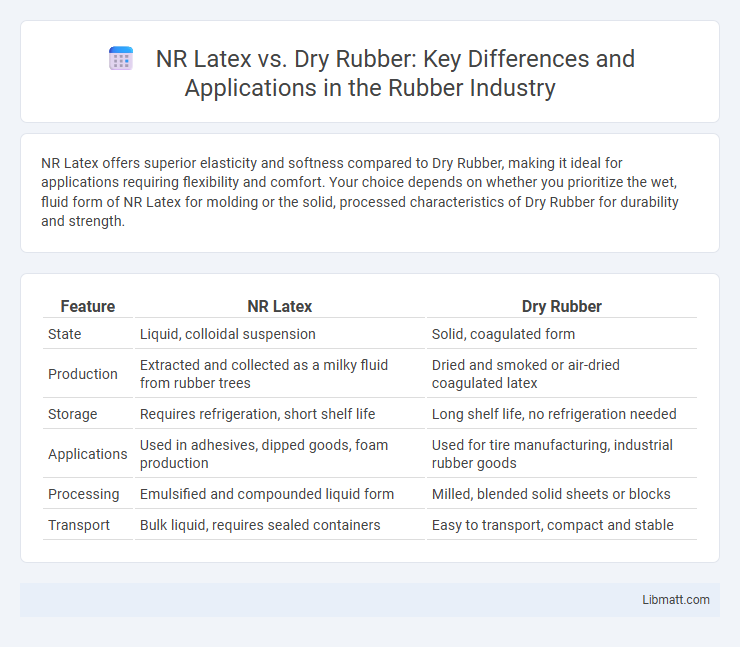
NR Latex offers superior elasticity and softness compared to Dry Rubber, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and comfort. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize the wet, fluid form of NR Latex for molding or the solid, processed characteristics of Dry Rubber for durability and strength.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | NR Latex | Dry Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| State | Liquid, colloidal suspension | Solid, coagulated form |
| Production | Extracted and collected as a milky fluid from rubber trees | Dried and smoked or air-dried coagulated latex |
| Storage | Requires refrigeration, short shelf life | Long shelf life, no refrigeration needed |
| Applications | Used in adhesives, dipped goods, foam production | Used for tire manufacturing, industrial rubber goods |
| Processing | Emulsified and compounded liquid form | Milled, blended solid sheets or blocks |
| Transport | Bulk liquid, requires sealed containers | Easy to transport, compact and stable |
Introduction to NR Latex and Dry Rubber
NR Latex, or Natural Rubber Latex, is a milky fluid harvested from rubber trees, prized for its elasticity and used in applications like gloves, balloons, and adhesives. Dry Rubber, derived by coagulating NR latex and drying the resulting rubber, offers a solid form suitable for manufacturing tires, footwear, and industrial products. Understanding the distinctions between NR Latex's liquid state and Dry Rubber's solid form helps you select the right material for your specific industrial or consumer needs.
Key Differences Between NR Latex and Dry Rubber
NR latex is a natural polymer in liquid form obtained from the Hevea brasiliensis tree, characterized by its high elasticity and suitability for dipping and coating applications. Dry rubber, derived from coagulated NR latex, is processed into solid sheets or blocks and used primarily in manufacturing tires, footwear, and industrial goods. The key differences lie in their physical state--latex being liquid and dry rubber solid--as well as their processing methods and application versatility.
Overview of Natural Rubber (NR) Latex
Natural Rubber (NR) Latex is a milky fluid harvested from rubber trees, primarily Hevea brasiliensis, and is valued for its elasticity, resilience, and biodegradability. This natural polymer consists of cis-1,4-polyisoprene particles suspended in water, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and strength, such as gloves, balloons, and adhesives. Your choice between NR Latex and dry rubber depends on the need for processing ease and specific product properties, with NR Latex offering superior stretch and tactile sensations in finished goods.
Overview of Dry Rubber Production
Dry rubber production involves coagulating fresh latex from rubber trees using acids, then pressing, drying, and smoking the coagulum to create solid sheets. This method reduces moisture content, enhances storage stability, and facilitates easier transportation compared to natural rubber latex (NR Latex), which is liquid and perishable. The primary product, technically specified rubber (TSR), undergoes strict grading based on impurity levels and physical characteristics to meet industrial standards.
Processing Methods: Latex vs Dry Rubber
NR (Natural Rubber) Latex undergoes a liquid-state processing method involving techniques like centrifugation, creaming, and compounding to produce products such as gloves, adhesives, and foams. Dry rubber processing involves coagulating latex into sheets or crumbs, followed by mastication, mixing with additives, and vulcanization to create solid rubber products like tires and footwear. The key difference lies in latex processing maintaining rubber in its colloidal form for flexible applications, whereas dry rubber processing transforms it into a dense, durable solid for heavy-duty uses.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
NR latex exhibits excellent elasticity, high tensile strength, and superior abrasion resistance due to its cis-1,4-polyisoprene molecular structure, while dry rubber offers enhanced durability and stability under heat and oxidation. Chemically, NR latex is a colloidal dispersion of natural rubber particles in water, making it highly flexible and easy to process, whereas dry rubber exists as a solid polymer form with reduced plasticizer content. Your choice depends on the application's need for either flexible, processable material or robust, aging-resistant rubber performance.
Major Applications of NR Latex
NR Latex is extensively used in medical gloves, condoms, and adhesive formulations due to its excellent elasticity and biocompatibility, making it ideal for sensitive applications requiring flexibility and durability. In contrast, Dry Rubber is preferred in automotive parts, footwear, and industrial products where resilience and abrasion resistance are critical. Your choice between NR Latex and Dry Rubber should depend on the specific application requirements, particularly whether elasticity or toughness is the priority.
Major Applications of Dry Rubber
Dry rubber, primarily composed of natural rubber latex that has been coagulated and dried, is widely used in tire manufacturing due to its excellent elasticity and resilience. It also plays a crucial role in producing industrial products like conveyor belts, hoses, and gaskets, where durability and resistance to wear are essential. Additionally, dry rubber is favored in footwear and molded goods for its superior mechanical properties compared to NR latex-based materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
NR latex, derived from the sap of rubber trees, is biodegradable and supports sustainable rubber plantation practices, making it environmentally favorable compared to synthetic options. Dry rubber, processed from coagulated latex, has a lower water content and reduced transportation weight, which can decrease its carbon footprint. For your sustainable choices, NR latex offers renewable benefits while dry rubber emphasizes efficient resource use in manufacturing.
Choosing Between NR Latex and Dry Rubber
Choosing between NR latex and dry rubber depends on application requirements such as elasticity, durability, and processing method. NR latex offers superior flexibility and is ideal for products needing high elasticity like gloves and balloons, while dry rubber provides enhanced strength and is better suited for heavy-duty items like tires and industrial seals. Consider factors such as curing process, environmental resistance, and end-use performance to select the optimal material for manufacturing.
NR Latex vs Dry Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com