, pressure, or proximity to provide diverse environmental data. Your choice depends on whether you need high-resolution visual analysis or broad multi-parameter sensing capabilities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vision System | Sensor Array |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Image capture and processing | Environmental data detection |
| Data Type | Visual data (images, video) | Physical parameters (temperature, pressure, proximity) |
| Typical Components | Cameras, lenses, image processors | Proximity sensors, accelerometers, gyroscopes |
| Application | Object recognition, navigation, inspection | Positioning, motion detection, environment monitoring |
| Data Processing Complexity | High (image analysis, AI integration) | Low to Medium (signal filtering, thresholding) |
| Cost | Higher (advanced hardware and software) | Lower to Moderate |
| Accuracy | High for visual detail | Varies by sensor type |
| Environment Dependence | Requires suitable lighting conditions | Less sensitive to lighting, depends on sensor type |
Introduction to Vision Systems and Sensor Arrays
Vision systems utilize cameras and image processing algorithms to capture and interpret visual data, enabling advanced inspection, guidance, and recognition tasks. Sensor arrays consist of multiple sensors arranged systematically to detect environmental changes like temperature, pressure, or light intensity, providing spatially distributed data. Your choice between these technologies depends on the complexity of the application and the type of data required for accurate analysis and decision-making.
Core Components of Vision Systems
Vision systems rely on core components such as high-resolution cameras, image processing units, and sophisticated software algorithms to capture and analyze visual data accurately. These components work together to interpret spatial and color information, enabling detailed inspection, measurement, and pattern recognition beyond the capabilities of a simple sensor array. Your choice of a vision system can significantly enhance automation precision and adaptability in complex industrial applications.
Key Technologies Behind Sensor Arrays
Sensor arrays rely on an intricate network of individual sensors, such as photodiodes or thermistors, that work collectively to capture spatial and temporal data with high precision. Key technologies behind sensor arrays include MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) fabrication, enabling miniaturization and integration, and advanced signal processing algorithms that enhance accuracy and noise reduction. Your choice between a vision system and a sensor array depends on whether you need detailed image analysis or multi-point environmental readings from tailored sensor elements.
How Vision Systems Interpret Data
Vision systems interpret data by capturing images through cameras and processing them using advanced algorithms to extract relevant features such as shape, color, and texture. Unlike sensor arrays that measure specific physical parameters like temperature or pressure, vision systems analyze visual information to identify patterns, detect objects, and make decisions based on spatial relationships. Your ability to leverage vision systems enables more comprehensive and accurate interpretation of complex environments compared to traditional sensor arrays.
Sensor Arrays: Detection and Measurement Capabilities
Sensor arrays excel in detection and measurement capabilities by capturing data across multiple points simultaneously, enabling precise spatial analysis of physical phenomena like temperature, pressure, or chemical concentrations. Unlike vision systems that rely heavily on image processing, sensor arrays provide direct quantitative measurements, enhancing accuracy in applications such as environmental monitoring, industrial automation, and healthcare diagnostics. Your choice of sensor arrays ensures reliable real-time detection and consistent measurement performance in complex environments.
Comparative Analysis: Accuracy and Precision
Vision systems typically offer higher accuracy and precision by capturing detailed spatial information and enabling complex image processing algorithms to interpret visual data. Sensor arrays provide more specialized measurements with consistent precision tailored to specific physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, or proximity, often excelling in environments with limited visibility. The choice between a vision system and sensor array depends on the application's requirement for detailed spatial analysis versus targeted, reliable parameter sensing.
Scalability and Integration Considerations
Vision systems offer high scalability through advanced image processing algorithms and can be easily integrated with AI and machine learning platforms for real-time analytics in complex environments. Sensor arrays provide modular scalability by adding or removing sensors to match application requirements, enabling flexible integration with existing control systems and industrial networks. While vision systems demand higher computational resources and careful calibration, sensor arrays benefit from simpler installation and lower latency, making them suitable for scalable, integrated solutions in diverse industrial settings.
Application Areas: Vision Systems vs Sensor Arrays
Vision systems excel in applications requiring detailed image analysis and pattern recognition, such as quality inspection in manufacturing, autonomous vehicles, and medical diagnostics. Sensor arrays are preferred in environments needing multi-point data acquisition like environmental monitoring, industrial process control, and robotics for spatial awareness. Your choice depends on whether precise visual data or diverse sensor inputs best suit the operational requirements.
Cost and Maintenance Comparison
Vision systems generally have higher upfront costs than sensor arrays due to advanced imaging technology and software requirements. Maintenance expenses for vision systems can be significant, involving regular calibration and software updates, whereas sensor arrays typically require less frequent maintenance and simpler servicing. The overall cost-effectiveness of each depends on application complexity and precision needs, with sensor arrays favored for lower-cost, simpler tasks.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting between a vision system and a sensor array depends heavily on the specific application requirements, such as precision, environmental conditions, and data complexity. Vision systems excel in tasks requiring detailed image analysis and pattern recognition, making them ideal for quality control and object identification. Sensor arrays offer faster response times and robustness in harsh environments, suitable for real-time monitoring and detecting multiple physical parameters simultaneously.
Vision System vs Sensor Array Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com