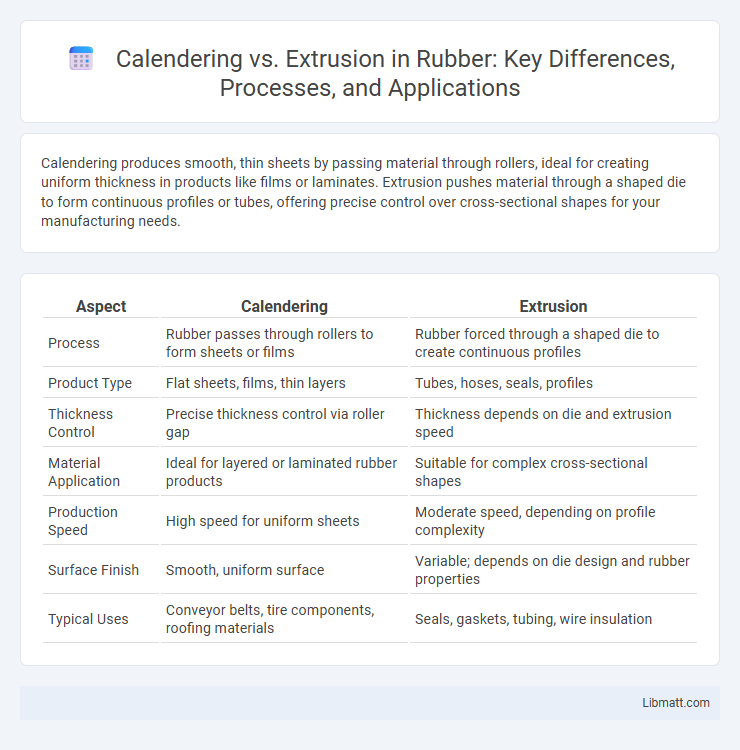
Calendering produces smooth, thin sheets by passing material through rollers, ideal for creating uniform thickness in products like films or laminates. Extrusion pushes material through a shaped die to form continuous profiles or tubes, offering precise control over cross-sectional shapes for your manufacturing needs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Calendering | Extrusion |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Rubber passes through rollers to form sheets or films | Rubber forced through a shaped die to create continuous profiles |
| Product Type | Flat sheets, films, thin layers | Tubes, hoses, seals, profiles |
| Thickness Control | Precise thickness control via roller gap | Thickness depends on die and extrusion speed |
| Material Application | Ideal for layered or laminated rubber products | Suitable for complex cross-sectional shapes |
| Production Speed | High speed for uniform sheets | Moderate speed, depending on profile complexity |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, uniform surface | Variable; depends on die design and rubber properties |
| Typical Uses | Conveyor belts, tire components, roofing materials | Seals, gaskets, tubing, wire insulation |
Introduction to Calendering and Extrusion
Calendering is a manufacturing process that involves passing materials like plastics, rubber, or textiles through a series of heated rollers to create thin, uniform sheets with precise thickness and smooth surfaces. Extrusion, by contrast, forces molten material through a shaped die to produce continuous profiles such as tubes, pipes, or films with consistent cross-sectional shapes. Understanding the fundamental differences between calendering and extrusion helps optimize your production methods for specific material properties and product requirements.
Definition and Overview of Calendering
Calendering is a manufacturing process where a material, typically polymer or rubber, is passed through a series of heated rollers to achieve a uniform thickness and smooth surface finish. This technique is commonly used to produce sheets, films, or coatings with precise dimensional control. Unlike extrusion, which involves shaping material by forcing it through a die, calendering emphasizes surface texture and thickness refinement.
Definition and Overview of Extrusion
Extrusion is a manufacturing process where material is forced through a die to create objects with a fixed cross-sectional profile, commonly used for producing pipes, sheets, and films. This method allows for continuous production and precise control of thickness and shape, making it ideal for materials like plastics and metals. Your choice between extrusion and calendering depends on the desired product characteristics, as extrusion offers more complex shapes compared to the flat sheets produced by calendering.
Key Differences Between Calendering and Extrusion
Calendering produces thin sheets or films by passing material through rollers under controlled pressure and temperature, while extrusion forces material through a shaped die to create continuous profiles or tubes. The calendering process excels in producing smooth, uniform surfaces ideal for vinyl flooring and rubber sheets, whereas extrusion is preferred for complex cross-sectional shapes used in pipes, window frames, and plastic films. Key differences include the final product form, with calendering yielding flat sheets and extrusion providing continuous lengths of varied shapes, alongside differing equipment and material flow dynamics.
Materials Used in Calendering vs Extrusion
Calendering primarily uses thermoplastic polymers such as PVC, rubber, and silicone to produce thin sheets or films with uniform thickness, ideal for applications like flooring and upholstery. Extrusion is versatile and processes a broader range of materials including polymers like polyethylene, polypropylene, and nylon, as well as metals and ceramics, forming continuous profiles, pipes, and complex cross-sections. Understanding the differences in material compatibility between calendering and extrusion helps optimize your manufacturing process for product durability and performance.
Applications of Calendering Technology
Calendering technology is widely applied in the production of plastic films, synthetic leather, and rubber sheets, offering precise control over thickness and surface texture. It is essential in manufacturing vinyl flooring, conveyor belts, and coated fabrics, where uniformity and high-quality finishes are critical. The process enhances material properties such as smoothness and gloss, making it ideal for automotive interiors, packaging materials, and textile laminates.
Applications of Extrusion Processes
Extrusion processes are widely used in manufacturing industries such as food production, plastics, and metal forming due to their ability to create complex cross-sectional profiles with high precision. You can find extrusion applied in producing pipes, sheets, films, and intricate components for automotive or aerospace applications. This method supports continuous production, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing and custom product design.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Calendering
Calendering offers precise control over film thickness and surface smoothness, making it ideal for producing uniform sheets in industries like plastics and rubber manufacturing. Its advantages include high production speed and excellent surface finish, while disadvantages involve limitations in handling highly viscous materials and potential equipment wear due to intense roller pressure. Compared to extrusion, calendering is less versatile in shaping complex profiles but excels in producing flat, consistent films with fine surface details.
Pros and Cons of Extrusion Methods
Extrusion methods offer precise control over product shapes and continuous production, making them ideal for manufacturing complex profiles with consistent cross-sections. However, extrusion can be energy-intensive and may require high initial investment in specialized machinery, potentially increasing production costs. Your choice depends on balancing these factors against the need for flexibility and surface finish quality, which calendering typically excels in.
Choosing Between Calendering and Extrusion
Choosing between calendering and extrusion depends on desired product characteristics and material type. Calendering excels in producing thin, smooth sheets with uniform thickness and surface finish, ideal for flexible vinyl and rubber applications. Extrusion offers versatility for creating complex profiles and continuous shapes, making it suitable for pipes, tubing, and custom cross-sections in plastics and metals.
Calendering vs Extrusion Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com