Carbonized rubber undergoes a heating process that increases its carbon content, enhancing durability and resistance to wear, while vulcanized rubber is treated with sulfur to improve elasticity, strength, and heat resistance. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right type for applications requiring either greater hardness and chemical stability or superior flexibility and resilience.
Table of Comparison
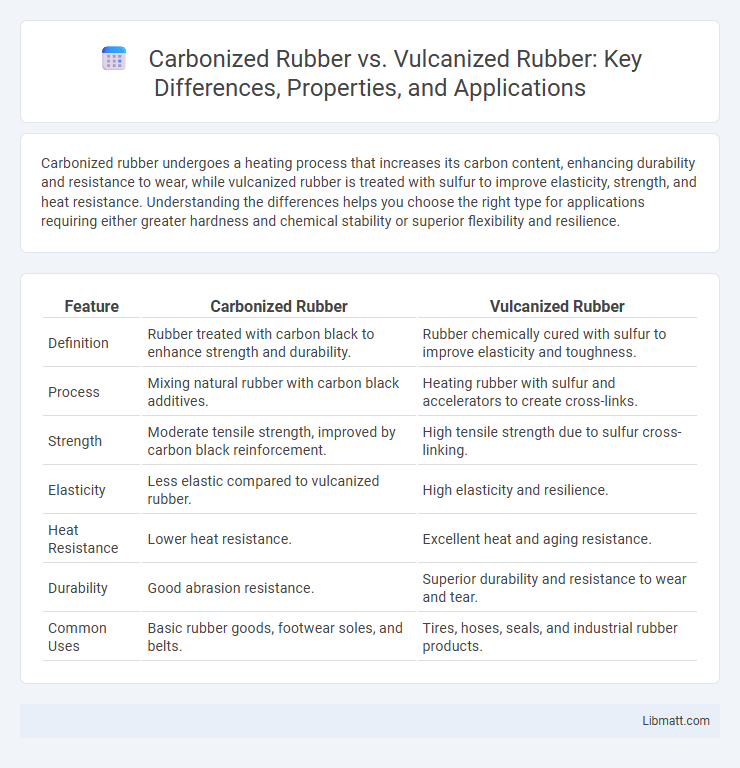
| Feature | Carbonized Rubber | Vulcanized Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rubber treated with carbon black to enhance strength and durability. | Rubber chemically cured with sulfur to improve elasticity and toughness. |
| Process | Mixing natural rubber with carbon black additives. | Heating rubber with sulfur and accelerators to create cross-links. |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength, improved by carbon black reinforcement. | High tensile strength due to sulfur cross-linking. |
| Elasticity | Less elastic compared to vulcanized rubber. | High elasticity and resilience. |
| Heat Resistance | Lower heat resistance. | Excellent heat and aging resistance. |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance. | Superior durability and resistance to wear and tear. |
| Common Uses | Basic rubber goods, footwear soles, and belts. | Tires, hoses, seals, and industrial rubber products. |
Introduction to Carbonized and Vulcanized Rubber
Carbonized rubber is produced by heating rubber in the absence of oxygen, which enhances its hardness and wear resistance by removing volatile components. Vulcanized rubber undergoes a chemical process where sulfur atoms form cross-links between polymer chains, significantly improving elasticity, strength, and durability. Your choice between these two types depends on the required performance characteristics for specific industrial or commercial applications.
Chemical Processes: Carbonization vs Vulcanization
Carbonized rubber undergoes a chemical process where rubber is exposed to high temperatures in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the removal of volatile components and a modified carbon structure that enhances hardness and durability. Vulcanized rubber undergoes a chemical reaction involving sulfur or other curatives, forming cross-links between polymer chains that improve elasticity, strength, and resistance to deformation. The carbonization process primarily alters the material's composition by thermal decomposition, while vulcanization is a controlled chemical bonding process that optimizes mechanical properties.
Key Differences in Manufacturing Methods
Carbonized rubber undergoes a process of heating rubber with carbon or carbon-rich materials at high temperatures, leading to partial carbon integration that enhances rigidity and thermal resistance. Vulcanized rubber is produced by heating raw rubber with sulfur or other cross-linking agents, creating sulfur bridges between polymer chains which significantly improve elasticity, strength, and durability. You should consider vulcanization when elasticity and mechanical performance are critical since manufacturing methods directly influence the rubber's structural properties and end-use applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Carbonized rubber exhibits increased hardness and rigidity due to the carbon buildup during the carbonization process, enhancing its abrasion resistance but reducing elasticity. Vulcanized rubber undergoes sulfur cross-linking, resulting in improved tensile strength, elasticity, and durability under varying temperatures and mechanical stresses. The vulcanization process produces rubber with superior resilience and flexibility compared to the stiffer and more brittle nature of carbonized rubber.
Durability and Longevity
Carbonized rubber, created by intense heat treatment, offers moderate durability but tends to harden and become brittle over time, reducing its longevity in demanding applications. Vulcanized rubber undergoes a chemical process with sulfur, significantly enhancing its elasticity, strength, and resistance to wear, making it far more durable and long-lasting for products exposed to heavy use and extreme conditions. Choosing vulcanized rubber ensures your items maintain flexibility and resilience, extending their functional lifespan substantially compared to carbonized rubber.
Common Applications in Industry
Carbonized rubber is primarily utilized in manufacturing automotive parts, footwear soles, and industrial belts due to its enhanced abrasion resistance and flexibility. Vulcanized rubber finds extensive application in tire production, sealing systems, and conveyor belts, benefiting from its superior elasticity, durability, and heat resistance. Both materials are essential in industries requiring specific mechanical properties tailored to operational demands and environmental exposure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbonized rubber involves a heat treatment process that breaks down rubber's molecular structure, often producing fewer emissions compared to vulcanization, which uses sulfur and produces sulfur dioxide, a harmful pollutant. Vulcanized rubber exhibits enhanced durability and recyclability, making it more sustainable for long-term applications despite its initial environmental cost. Both methods impact the environment differently, with carbonized rubber offering lower immediate emissions, while vulcanized rubber supports extended product life and reduced waste.
Cost Effectiveness and Economic Factors
Carbonized rubber involves a simpler and less energy-intensive process, resulting in lower production costs compared to vulcanized rubber, which requires sulfur and higher temperatures. Despite higher initial costs, vulcanized rubber offers enhanced durability and elasticity, leading to longer product life and reduced replacement expenses. For applications demanding long-term performance, the economic benefits of vulcanized rubber often outweigh its upfront cost disadvantage.
Performance Under Extreme Conditions
Carbonized rubber exhibits moderate performance under extreme conditions, offering improved heat resistance and flexibility but limited durability compared to vulcanized rubber. Vulcanized rubber undergoes a chemical process that significantly enhances its strength, elasticity, and resistance to temperature fluctuations, making it ideal for high-stress environments. Your choice of material depends on the specific demands of the application, with vulcanized rubber generally providing superior resilience and longevity in harsh conditions.
Future Trends in Rubber Technology
Future trends in rubber technology emphasize the integration of sustainable processes, with carbonized rubber gaining attention for its eco-friendly production and potential applications in energy storage and composite materials. Vulcanized rubber continues to evolve through advanced curing techniques and nanotechnology enhancements, improving durability, elasticity, and thermal resistance in automotive and industrial sectors. Innovations targeting recyclability and performance optimization are driving research investments, positioning both carbonized and vulcanized rubber as critical components in the development of next-generation smart materials.
Carbonized Rubber vs Vulcanized Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com