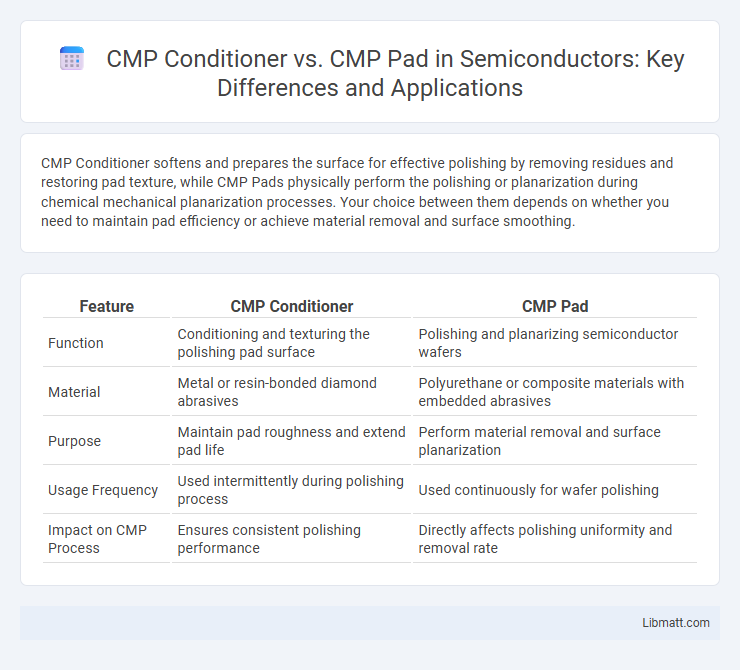
CMP Conditioner softens and prepares the surface for effective polishing by removing residues and restoring pad texture, while CMP Pads physically perform the polishing or planarization during chemical mechanical planarization processes. Your choice between them depends on whether you need to maintain pad efficiency or achieve material removal and surface smoothing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | CMP Conditioner | CMP Pad |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Conditioning and texturing the polishing pad surface | Polishing and planarizing semiconductor wafers |
| Material | Metal or resin-bonded diamond abrasives | Polyurethane or composite materials with embedded abrasives |
| Purpose | Maintain pad roughness and extend pad life | Perform material removal and surface planarization |
| Usage Frequency | Used intermittently during polishing process | Used continuously for wafer polishing |
| Impact on CMP Process | Ensures consistent polishing performance | Directly affects polishing uniformity and removal rate |
Introduction to CMP Process and Key Components
The CMP process, or Chemical Mechanical Planarization, is essential for wafer surface planarization in semiconductor manufacturing, combining chemical reactions and mechanical polishing to achieve ultra-flat surfaces. Key components in the CMP process include the CMP conditioner, used to maintain pad surface texture and ensure consistent material removal rates, and the CMP pad, a specialized disc that interfaces directly with the wafer. Your choice between a CMP conditioner and CMP pad impacts the effectiveness and uniformity of the planarization, influencing overall device performance.
Understanding CMP Conditioners: Function and Types
CMP conditioners play a crucial role in chemical mechanical planarization by maintaining the abrasiveness and effectiveness of CMP pads during wafer polishing. These conditioners typically come in various types, including fixed abrasive, non-abrasive, and diamond grit-based, each designed to optimize pad surface texture and prolong pad life. Understanding the specific function and type of CMP conditioner used can significantly impact wafer flatness and overall semiconductor device performance.
Overview of CMP Pads: Materials and Designs
CMP pads are made from materials like polyurethane, felt, and non-woven fibers, with designs tailored to specific polishing needs by varying hardness and porosity. These pads feature microstructures, including pores and grooves, that control slurry distribution and enhance removal rates during chemical mechanical planarization. Different pad types, such as abrasive, non-abrasive, and hybrid, are engineered to optimize planarization efficiency and surface finish quality in semiconductor manufacturing.
Key Differences Between CMP Conditioner and CMP Pad
CMP conditioner features a softer texture designed to gently refresh and restore polishing pads used in chemical mechanical planarization, while CMP pads are the primary abrasive surfaces responsible for material removal on wafers. Key differences include the conditioner's role in enhancing pad surface uniformity and prolonging pad life, whereas CMP pads focus on effective polishing performance through their abrasive composition. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize CMP process control and maintain your equipment's efficiency.
Roles of Conditioners and Pads in Wafer Planarization
CMP conditioners refine the surface of the polishing pad, enhancing its texture and restoring pad roughness to maintain consistent wafer planarization. CMP pads provide the primary contact surface that facilitates the mechanical and chemical removal of wafer material, ensuring uniform planarization across the wafer. Your choice of conditioner and pad combination directly impacts the efficiency and uniformity of the chemical mechanical planarization process.
Performance Impact: Conditioner vs Pad Efficiency
CMP conditioners enhance pad surface texture, improving CMP pad efficiency by maintaining consistent abrasive properties and extending pad lifespan. CMP pads directly affect material removal rates and uniformity, with pad wear influencing overall performance more than conditioners alone. Your choice between CMP conditioner and CMP pad significantly impacts slurry distribution, surface planarity, and process stability in chemical mechanical planarization.
Lifespan and Maintenance: Conditioner vs Pad
CMP conditioners generally have a longer lifespan than CMP pads due to their durable materials designed to maintain surface smoothness and reduce wear. While CMP pads require more frequent replacement because they experience higher abrasion and contamination buildup, conditioners demand less maintenance but should be monitored to ensure consistent performance. Selecting the right product affects your overall process efficiency by minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Common Issues and Solutions for Conditioners and Pads
Common issues with CMP conditioners and pads include uneven material removal, pad glazing, and contamination, which can reduce polishing efficiency and surface quality. Solutions involve regular pad conditioning to restore texture, using appropriate conditioning pressure and slurry flow rates, and timely replacement of worn pads to maintain consistent planarization. You can improve CMP process performance by closely monitoring pad wear and implementing a tailored maintenance schedule based on specific tool and slurry conditions.
Selecting the Right Conditioner and Pad for CMP Applications
Selecting the right conditioner and pad for CMP applications is critical to achieving optimal planarization and surface quality. CMP conditioners, designed with durable abrasives like diamond particles, maintain the pad's surface texture and uniformity, while various CMP pads--such as polyurethane or fixed-abrasive types--are chosen based on wafer material and target removal rates. Proper matching of conditioner type with pad hardness and polishing slurry chemistry significantly enhances process stability, removal efficiency, and wafer defect control.
Future Trends in CMP Conditioner and Pad Technologies
Future trends in CMP conditioner and pad technologies emphasize enhanced wafer surface uniformity and reduced defectivity through advanced materials and nano-textured surfaces. Integration of real-time sensor feedback and AI-driven process controls is driving improvements in pad conditioning precision and longevity. Innovations in eco-friendly materials and recyclable components are gaining traction to address sustainability challenges in semiconductor manufacturing.
CMP Conditioner vs CMP Pad Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com