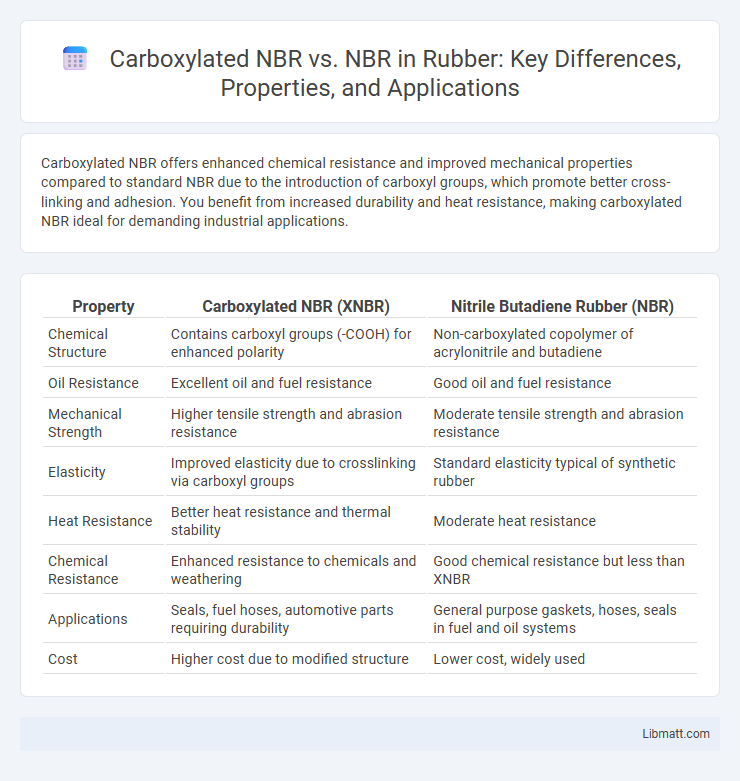
Carboxylated NBR offers enhanced chemical resistance and improved mechanical properties compared to standard NBR due to the introduction of carboxyl groups, which promote better cross-linking and adhesion. You benefit from increased durability and heat resistance, making carboxylated NBR ideal for demanding industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carboxylated NBR (XNBR) | Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Contains carboxyl groups (-COOH) for enhanced polarity | Non-carboxylated copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene |
| Oil Resistance | Excellent oil and fuel resistance | Good oil and fuel resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate tensile strength and abrasion resistance |
| Elasticity | Improved elasticity due to crosslinking via carboxyl groups | Standard elasticity typical of synthetic rubber |
| Heat Resistance | Better heat resistance and thermal stability | Moderate heat resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Enhanced resistance to chemicals and weathering | Good chemical resistance but less than XNBR |
| Applications | Seals, fuel hoses, automotive parts requiring durability | General purpose gaskets, hoses, seals in fuel and oil systems |
| Cost | Higher cost due to modified structure | Lower cost, widely used |
Introduction to NBR and Carboxylated NBR
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and other chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Carboxylated NBR (XNBR) incorporates carboxyl groups into the polymer chain, enhancing its mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and adhesion properties compared to standard NBR. Your choice between NBR and Carboxylated NBR depends on the required durability and chemical resistance in your specific application.
Chemical Structure Differences
Carboxylated NBR (XNBR) contains carboxyl groups (-COOH) introduced into the nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) backbone, enhancing polarity and intermolecular interactions. This modification enables stronger hydrogen bonding and crosslinking density compared to standard NBR, which primarily consists of acrylonitrile and butadiene units without reactive carboxyl functionalities. The presence of carboxyl groups in XNBR improves mechanical properties and chemical resistance over conventional NBR due to its altered chemical structure.
Key Physical and Mechanical Properties
Carboxylated NBR (XNBR) exhibits enhanced tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and improved oil and fuel resistance compared to standard NBR due to the presence of carboxyl groups that enable stronger cross-linking. XNBR also demonstrates higher hardness and better low-temperature flexibility, making it more suitable for dynamic applications requiring durability under stress. The increased polarity from carboxylation improves adhesion properties, expanding potential uses in automotive seals, hoses, and gloves.
Resistance to Chemicals and Oils
Carboxylated NBR exhibits enhanced resistance to chemicals and oils compared to standard NBR due to the presence of carboxyl groups that improve polymer crosslinking and polarity. This increased polarity improves interaction with polar solvents and oils, extending material durability in aggressive chemical environments. Consequently, carboxylated NBR is preferred in applications requiring superior resistance to hydrocarbons, fuels, and lubricants.
Heat and Temperature Performance
Carboxylated NBR exhibits enhanced heat resistance compared to standard NBR due to the presence of carboxyl groups, which improve cross-linking and stability at elevated temperatures. This modification allows Carboxylated NBR to maintain flexibility and mechanical integrity in applications exposed to higher thermal conditions, often surpassing the temperature limits of conventional NBR. When selecting materials for your project requiring superior thermal performance, Carboxylated NBR provides better durability and heat aging properties.
Applications in Various Industries
Carboxylated NBR (XNBR) offers enhanced chemical resistance and mechanical strength compared to standard NBR, making it ideal for automotive fuel hoses and sealants in the oil and gas industry. Its improved abrasion resistance and heat stability extend applications to industrial gloves and conveyor belts, outperforming typical NBR in demanding environments. NBR remains widely used in applications such as gaskets, O-rings, and flexible tubing where moderate resistance to oils and fuels is required.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Carboxylated NBR typically costs more than standard NBR due to its enhanced chemical resistance and improved mechanical properties, which require additional processing steps. Standard NBR is more widely available and generally less expensive, making it a cost-effective choice for applications with less demanding environmental conditions. Your decision between Carboxylated NBR and NBR should balance performance needs against budget constraints and material accessibility.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Carboxylated NBR exhibits improved compatibility with polar fillers and enhanced adhesion properties compared to standard NBR, facilitating easier mixing and compounding during processing. Its increased crosslink density leads to faster cure rates and better control over vulcanization, optimizing manufacturing efficiency. However, processing temperatures must be carefully managed to prevent premature degradation due to the sensitive carboxyl groups in Carboxylated NBR.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carboxylated NBR (XNBR) offers enhanced chemical resistance and mechanical properties compared to standard NBR, leading to longer product lifespans and reduced material waste, which positively impacts environmental sustainability. The incorporation of carboxyl groups improves recyclability and facilitates more efficient downcycling options, decreasing overall environmental footprint. Understanding these differences helps you make more eco-conscious choices in applications requiring durable, sustainable elastomer solutions.
Choosing Between Carboxylated NBR and NBR
Choosing between Carboxylated NBR and standard NBR depends on your application's need for enhanced chemical resistance and mechanical strength. Carboxylated NBR offers improved oil resistance, abrasion resistance, and better adhesion due to added carboxyl groups, making it ideal for automotive seals, hoses, and gaskets. If your project requires superior durability under harsh conditions, Carboxylated NBR provides measurable performance benefits compared to conventional NBR.
Carboxylated NBR vs NBR Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com