SBR offers excellent abrasion resistance and durability, making it ideal for tire manufacturing and industrial applications, while SBS provides superior elasticity and flexibility, commonly used in roofing and paving materials. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize toughness and cost-effectiveness (SBR) or enhanced performance in extreme temperatures and flexibility (SBS).
Table of Comparison
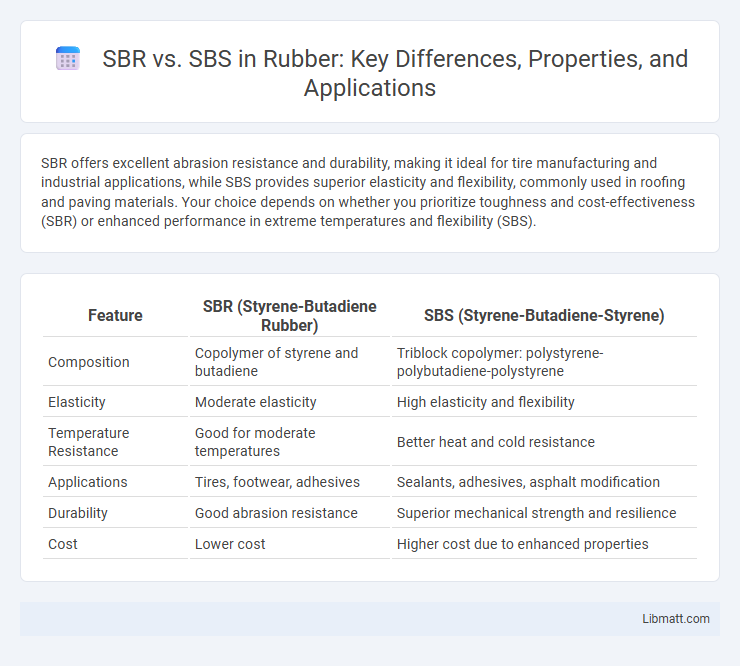
| Feature | SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) | SBS (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copolymer of styrene and butadiene | Triblock copolymer: polystyrene-polybutadiene-polystyrene |
| Elasticity | Moderate elasticity | High elasticity and flexibility |
| Temperature Resistance | Good for moderate temperatures | Better heat and cold resistance |
| Applications | Tires, footwear, adhesives | Sealants, adhesives, asphalt modification |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance | Superior mechanical strength and resilience |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to SBR and SBS
SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) and SBS (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) are widely used synthetic polymers in the rubber and plastics industries, valued for their durability and elasticity. SBR is a copolymer consisting of styrene and butadiene, primarily used in tires, footwear, and conveyor belts due to its abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness. SBS is a triblock copolymer with styrene end blocks and a butadiene midblock, offering enhanced flexibility and toughness for applications like asphalt modification, adhesives, and sealants, making it a versatile choice for your material needs.
What is SBR?
SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) is a synthetic rubber commonly used in tire manufacturing and industrial applications due to its abrasion resistance and aging stability. It consists of styrene and butadiene monomers, providing a balance of durability and flexibility for various products. Your choice between SBR and SBS depends on specific performance needs, with SBR excelling in general purpose rubber applications.
What is SBS?
Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene (SBS) is a type of thermoplastic elastomer widely used in asphalt modification to enhance pavement flexibility and durability. SBS consists of polystyrene end blocks and a polybutadiene mid-block, providing excellent elasticity, temperature resistance, and improved adhesion in road construction. Its ability to increase asphalt resistance to deformation and cracking makes SBS a preferred choice for high-performance pavements.
Chemical Structure: SBR vs SBS
SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) is a copolymer consisting of styrene and butadiene units randomly linked, resulting in an amorphous and less crystalline structure that enhances abrasion resistance and aging stability. SBS (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) is a block copolymer with polystyrene end blocks and a polybutadiene mid-block, providing a thermoplastic elastomer structure that combines rubber elasticity with thermoplastic processability. The distinct chemical architecture of SBS offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to the more uniform, random distribution of monomers in SBR.
Physical Properties Comparison
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) and Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene (SBS) both exhibit distinct physical properties critical for various industrial applications. SBR typically offers excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability, with a density around 0.94 g/cm3 and tensile strength ranging from 15 to 25 MPa. SBS, a thermoplastic elastomer, combines rubber-like elasticity with greater flexibility and impact resistance, showing elongation at break up to 600% and a higher tensile strength, often exceeding 30 MPa, which stems from its block copolymer architecture.
Applications and Uses
SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) is widely used in tire manufacturing, conveyor belts, and footwear due to its excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability. SBS (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) is preferred in the production of asphalt modifiers, adhesives, and sealants because of its thermoplastic elastomer properties, offering enhanced flexibility and strength. Both materials play critical roles in industries requiring durable yet flexible polymers, with SBR excelling in mechanical applications and SBS dominating in construction and automotive sealing technologies.
Advantages of SBR
SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) offers superior abrasion resistance and excellent aging stability, making it ideal for tire treads and conveyor belts. Its cost-effectiveness and better processing properties compared to SBS (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) enable efficient manufacturing in high-volume applications. You benefit from SBR's enhanced durability and versatility across a wide range of industrial uses.
Advantages of SBS
SBS (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) offers superior elasticity and temperature resistance compared to SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber), making it ideal for applications requiring durable flexibility. SBS enhances the performance of asphalt by improving crack resistance and waterproofing, extending the lifespan of road surfaces and roofing materials. Your projects benefit from SBS's ability to maintain integrity under extreme weather conditions, ensuring long-term reliability and cost efficiency.
Key Differences Between SBR and SBS
SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent abrasion resistance and aging stability, commonly used in tires and footwear. SBS (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) is a block copolymer combining rubber elasticity with plastic strength, widely utilized in adhesives, sealants, and flexible pavements. The key differences lie in their molecular structure, with SBR being a random copolymer offering general-purpose rubber properties, while SBS exhibits thermoplastic elastomer behavior, enabling enhanced flexibility and toughness.
Choosing the Right Material: SBR or SBS
SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) offers excellent abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for applications requiring durability in tires, footwear, and conveyor belts. SBS (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) provides superior elasticity and weather resistance, often preferred for waterproofing membranes and flexible sealants. Evaluate Your project's needs for flexibility, temperature resistance, and longevity to choose between the more rigid SBR or the more elastic SBS.
SBR vs SBS Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com