Dynamic rubber seals flex and move with components to prevent fluid leakage in applications such as rotating shafts or pistons, while static rubber seals remain stationary between two surfaces to block fluid passage. Your choice depends on whether the seal must accommodate motion or maintain a fixed barrier under pressure.
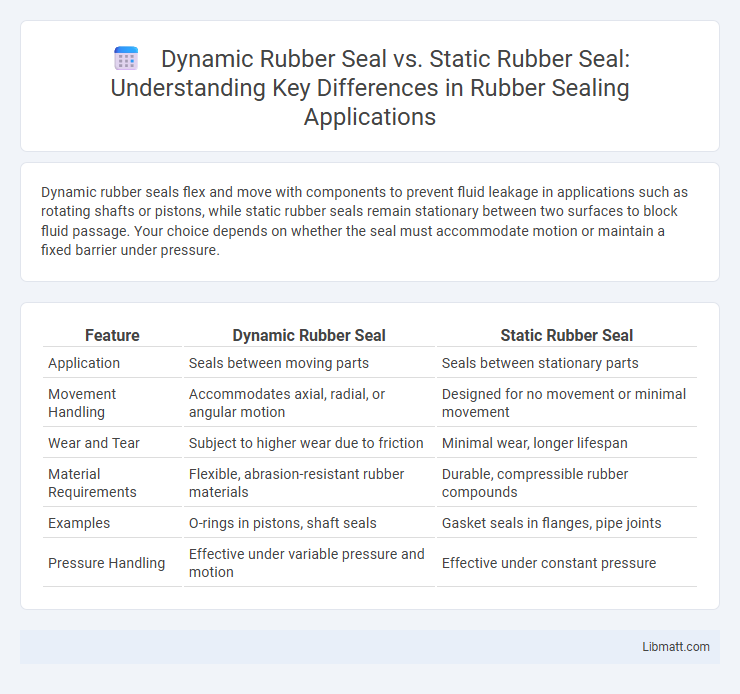
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dynamic Rubber Seal | Static Rubber Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Seals between moving parts | Seals between stationary parts |
| Movement Handling | Accommodates axial, radial, or angular motion | Designed for no movement or minimal movement |
| Wear and Tear | Subject to higher wear due to friction | Minimal wear, longer lifespan |
| Material Requirements | Flexible, abrasion-resistant rubber materials | Durable, compressible rubber compounds |
| Examples | O-rings in pistons, shaft seals | Gasket seals in flanges, pipe joints |
| Pressure Handling | Effective under variable pressure and motion | Effective under constant pressure |
Introduction to Rubber Seals
Rubber seals serve a critical role in preventing leaks and maintaining pressure in various mechanical systems. Dynamic rubber seals are specifically designed to accommodate movement between surfaces, ensuring a tight seal during motion, while static rubber seals maintain sealing integrity between stationary parts. Choosing the right seal for your application depends on understanding these operational differences to optimize performance and longevity.
Overview of Dynamic Rubber Seals
Dynamic rubber seals are designed to prevent fluid or gas leakage in applications involving relative motion between sealing surfaces, such as rotating shafts or reciprocating pistons. These seals must maintain flexibility and resilience under variable pressure and friction conditions to ensure long-lasting performance. Understanding the characteristics of dynamic rubber seals can help you choose the right solution for equipment requiring reliable sealing in motion environments.
Overview of Static Rubber Seals
Static rubber seals maintain sealing integrity by remaining stationary between two surfaces, preventing fluid or gas leakage under pressure. Designed for applications with no relative motion, these seals provide reliable performance in pipe joints, flanges, and valve covers. Your choice of material, such as EPDM or nitrile, impacts resistance to temperature, chemicals, and aging, ensuring effective static sealing.
Key Differences Between Dynamic and Static Seals
Dynamic rubber seals accommodate relative motion between sealing surfaces, maintaining a secure barrier despite axial or radial movements, while static rubber seals function effectively only when surfaces are stationary. Dynamic seals require enhanced elasticity and wear resistance to prevent leakage under friction and pressure changes, contrasting with static seals that primarily rely on compression to create a tight seal. Material selection and design considerations differ significantly, as dynamic seals often incorporate special compounds and geometries to handle dynamic stresses, whereas static seals focus on optimal shape and surface contact for a consistent, immobile seal.
Material Selection for Dynamic vs Static Seals
Material selection for dynamic rubber seals prioritizes flexibility, abrasion resistance, and the ability to withstand continuous movement, with compounds like nitrile, Viton, or silicone commonly used to ensure durability under dynamic conditions. Static rubber seals require materials that provide excellent compression set resistance and chemical stability, often utilizing EPDM or neoprene to maintain a tight seal without movement. Understanding your application's specific pressure, temperature, and chemical exposure will guide you in choosing the appropriate material for dynamic versus static seals.
Common Applications of Dynamic Rubber Seals
Dynamic rubber seals are primarily used in applications involving relative motion between sealing surfaces, such as in hydraulic cylinders, pneumatic systems, and rotating shafts. These seals ensure fluid containment and prevent leakage in environments requiring constant movement and pressure variations. Your machinery's performance and longevity depend on the accurate selection of dynamic rubber seals to accommodate dynamic sealing needs.
Common Applications of Static Rubber Seals
Static rubber seals are commonly used in applications where there is no relative movement between the sealing surfaces, such as in flange joints, pipe connections, and valve covers. These seals provide excellent resistance to leaks and maintain a reliable barrier in systems involving liquids, gases, and chemicals. You will often find static rubber seals in automotive engines, hydraulic systems, and industrial equipment requiring durable, long-lasting sealing solutions.
Performance Factors and Seal Life
Dynamic rubber seals excel in flexibility and resilience, accommodating motion while maintaining effective sealing under varying pressure and temperature conditions. Static rubber seals offer superior durability and longer service life when installed in stationary applications due to minimal movement and consistent compression. Understanding these performance factors helps you select the right seal to maximize efficiency and extend seal life in your specific engineering environment.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Dynamic rubber seals require precise installation to accommodate movement and prevent leaks, often involving more complex alignment and flexibility checks. Static rubber seals generally have simpler installation processes as they remain stationary, focusing on creating a tight, consistent seal without movement stress. Your maintenance approach should account for dynamic seals needing frequent inspections and lubrication, while static seals often require less upkeep but must be monitored for compression set and aging.
Choosing the Right Seal for Your Application
Selecting the right seal depends on whether your application involves movement or remains stationary: Dynamic rubber seals are designed to maintain a tight barrier during motion, such as rotating shafts or pistons, while static rubber seals provide effective sealing in fixed joints and flanges where no relative movement occurs. Key factors to consider include pressure, temperature, and environmental exposure, which influence the seal material and design choice to ensure durability and leak prevention. Your optimal seal choice enhances system reliability and minimizes maintenance costs by matching the seal type to the operational dynamics of your equipment.
Dynamic Rubber Seal vs Static Rubber Seal Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com