Carbon black and silica are widely used reinforcements in tire manufacturing, with carbon black providing excellent abrasion resistance and tensile strength, while silica enhances rolling resistance and wet traction for improved fuel efficiency and safety. Your choice between carbon black and silica reinforcement depends on the desired balance of durability, performance, and environmental impact in the final product.
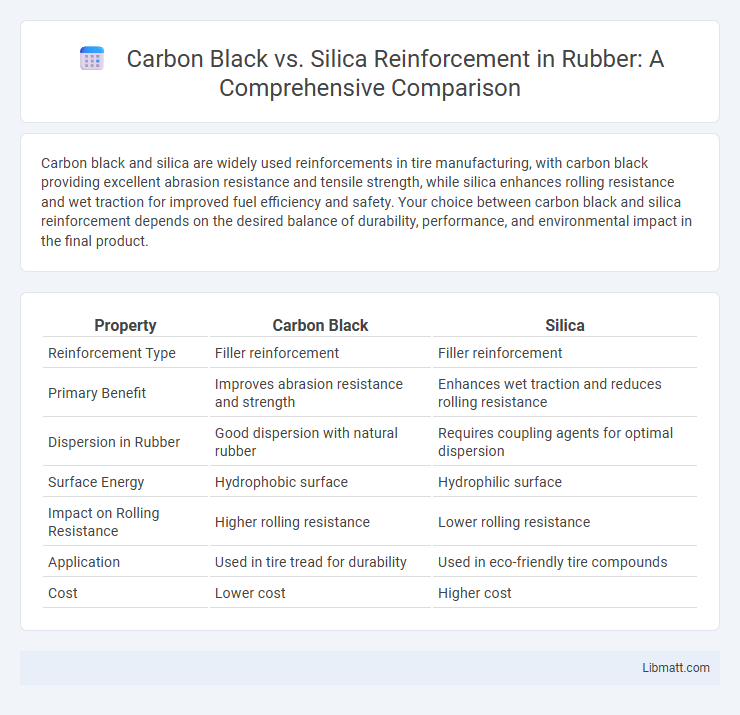
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Black | Silica |
|---|---|---|
| Reinforcement Type | Filler reinforcement | Filler reinforcement |
| Primary Benefit | Improves abrasion resistance and strength | Enhances wet traction and reduces rolling resistance |
| Dispersion in Rubber | Good dispersion with natural rubber | Requires coupling agents for optimal dispersion |
| Surface Energy | Hydrophobic surface | Hydrophilic surface |
| Impact on Rolling Resistance | Higher rolling resistance | Lower rolling resistance |
| Application | Used in tire tread for durability | Used in eco-friendly tire compounds |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Reinforcement Fillers in Rubber Compounds
Reinforcement fillers such as carbon black and silica significantly enhance the mechanical properties of rubber compounds by improving strength, abrasion resistance, and durability. Carbon black provides excellent tensile strength and wear resistance due to its strong interaction with rubber polymers, while silica offers better rolling resistance and wet traction, making it ideal for tire applications. The choice between carbon black and silica depends on the desired balance of performance characteristics, processing behavior, and end-use requirements in rubber formulations.
Overview of Carbon Black and Silica
Carbon black and silica are widely used reinforcing fillers in the rubber industry, each offering distinct advantages. Carbon black enhances tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and conductivity, making it ideal for tires and industrial products. Silica improves wet traction and rolling resistance, contributing to better fuel efficiency and safer performance, especially in automotive applications.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Carbon black consists primarily of elemental carbon in a quasi-spherical structure with high surface area, contributing to excellent abrasion resistance and conductivity in reinforced polymers. Silica features a silicon-oxygen tetrahedral network, resulting in a polar surface and stronger filler-polymer interactions, which enhance wet traction and reduce rolling resistance in tire compounds. The chemical differences influence dispersion, bonding mechanisms, and the overall mechanical performance of rubber composites.
Mechanical Performance: Strength and Durability
Carbon black offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for applications demanding high durability and mechanical performance. Silica reinforcement enhances wet traction and reduces rolling resistance but generally provides lower tensile strength compared to carbon black. Your choice depends on whether strength or energy efficiency is the priority in your material design.
Impact on Tire Rolling Resistance and Fuel Efficiency
Carbon black reinforcement significantly reduces tire rolling resistance by enhancing tread compound stiffness and abrasion resistance, which leads to improved fuel efficiency in vehicles. Silica, combined with optimized coupling agents, lowers rolling resistance even further by reducing hysteresis loss in the tire, resulting in superior wet traction and energy-saving benefits. Tires incorporating silica reinforcement generally exhibit better fuel economy due to decreased rolling resistance compared to traditional carbon black-based tires.
Abrasion Resistance: Carbon Black vs Silica
Carbon black offers superior abrasion resistance compared to silica due to its strong filler-polymer interactions and high hardness, making it ideal for heavy-duty tire treads and industrial applications. Silica provides improved wet traction and lower rolling resistance but typically results in lower abrasion resistance due to weaker filler dispersion and surface properties. Your choice depends on balancing abrasion durability with other performance factors, where carbon black remains the preferred reinforcement for maximum wear resistance.
Dispersion and Processing Characteristics
Silica offers superior dispersion in rubber compounds due to its polar surface chemistry, which enhances filler-polymer interaction and reduces agglomeration compared to carbon black. Processing silica requires coupling agents like silanes to improve compatibility and ensure uniform distribution during mixing, whereas carbon black disperses more easily but may cause higher compound viscosity. Silica-reinforced compounds generally yield better wear resistance and lower rolling resistance in tires, attributed to optimized filler dispersion and enhanced processing characteristics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Carbon black production generates significant CO2 emissions and relies on fossil fuels, leading to a larger environmental footprint compared to silica. Silica reinforcement, often derived from renewable sources or waste byproducts, offers improved sustainability with lower greenhouse gas emissions and enhanced tire fuel efficiency. Choosing silica can help reduce Your product's environmental impact through better rolling resistance and longer tire life.
Cost Analysis: Production and Application
Carbon black offers lower production costs due to established manufacturing processes and widespread availability, making it a cost-effective reinforcement for rubber and tire industries. Silica reinforcement, while more expensive due to complex production techniques and the need for coupling agents, provides enhanced performance benefits such as improved fuel efficiency and reduced rolling resistance in tires. The higher initial investment in silica is often justified by long-term savings and superior product performance in specialized applications.
Future Trends in Rubber Reinforcement Technology
Future trends in rubber reinforcement technology emphasize a shift from traditional carbon black toward silica-based fillers to enhance performance and sustainability. Silica reinforcement offers improved rolling resistance, wet traction, and reduced environmental impact compared to carbon black, aligning with automotive manufacturers' goals for eco-friendly tires. Advancements in nano-silica composites and hybrid filler systems promise to optimize mechanical properties, durability, and fuel efficiency in next-generation elastomer applications.
Carbon black vs Silica reinforcement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com