Fabless companies focus on designing and marketing semiconductor chips while outsourcing manufacturing to foundries, enabling cost-effective innovation without heavy capital investment. IDM (Integrated Device Manufacturer) handles both design and manufacturing in-house, offering greater control over production and quality but requiring significant infrastructure and resources.
Table of Comparison
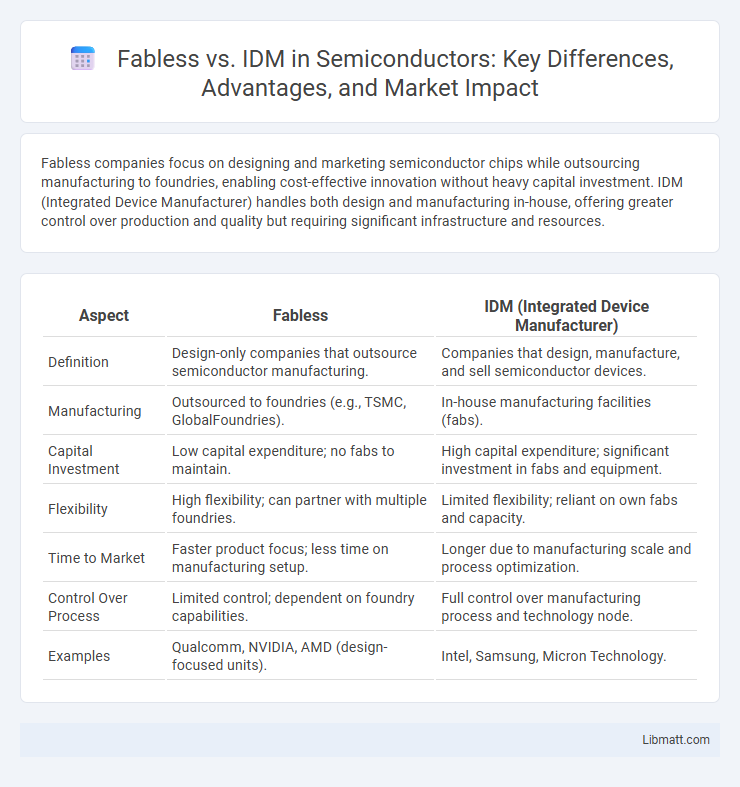
| Aspect | Fabless | IDM (Integrated Device Manufacturer) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Design-only companies that outsource semiconductor manufacturing. | Companies that design, manufacture, and sell semiconductor devices. |
| Manufacturing | Outsourced to foundries (e.g., TSMC, GlobalFoundries). | In-house manufacturing facilities (fabs). |
| Capital Investment | Low capital expenditure; no fabs to maintain. | High capital expenditure; significant investment in fabs and equipment. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; can partner with multiple foundries. | Limited flexibility; reliant on own fabs and capacity. |
| Time to Market | Faster product focus; less time on manufacturing setup. | Longer due to manufacturing scale and process optimization. |
| Control Over Process | Limited control; dependent on foundry capabilities. | Full control over manufacturing process and technology node. |
| Examples | Qualcomm, NVIDIA, AMD (design-focused units). | Intel, Samsung, Micron Technology. |
Introduction to Fabless and IDM Models
Fabless semiconductor companies design and sell integrated circuits while outsourcing manufacturing to specialized foundries, allowing them to focus on innovation and reduce capital expenditure. Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) control the entire semiconductor production process, from design to fabrication, ensuring tighter quality control and supply chain integration. This fundamental difference in operational models impacts cost structures, time-to-market, and strategic flexibility within the semiconductor industry.
Key Differences Between Fabless and IDM
Fabless companies design semiconductors but outsource manufacturing to specialized foundries, enabling lower capital expenditure and faster innovation cycles. Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) handle both design and fabrication in-house, which allows for tighter process control and potentially higher yields. Your choice between fabless and IDM depends on factors like cost, control over production, and market agility.
