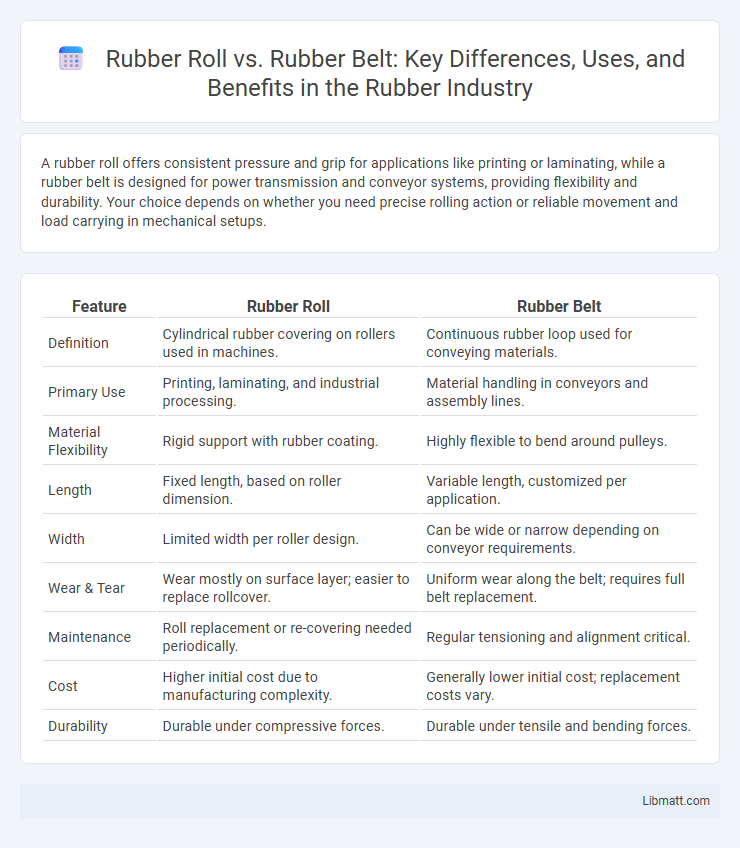
A rubber roll offers consistent pressure and grip for applications like printing or laminating, while a rubber belt is designed for power transmission and conveyor systems, providing flexibility and durability. Your choice depends on whether you need precise rolling action or reliable movement and load carrying in mechanical setups.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rubber Roll | Rubber Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cylindrical rubber covering on rollers used in machines. | Continuous rubber loop used for conveying materials. |
| Primary Use | Printing, laminating, and industrial processing. | Material handling in conveyors and assembly lines. |
| Material Flexibility | Rigid support with rubber coating. | Highly flexible to bend around pulleys. |
| Length | Fixed length, based on roller dimension. | Variable length, customized per application. |
| Width | Limited width per roller design. | Can be wide or narrow depending on conveyor requirements. |
| Wear & Tear | Wear mostly on surface layer; easier to replace rollcover. | Uniform wear along the belt; requires full belt replacement. |
| Maintenance | Roll replacement or re-covering needed periodically. | Regular tensioning and alignment critical. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to manufacturing complexity. | Generally lower initial cost; replacement costs vary. |
| Durability | Durable under compressive forces. | Durable under tensile and bending forces. |
Introduction to Rubber Roll and Rubber Belt
Rubber rolls are cylindrical components typically used in industrial machinery to provide traction, transfer motion, or apply pressure during processing. Rubber belts, on the other hand, are continuous loops of rubber material designed for power transmission and conveying systems, linking pulleys or rollers to move objects or machinery parts efficiently. Both play crucial roles in mechanical systems but differ in form and specific industrial applications.
Material Composition and Structure
Rubber rolls are typically composed of a solid rubber layer bonded to a core, often made from metal or plastic, providing durability and precise thickness control for applications like printing or laminating. Rubber belts consist of multiple layers, including a textile reinforcing layer sandwiched between rubber compounds, offering flexibility and tensile strength essential for conveyor systems. The structural difference allows rubber rolls to maintain rigidity and uniform surface contact, while rubber belts deliver elasticity and resistance to stretching under dynamic loads.
Key Applications in Industry
Rubber rolls are extensively used in printing, paper manufacturing, and metal processing industries for applications requiring precise pressure distribution and surface finishing. Rubber belts primarily function in conveyor systems, material handling, and automotive industries where flexibility and durability are essential for continuous motion and load transport. Both products play crucial roles in industrial automation, with rubber rolls offering high friction and cushioning, while rubber belts provide efficient power transmission and conveyor movement.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Rubber rolls typically offer superior performance in applications requiring consistent surface contact and pressure distribution, enhancing grip and reducing slippage. Rubber belts excel in flexibility and endurance, especially in dynamic conveyor systems, providing excellent resistance to wear, heat, and chemical exposure. In terms of durability, rubber belts generally outperform rubber rolls due to reinforced materials and construction designed to withstand continuous motion and tensile stress.
Cost Analysis and Investment
Rubber rolls typically require a higher initial investment due to their complex manufacturing process but offer longer durability and lower maintenance costs over time, making them cost-effective for high-demand industrial applications. Rubber belts, while generally less expensive upfront, may incur higher replacement and downtime costs due to faster wear and tear, impacting your overall operational efficiency. Careful cost analysis balancing initial outlay against longevity and maintenance can guide the best investment decision for your specific industrial needs.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Rubber rolls require precise alignment during installation to ensure even pressure distribution, which helps prevent premature wear and extends their lifespan. Rubber belts, on the other hand, need proper tensioning and tracking adjustments to avoid slippage and misalignment, making routine inspections essential. Your maintenance schedule should include regular cleaning, lubrication of moving parts, and timely replacement of worn components to maintain optimal performance for both rubber rolls and belts.
Advantages of Rubber Rolls
Rubber rolls provide enhanced durability and flexibility ideal for industrial applications requiring consistent pressure and impact resistance. Their seamless surface ensures uniform contact, reducing slippage and wear compared to rubber belts. You benefit from easier maintenance and longer lifespan, making rubber rolls a cost-effective solution for heavy-duty machinery.
Advantages of Rubber Belts
Rubber belts offer superior flexibility and durability compared to rubber rolls, making them ideal for continuous motion applications in conveyor systems. Their seamless construction reduces the risk of slippage and wear, enhancing operational efficiency in industries such as manufacturing and logistics. The ease of installation and maintenance of rubber belts also contributes to lower downtime and increased productivity.
Factors to Consider When Choosing
When selecting between a rubber roll and a rubber belt, consider factors such as load capacity, flexibility, and application type; rubber rolls offer high durability for heavy-duty industrial processing, while rubber belts excel in continuous, dynamic motion tasks like conveyor systems. Material composition and resistance to environmental elements like heat, chemicals, and abrasion also influence the choice, with specific rubber compounds tailored for either rolls or belts to enhance performance and lifespan. Maintenance requirements and cost-efficiency further drive decision-making, ensuring the chosen option aligns with operational demands and budget constraints.
Conclusion: Which Is Right for Your Operations?
Rubber rolls excel in applications requiring precise pressure distribution and durability, making them ideal for printing, laminating, and material handling in industrial settings. Rubber belts offer flexibility and continuous motion capabilities, perfect for conveyor systems and packaging lines needing efficient material transport. Choosing between rubber rolls and rubber belts depends on your operational needs for precision, load capacity, and motion type to optimize performance and longevity.
Rubber Roll vs Rubber Belt Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com