Solid gaskets provide superior durability and resistance to high pressure and temperature, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications, while foam gaskets offer excellent compression and sealing for irregular surfaces and vibration dampening. Choosing the right gasket depends on your specific needs for sealing performance, material compatibility, and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
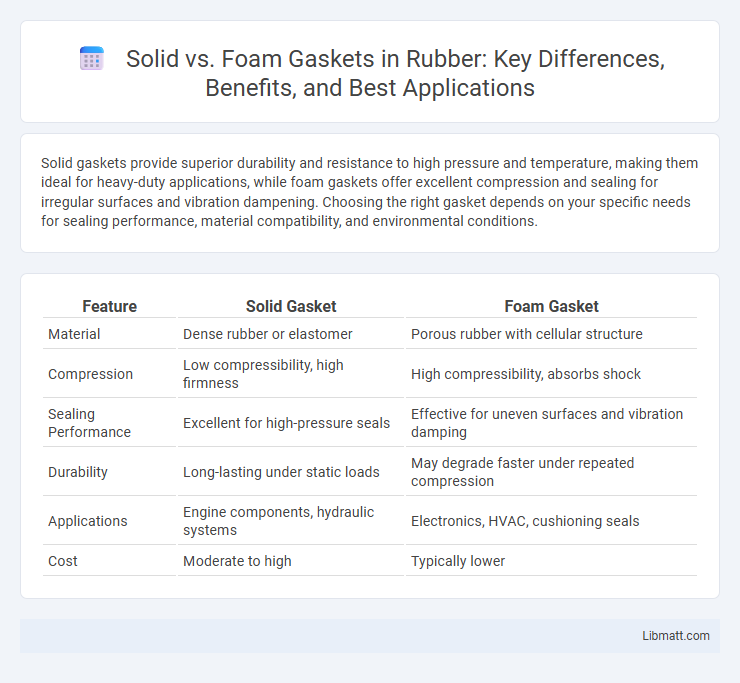
| Feature | Solid Gasket | Foam Gasket |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Dense rubber or elastomer | Porous rubber with cellular structure |
| Compression | Low compressibility, high firmness | High compressibility, absorbs shock |
| Sealing Performance | Excellent for high-pressure seals | Effective for uneven surfaces and vibration damping |
| Durability | Long-lasting under static loads | May degrade faster under repeated compression |
| Applications | Engine components, hydraulic systems | Electronics, HVAC, cushioning seals |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Typically lower |
Introduction to Gasket Types
Solid gaskets are made from robust materials like metal or compressed fiber, providing high durability and excellent resistance to pressure and temperature. Foam gaskets offer flexibility and superior sealing for irregular surfaces due to their compressible and lightweight nature. Choosing the right gasket type ensures Your application's optimal sealing performance and longevity.
What is a Solid Gasket?
A solid gasket is a durable sealing component made from materials such as rubber, metal, or composite substances designed to create a tight, leak-proof seal between two mating surfaces in mechanical assemblies. Its continuous, dense structure provides excellent resistance to high pressure, temperature variations, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for industrial applications such as automotive engines and piping systems. Solid gaskets maintain structural integrity under stress, ensuring efficient sealing performance and preventing fluid or gas leakage.
What is a Foam Gasket?
A foam gasket is a sealing material made from flexible, compressible foam that fills gaps to prevent air, dust, and moisture infiltration. Its porous structure provides excellent cushioning and vibration dampening properties, ideal for applications requiring lightweight, resilient seals. You can choose foam gaskets for environments needing easy installation combined with effective insulation and noise reduction.
Material Composition: Solid vs Foam Gaskets
Solid gaskets are typically composed of materials like metal, graphite, or rubber, providing high durability and resistance to pressure and temperature. Foam gaskets, made from materials such as polyurethane, neoprene, or silicone foam, offer superior flexibility and compressibility, making them ideal for sealing irregular surfaces and absorbing vibrations. Your choice depends on the specific application requirements for sealing effectiveness, chemical compatibility, and environmental conditions.
Key Performance Differences
Solid gaskets offer superior durability and strength, making them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, while foam gaskets provide excellent compressibility and sealing for irregular surfaces. Foam gaskets excel in vibration absorption and are often preferred in automotive and HVAC systems for their flexibility and resilience. Solid gaskets typically resist chemicals and wear better, whereas foam variants prioritize sealing effectiveness and noise reduction in less demanding environments.
Applications of Solid Gaskets
Solid gaskets are commonly used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications such as in automotive engines, chemical processing, and power plants due to their durability and ability to maintain a tight seal under extreme conditions. These gaskets are ideal for sealing flanges, valves, and pumps where leakage prevention is critical. Your equipment benefits from solid gaskets when reliability and long-term performance are essential in demanding industrial environments.
Applications of Foam Gaskets
Foam gaskets excel in applications requiring effective sealing against air, dust, moisture, and vibration control in automotive, HVAC, and electronic enclosures. Their compressibility and flexibility make them ideal for irregular surfaces and gaps, providing superior cushioning and insulation compared to solid gaskets. Industries such as aerospace and manufacturing rely on foam gaskets for lightweight, durable, and adaptable sealing solutions in dynamic environments.
Pros and Cons: Solid vs Foam Gaskets
Solid gaskets offer superior durability and resistance to high pressure and temperature, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications, but they can be less flexible and harder to install in irregular surfaces. Foam gaskets excel in compressibility and sealing irregular gaps, providing excellent cushioning and noise reduction, yet they typically have lower chemical and heat resistance, limiting their use in demanding environments. Selecting between solid and foam gaskets requires balancing the need for mechanical strength versus flexibility, depending on the specific sealing and environmental requirements.
Choosing the Right Gasket for Your Needs
Selecting the right gasket depends on the specific application requirements, where solid gaskets offer superior strength and chemical resistance for high-pressure environments, while foam gaskets provide enhanced flexibility and cushioning for sealing irregular surfaces. Solid gaskets, typically made from materials such as rubber, silicone, or metal, ensure long-lasting durability and effective sealing against fluids and gases. Foam gaskets, made from materials like neoprene or polyurethane, excel in applications requiring compression sealing and vibration absorption, making them ideal for automotive and HVAC systems.
Summary: Which Gasket is Best?
Solid gaskets offer superior durability and chemical resistance, making them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Foam gaskets provide excellent cushioning and sealing for irregular surfaces but may degrade faster in harsh environments. The best gasket depends on the specific operational demands, with solid gaskets favored for heavy-duty industrial use and foam gaskets suited for light-duty or flexible sealing needs.
Solid vs Foam Gasket Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com