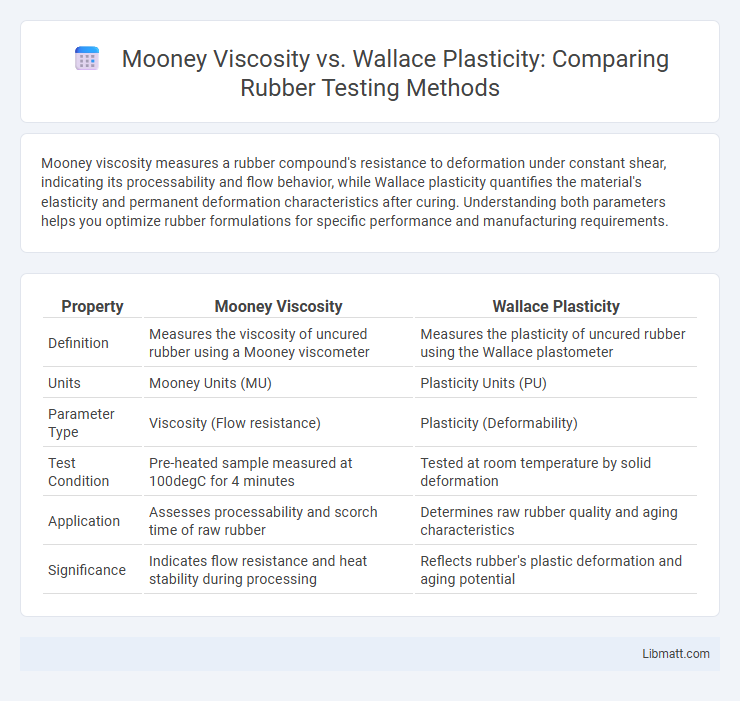
Mooney viscosity measures a rubber compound's resistance to deformation under constant shear, indicating its processability and flow behavior, while Wallace plasticity quantifies the material's elasticity and permanent deformation characteristics after curing. Understanding both parameters helps you optimize rubber formulations for specific performance and manufacturing requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mooney Viscosity | Wallace Plasticity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures the viscosity of uncured rubber using a Mooney viscometer | Measures the plasticity of uncured rubber using the Wallace plastometer |
| Units | Mooney Units (MU) | Plasticity Units (PU) |
| Parameter Type | Viscosity (Flow resistance) | Plasticity (Deformability) |
| Test Condition | Pre-heated sample measured at 100degC for 4 minutes | Tested at room temperature by solid deformation |
| Application | Assesses processability and scorch time of raw rubber | Determines raw rubber quality and aging characteristics |
| Significance | Indicates flow resistance and heat stability during processing | Reflects rubber's plastic deformation and aging potential |
Introduction to Mooney Viscosity and Wallace Plasticity
Mooney Viscosity measures the shear viscosity of rubber compounds, providing critical insights into their processing characteristics under specific temperature and strain conditions. Wallace Plasticity evaluates the plastic deformation behavior of raw rubber, indicating its resistance to permanent set and suitability for dynamic applications. Understanding these parameters helps you optimize rubber formulation for enhanced performance and manufacturing efficiency.
Defining Mooney Viscosity
Mooney Viscosity measures the viscosity of rubber compounds under specific temperature and shear conditions, providing insights into processability and curing behavior. It is determined using a Mooney viscometer, which evaluates the torque required to rotate a disk in the rubber sample, reflecting the compound's flow characteristics before vulcanization. Understanding Mooney Viscosity is critical for optimizing rubber manufacturing processes and predicting final material properties.
Understanding Wallace Plasticity
Wallace Plasticity measures the deformation behavior of rubber compounds under specific stress and strain conditions, providing insights into their elasticity and flexibility. Unlike Mooney Viscosity, which assesses the material's viscosity at a set temperature, Wallace Plasticity reflects how your rubber responds to continuous mechanical forces, influencing processing and final product performance. Understanding Wallace Plasticity helps optimize compound formulations for improved durability and manufacturing efficiency.
Measurement Methods: Mooney vs Wallace
Mooney viscosity is measured using a Mooney viscometer, which assesses the torque required to rotate a disc within a rubber sample at a specific temperature, providing data on the rubber's viscosity under shear. Wallace plasticity is determined through a Wallace plastometer that measures the flow time of a rubber sample passing through a narrow slit at a controlled temperature, reflecting the material's plasticity and processability. Your choice between these methods depends on whether you need insights into the rubber's viscous behavior or its plastic deformation characteristics during processing.
Key Differences Between Mooney Viscosity and Wallace Plasticity
Mooney Viscosity measures the resistance of uncured rubber to flow, providing insight into processing characteristics and molecular weight, while Wallace Plasticity evaluates the plastic deformation behavior and stress relaxation of rubber under constant strain. The key difference lies in Mooney Viscosity's focus on viscosity under shear, whereas Wallace Plasticity emphasizes permanent deformation and elasticity changes over time. Understanding these properties helps you optimize rubber compound formulations for performance and durability.
Applications in the Rubber Industry
Mooney Viscosity measures the flow characteristics and processing behavior of raw rubber, critical for controlling manufacturing parameters like mixing and extrusion. Wallace Plasticity evaluates the vulcanized rubber's elastic and plastic deformation, providing insight into final product performance such as durability and flexibility. Understanding both Mooney Viscosity and Wallace Plasticity helps you optimize rubber formulations for applications ranging from tires to industrial seals.
Factors Influencing Mooney Viscosity and Wallace Plasticity
Mooney viscosity is influenced by molecular weight, polymer structure, and temperature, affecting the rubber's processability and flow behavior during mixing and shaping. Wallace plasticity primarily depends on the polymer's crosslink density, filler content, and aging conditions, reflecting the material's resistance to deformation and permanent set. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing rubber compound performance in industrial applications.
Importance in Material Quality Control
Mooney Viscosity and Wallace Plasticity are critical parameters in material quality control, reflecting the elastomer's flow characteristics and stiffness, respectively. Monitoring Mooney Viscosity ensures consistent polymer molecular weight and processing behavior, while Wallace Plasticity gauges the polymer's resistance to deformation and aging, impacting durability. Your production quality relies on balancing these properties to achieve optimal performance and longevity in rubber products.
Comparative Advantages and Limitations
Mooney viscosity offers a quick and reliable measurement of raw rubber's processability under heat and shear, making it ideal for quality control in rubber manufacturing. Wallace plasticity provides a more detailed assessment of vulcanized rubber's elasticity and plastic deformation characteristics, crucial for predicting long-term material performance. While Mooney viscosity is limited in evaluating cured rubber properties, Wallace plasticity lacks immediacy and is less suited for rapid production adjustments.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Test for Rubber Characterization
Mooney Viscosity measures the rubber's resistance to shearing under defined temperature and time, providing essential data on processability and polymer molecular weight distribution. Wallace Plasticity evaluates the material's elastic recovery and deformation behavior at room temperature, critical for predicting performance in applications requiring dimensional stability. Choosing between Mooney Viscosity and Wallace Plasticity depends on the specific rubber property under investigation; Mooney Viscosity is ideal for processing parameters, while Wallace Plasticity offers insights into mechanical durability and product lifespan.
Mooney Viscosity vs Wallace Plasticity Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com