Rubber paste offers a thicker consistency ideal for bonding heavy-duty materials, while rubber solution provides a thinner, more flexible adhesive suited for precise applications. Your choice depends on the specific project needs, where paste ensures strong durability and solution allows easier spreading and faster drying.
Table of Comparison
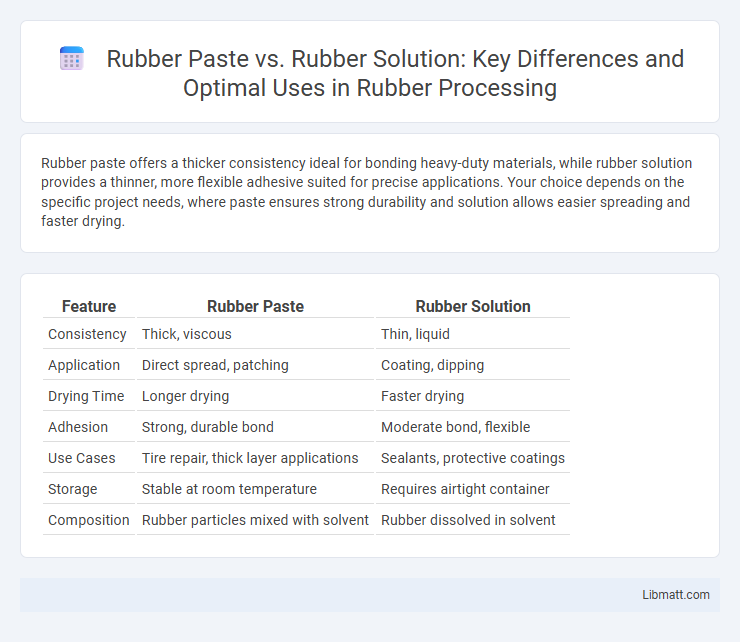
| Feature | Rubber Paste | Rubber Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Consistency | Thick, viscous | Thin, liquid |
| Application | Direct spread, patching | Coating, dipping |
| Drying Time | Longer drying | Faster drying |
| Adhesion | Strong, durable bond | Moderate bond, flexible |
| Use Cases | Tire repair, thick layer applications | Sealants, protective coatings |
| Storage | Stable at room temperature | Requires airtight container |
| Composition | Rubber particles mixed with solvent | Rubber dissolved in solvent |
Introduction to Rubber Paste and Rubber Solution
Rubber paste is a thick, adhesive material made by mixing raw rubber with solvents and fillers, commonly used in tire retreading and industrial repairs for strong, flexible bonding. Rubber solution, on the other hand, is a liquid dispersion of raw rubber particles in solvents, providing easier application and quicker drying times ideal for surface coatings and light repairs. Understanding the differences between rubber paste and rubber solution ensures you choose the right product for your specific rubber repair or fabrication needs.
Chemical Composition and Formulation
Rubber paste typically consists of concentrated rubber particles mixed with solvents and stabilizers, designed to maintain high viscosity for effective bonding and sealing. Rubber solution, on the other hand, contains dissolved rubber polymers in solvents, resulting in a lower viscosity liquid ideal for detailed applications and faster drying times. Your choice depends on the chemical composition needed for specific adhesion properties and the desired formulation consistency for your project.
Distinct Properties and Characteristics
Rubber paste features a thicker, more viscous consistency that provides enhanced elasticity and strong adhesive qualities, making it ideal for applications requiring durable bonding and flexibility. Rubber solution is typically a thinner, solvent-based form, allowing for easier penetration and quicker drying times, suitable for surface coatings and minor repairs. The choice between rubber paste and rubber solution depends on the specific requirements of viscosity, drying time, and application type in industrial or repair contexts.
Common Applications in Industry
Rubber paste is frequently used in tire retreading, shoe manufacturing, and sealing applications due to its thick consistency and strong adhesive properties. Rubber solution, with its more fluid form, is preferred for coating fabrics, adhesives in automotive parts, and flexible bonding processes in electronics. Understanding the differences in these materials can help you choose the best option for industrial applications requiring durability and flexibility.
Advantages of Rubber Paste
Rubber paste offers superior adhesion and flexibility compared to rubber solution, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring durable bonding. It provides faster drying times and better resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and temperature variations. Its thicker consistency allows for easier control and precise application, reducing wastage and enhancing overall efficiency in industrial and repair settings.
Benefits of Using Rubber Solution
Rubber solution offers superior adhesion and flexibility compared to rubber paste, making it ideal for strong, durable repairs and bonding in various applications. Its fast-drying properties and ability to penetrate surfaces ensure a reliable, long-lasting seal that resists water and environmental damage. Choosing rubber solution enhances the performance and longevity of your projects by providing a more consistent and professional finish.
Comparison of Performance and Efficiency
Rubber paste offers higher viscosity and enhanced bonding strength, making it ideal for applications requiring strong adhesion and durability, while rubber solution provides lower viscosity, facilitating easier application and faster drying times. Rubber paste tends to deliver superior abrasion and chemical resistance, whereas rubber solution excels in flexibility and penetration on porous surfaces. Efficiency-wise, rubber solution allows for quicker processing and less material waste in large-scale manufacturing, whereas rubber paste is preferred for heavy-duty tasks demanding robust performance.
Safety and Handling Considerations
Rubber paste generally poses fewer health risks than rubber solution due to its thicker consistency, which reduces the inhalation of harmful fumes. Rubber solutions often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as toluene or hexane, requiring stringent ventilation and protective equipment during handling to prevent respiratory and skin exposure. Proper storage in sealed containers and adherence to safety data sheet (SDS) guidelines are crucial for both materials to minimize fire hazards and chemical exposure.
Environmental Impact and Disposal
Rubber paste typically contains fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and is less harmful to the environment compared to rubber solution, which often includes solvents that contribute to air pollution and pose disposal challenges. Disposal of rubber paste generally requires less stringent handling due to its lower toxicity, while rubber solution demands careful management to prevent soil and water contamination. Choosing rubber paste reduces environmental risks and simplifies regulatory compliance related to waste treatment.
Choosing the Right Product for Your Needs
Rubber paste offers a thicker consistency ideal for bonding heavier materials or filling gaps, while rubber solution provides a thinner, more liquid form suited for seamless coatings and light adhesive applications. Selecting the right product depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as the type of materials involved, drying time, and desired durability. Evaluating these factors ensures optimal performance and longevity in rubber repair or fabrication tasks.
Rubber Paste vs Rubber Solution Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com