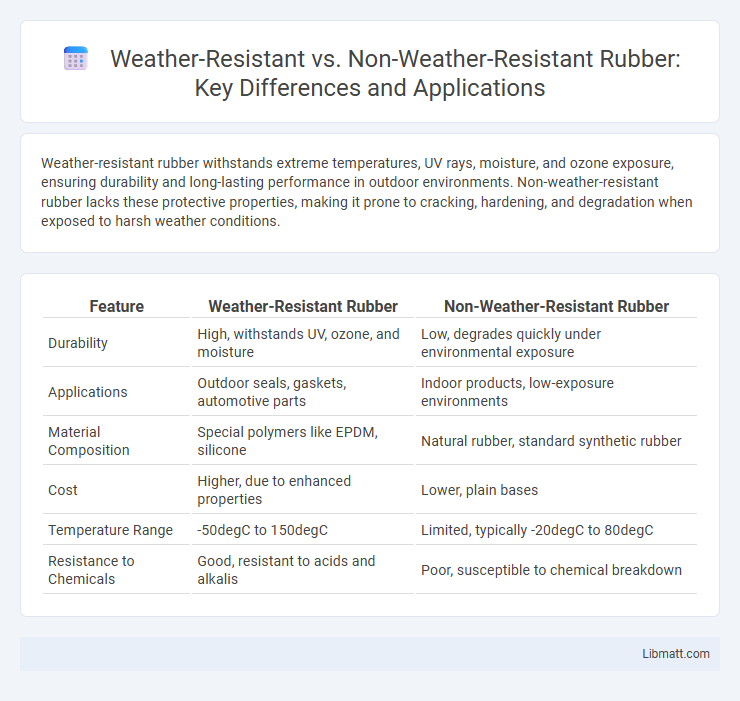
Weather-resistant rubber withstands extreme temperatures, UV rays, moisture, and ozone exposure, ensuring durability and long-lasting performance in outdoor environments. Non-weather-resistant rubber lacks these protective properties, making it prone to cracking, hardening, and degradation when exposed to harsh weather conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Weather-Resistant Rubber | Non-Weather-Resistant Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High, withstands UV, ozone, and moisture | Low, degrades quickly under environmental exposure |
| Applications | Outdoor seals, gaskets, automotive parts | Indoor products, low-exposure environments |
| Material Composition | Special polymers like EPDM, silicone | Natural rubber, standard synthetic rubber |
| Cost | Higher, due to enhanced properties | Lower, plain bases |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 150degC | Limited, typically -20degC to 80degC |
| Resistance to Chemicals | Good, resistant to acids and alkalis | Poor, susceptible to chemical breakdown |
Introduction to Rubber and Its Applications
Rubber is a versatile polymer widely used in industrial, automotive, and consumer products due to its elasticity and durability. Weather-resistant rubber is specially formulated to withstand UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for outdoor applications such as seals, gaskets, and hoses. Non-weather-resistant rubber, while effective in controlled environments, degrades quickly when exposed to harsh weather conditions, limiting its use to indoor or protected settings.
Understanding Weather-Resistant Rubber
Weather-resistant rubber exhibits superior durability against UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures, making it ideal for outdoor applications prone to harsh environmental conditions. Non-weather-resistant rubber, however, tends to degrade quickly when exposed to moisture and sunlight, leading to cracks and reduced lifespan. Understanding these differences helps you select the right rubber material to ensure long-term performance and reliability in your projects.
Defining Non-Weather-Resistant Rubber
Non-weather-resistant rubber lacks the chemical additives and molecular structure needed to withstand prolonged exposure to UV rays, ozone, and moisture, resulting in rapid degradation such as cracking and hardening. This type of rubber is primarily used in indoor applications where environmental stressors are minimal. Its vulnerability to weather elements limits its lifespan and functional reliability in outdoor conditions compared to weather-resistant rubber.
Key Differences Between Weather-Resistant and Non-Weather-Resistant Rubber
Weather-resistant rubber is formulated with additives such as antioxidants and UV stabilizers to withstand exposure to sunlight, ozone, and extreme temperatures, enhancing durability in outdoor environments. Non-weather-resistant rubber lacks these protective compounds, making it prone to cracking, hardening, and degradation when exposed to harsh weather conditions. The key differences lie in their chemical composition and performance longevity, with weather-resistant rubber being ideal for applications requiring prolonged exposure to the elements.
Material Composition and Additives
Weather-resistant rubber typically incorporates additives like antioxidants, UV stabilizers, and ozone protectants that enhance durability against sun exposure, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. Non-weather-resistant rubber often lacks these specialized compounds, making it more susceptible to cracking, brittleness, and degradation when exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Your choice between the two materials should consider the specific environmental challenges the rubber product will face to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Performance in Outdoor and Extreme Environments
Weather-resistant rubber maintains its flexibility, durability, and structural integrity under extreme temperatures, UV exposure, and moisture, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Non-weather-resistant rubber often deteriorates quickly when exposed to harsh elements, leading to cracking, brittleness, and reduced performance. Choosing weather-resistant rubber ensures your equipment or products withstand outdoor and extreme environmental conditions effectively.
Durability and Longevity Comparisons
Weather-resistant rubber exhibits enhanced durability and longevity due to its ability to withstand extreme temperatures, UV exposure, and moisture without significant degradation. In contrast, non-weather-resistant rubber typically deteriorates faster when exposed to environmental elements, leading to cracking, brittleness, and loss of elasticity. The superior chemical formulation of weather-resistant rubber significantly extends its service life in outdoor applications compared to standard non-weather-resistant variants.
Common Uses for Weather-Resistant Rubber
Weather-resistant rubber is commonly used in outdoor applications such as seals, gaskets, and hoses exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Its ability to withstand UV radiation, ozone, moisture, and temperature fluctuations makes it ideal for automotive parts, roofing membranes, and electrical insulation. In contrast, non-weather-resistant rubber is typically reserved for indoor or controlled environments where exposure to elements is minimal.
Typical Applications of Non-Weather-Resistant Rubber
Non-weather-resistant rubber is commonly used in indoor applications such as gaskets, seals, and vibration dampening components where exposure to UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures is minimal. This type of rubber excels in environments with controlled conditions, including automotive interior parts, flooring, and industrial machinery components. Its affordability and flexibility make it suitable for short-term or protected use without the need for specialized weatherproofing.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Needs
Weather-resistant rubber offers superior durability against UV rays, ozone, temperature fluctuations, and moisture, making it ideal for outdoor applications such as seals, gaskets, and automotive parts exposed to harsh environments. Non-weather-resistant rubber, while suitable for indoor or controlled environments, tends to degrade faster when exposed to sunlight or extreme weather conditions, leading to cracks and loss of elasticity. Selecting the right rubber involves assessing exposure conditions, environmental stresses, and longevity requirements to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Weather-resistant vs Non-weather-resistant rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com