Historical Evolution of Semiconductor Business Models
The semiconductor industry's historical evolution showcases a shift from Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs), which combined design, manufacturing, and testing of chips in-house, to fabless companies specializing solely in design while outsourcing fabrication to foundries. This transition accelerated in the 1980s and 1990s as capital-intensive manufacturing costs soared, prompting firms like Qualcomm and NVIDIA to adopt fabless models to enhance innovation agility and reduce operational expenses. The rise of foundry giants such as TSMC and GlobalFoundries further solidified the fabless-IDM ecosystem, reshaping competitive dynamics within the semiconductor business landscape.
Advantages of the Fabless Approach
The fabless approach offers cost efficiency by eliminating the need for expensive semiconductor fabrication facilities, allowing companies to focus on research, design, and innovation. It enables faster time-to-market as fabless firms can leverage specialized foundries with advanced manufacturing technologies. Your ability to scale production flexibly and reduce capital expenditure makes the fabless model highly advantageous in the competitive semiconductor industry.
Benefits of the IDM Model
The Integrated Device Manufacturer (IDM) model offers significant benefits by controlling the entire semiconductor production process, from design to fabrication, ensuring higher quality control and faster time-to-market for complex chips. IDMs leverage in-house manufacturing capabilities to optimize yield, reduce dependency on external foundries, and enhance proprietary technology development. This end-to-end integration supports improved supply chain stability and responsiveness to market demand fluctuations.
Challenges Faced by Fabless Companies
Fabless companies face significant challenges in managing supply chain dependencies due to reliance on external foundries for semiconductor fabrication, leading to potential production delays and capacity constraints. They often encounter difficulties in protecting intellectual property while collaborating with multiple manufacturing partners, which can increase the risk of design leaks. Moreover, fabless companies must continuously invest in advanced design tools and talent to stay competitive in rapidly evolving technology landscapes without the control over manufacturing processes possessed by IDM counterparts.
Limitations of the IDM Structure
The Integrated Device Manufacturer (IDM) structure faces limitations such as high capital expenditure due to owning and operating semiconductor fabs, which reduces agility in responding to market fluctuations. IDMs typically encounter slower innovation cycles because manufacturing resources are tied to in-house processes rather than leveraging specialized external foundries. This vertical integration can constrain scalability and limit access to advanced process technologies available through fabless-foundry partnerships.
Market Trends: Fabless and IDM Adoption
Fabless semiconductor companies dominate the market by outsourcing chip fabrication to specialized foundries, enabling rapid innovation and cost efficiency, with their market share surpassing 60% globally. Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) maintain strong adoption in industries requiring tight process control and vertical integration, such as automotive and aerospace, preserving around 30-35% of the market. Market trends indicate a growing preference for fabless models driven by advances in foundry technology and increased demand for customized, high-performance chips in consumer electronics and IoT applications.
Notable Companies: Fabless vs IDM Leaders
Notable fabless companies like Qualcomm, NVIDIA, and AMD focus on chip design and outsource manufacturing to specialized foundries such as TSMC and GlobalFoundries, enabling flexibility and innovation in semiconductor development. IDM leaders like Intel, Samsung, and Micron integrate design, manufacturing, and testing within their own facilities, providing tighter control over production and supply chain reliability. Understanding whether your business benefits more from fabless agility or IDM vertical integration is crucial for strategic semiconductor partnerships.
Future Outlook: Fabless and IDM in Semiconductor Industry
The future outlook for fabless semiconductor companies centers on innovation-driven growth through advanced chip design and reliance on specialized foundries for manufacturing, enabling rapid adaptation to market demands. Integrated Device Manufacturers (IDMs) focus on vertical integration, investing in cutting-edge fabrication facilities to achieve greater control over production quality and supply chain stability. Both models will coexist and evolve, with fabless firms leveraging agile design capabilities while IDMs enhance process technologies to meet the increasing complexity of semiconductor applications.
Fabless vs IDM Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com