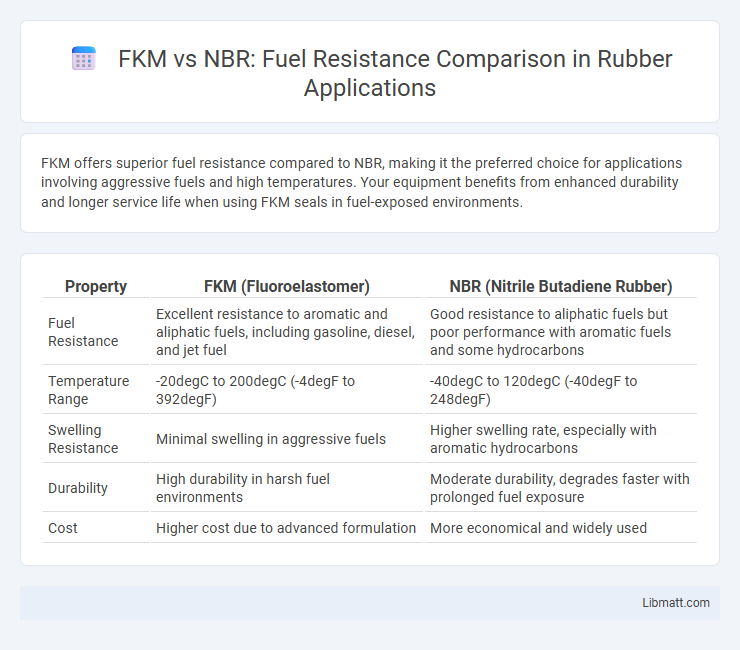
FKM offers superior fuel resistance compared to NBR, making it the preferred choice for applications involving aggressive fuels and high temperatures. Your equipment benefits from enhanced durability and longer service life when using FKM seals in fuel-exposed environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | FKM (Fluoroelastomer) | NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Resistance | Excellent resistance to aromatic and aliphatic fuels, including gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel | Good resistance to aliphatic fuels but poor performance with aromatic fuels and some hydrocarbons |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 200degC (-4degF to 392degF) | -40degC to 120degC (-40degF to 248degF) |
| Swelling Resistance | Minimal swelling in aggressive fuels | Higher swelling rate, especially with aromatic hydrocarbons |
| Durability | High durability in harsh fuel environments | Moderate durability, degrades faster with prolonged fuel exposure |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced formulation | More economical and widely used |
Introduction to Fuel Resistance in Elastomers
Fuel resistance in elastomers is crucial for applications exposed to hydrocarbons, where materials like FKM (fluoroelastomer) and NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber) are commonly compared. FKM offers superior chemical stability and resistance to a broader range of fuels and oils, making it ideal for high-performance automotive and aerospace seals. Your choice between FKM and NBR should consider temperature range, fuel composition, and durability requirements to ensure optimal sealing performance and longevity.
Overview of FKM (Fluoroelastomer)
FKM (Fluoroelastomer) is a high-performance synthetic rubber known for its exceptional resistance to fuels, oils, and chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace applications. Its fluorine content provides superior heat and oxidation resistance compared to NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber), allowing it to maintain flexibility and durability in harsh environments. You can rely on FKM seals and gaskets for long-lasting fuel resistance, particularly in demanding temperature and chemical exposure conditions.
Overview of NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber)
NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and other chemicals, making it a popular choice for fuel system components and seals. Its chemical structure allows it to maintain flexibility and durability under exposure to hydrocarbons, particularly in applications involving gasoline, diesel, and mineral oils. NBR typically offers good abrasion resistance and physical strength, but it is less effective in high-temperature environments compared to FKM rubber.
Chemical Structure: FKM vs NBR
FKM (fluoroelastomer) features a highly fluorinated polymer backbone, providing strong resistance to fuels, oils, and chemicals due to its carbon-fluorine bonds' stability. NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber) consists of copolymers of acrylonitrile and butadiene, offering excellent resistance to petroleum-based fuels but lower resistance to ozone and weathering. Your choice depends on the specific fuel environment; FKM excels in harsh chemical exposure while NBR is cost-effective for moderate fuel resistance.
Resistance to Fuels: Key Comparisons
FKM offers superior resistance to a wide range of fuels, including gasoline, diesel, and aviation fuel, making it ideal for high-performance automotive and aerospace applications. NBR performs well against oils and some fuels but degrades faster when exposed to aggressive fuels or prolonged contact with hydrocarbons. Your choice between FKM and NBR should consider the specific fuel types and operating conditions to ensure optimal seal longevity and performance.
Temperature Performance in Fuel Applications
FKM exhibits superior temperature performance in fuel applications, maintaining stability and flexibility from -20degC to 200degC, which makes it ideal for high-heat environments such as automotive fuel systems. NBR typically performs well within a narrower temperature range of -40degC to 120degC but tends to harden or degrade when exposed to higher temperatures, limiting its use in more demanding fuel conditions. The enhanced thermal resistance of FKM ensures longer service life and better resilience against fuel-induced swelling and breakdown.
Compatibility with Fuel Additives and Blends
FKM exhibits superior compatibility with a wide range of fuel additives and blends, including oxygenates and biofuels, due to its excellent chemical resistance and stable fluoropolymer structure. NBR struggles with certain fuel additives, particularly ethanol and methanol blends, which can cause swelling and degradation, limiting its use in modern fuel systems. The enhanced fuel resistance of FKM makes it the preferred choice for seals and gaskets in advanced fuel applications where exposure to additives and complex blends is common.
Long-Term Aging and Degradation
FKM (fluoroelastomer) exhibits superior fuel resistance compared to NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber) due to its excellent long-term aging properties and low degradation rate in harsh hydrocarbon environments. Over extended exposure to fuels, FKM maintains its elasticity, chemical stability, and mechanical integrity, while NBR tends to swell, harden, and degrade faster, resulting in reduced sealing performance. For applications requiring durable fuel resistance and extended service life, selecting FKM ensures better reliability and reduced maintenance costs for your equipment.
Industry Applications: FKM vs NBR in Fuel Systems
FKM exhibits exceptional fuel resistance, making it ideal for high-performance fuel systems in automotive and aerospace industries where exposure to aggressive fuels and high temperatures is common. NBR, while cost-effective and widely used in standard fuel systems such as fuel hoses and seals, has limited resistance to aromatic fuels and additives, restricting its use in more demanding environments. Industry applications favor FKM over NBR for critical components like fuel injectors, seals, and o-rings in advanced engines requiring superior chemical and temperature stability.
Choosing the Right Elastomer for Fuel Resistance
FKM (fluoroelastomer) exhibits superior fuel resistance compared to NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber), making it the preferred choice for applications involving exposure to harsh fuels and chemicals. NBR offers good resistance to petroleum-based fuels but degrades faster in the presence of aggressive hydrocarbons or high-temperature environments. Selecting FKM ensures enhanced durability and longevity in fuel system components, especially where compatibility with a wide range of fuels and high thermal stability is critical.
Fuel resistance: FKM vs NBR Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com