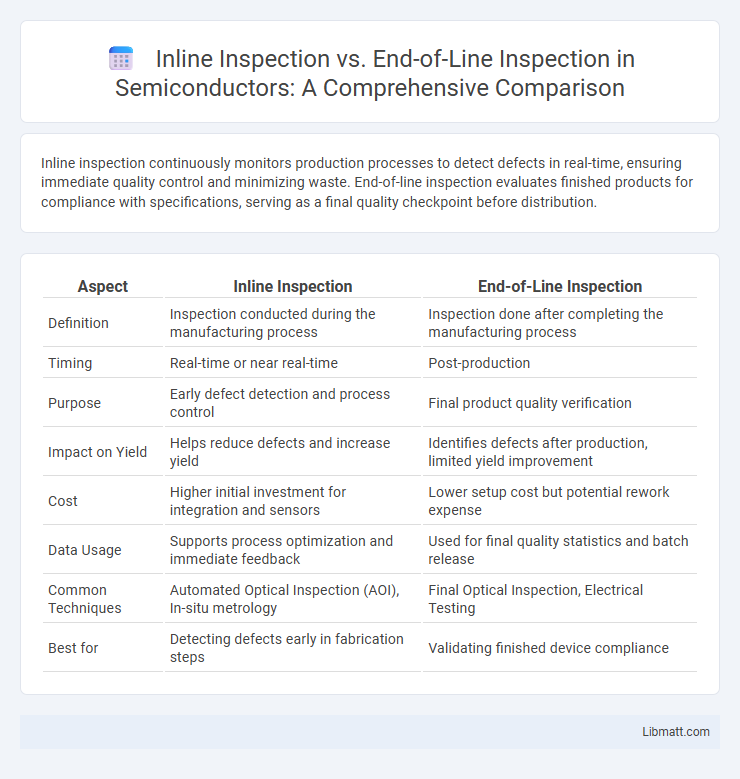
Inline inspection continuously monitors production processes to detect defects in real-time, ensuring immediate quality control and minimizing waste. End-of-line inspection evaluates finished products for compliance with specifications, serving as a final quality checkpoint before distribution.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Inline Inspection | End-of-Line Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inspection conducted during the manufacturing process | Inspection done after completing the manufacturing process |
| Timing | Real-time or near real-time | Post-production |
| Purpose | Early defect detection and process control | Final product quality verification |
| Impact on Yield | Helps reduce defects and increase yield | Identifies defects after production, limited yield improvement |
| Cost | Higher initial investment for integration and sensors | Lower setup cost but potential rework expense |
| Data Usage | Supports process optimization and immediate feedback | Used for final quality statistics and batch release |
| Common Techniques | Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), In-situ metrology | Final Optical Inspection, Electrical Testing |
| Best for | Detecting defects early in fabrication steps | Validating finished device compliance |
Introduction to Inline and End-of-Line Inspection
Inline inspection integrates quality checks directly into the production process, enabling real-time defect detection and immediate corrective actions. End-of-line inspection occurs after manufacturing completion, focusing on final product verification and quality assurance before distribution. Your choice between these methods depends on production speed, defect tolerance, and overall quality control strategy.
Defining Inline Inspection: Key Features
Inline inspection involves continuous monitoring and testing integrated directly within the production process, enabling real-time data collection and immediate detection of defects. Key features include automated sensors, non-destructive testing methods, and seamless integration with manufacturing equipment to minimize downtime. This approach enhances quality control by ensuring immediate corrective actions and maintaining consistent product standards throughout production.
Understanding End-of-Line Inspection Processes
End-of-Line Inspection processes involve evaluating the final product after all manufacturing stages to ensure it meets quality standards and specifications before shipping. This inspection method focuses on detecting defects, verifying functionality, and confirming compliance with safety regulations at the end of the production line. Your quality assurance depends on accurately identifying issues at this critical checkpoint to prevent defective products from reaching customers.
Core Differences Between Inline and End-of-Line Inspection
Inline inspection occurs continuously during the manufacturing process, allowing real-time defect detection and immediate correction, while end-of-line inspection takes place after the production cycle, focusing on final product quality verification. Inline inspection integrates sensor technologies and automated systems for seamless quality control, whereas end-of-line inspection relies on manual checks or separate testing stations, often resulting in higher defect escape rates. The core difference lies in timing and integration, with inline inspection enabling proactive quality management and end-of-line inspection serving as a reactive quality assurance measure.
Advantages of Inline Inspection Systems
Inline inspection systems enable real-time quality control by continuously monitoring products during the manufacturing process, reducing defects and minimizing waste. These systems provide immediate feedback, allowing for swift adjustments that enhance production efficiency and maintain consistent product standards. Inline inspections also decrease downtime and labor costs compared to end-of-line inspection methods, boosting overall operational productivity.
Benefits of End-of-Line Inspection Methods
End-of-line inspection methods provide comprehensive quality control by thoroughly examining finished products, ensuring defects are identified before distribution. These inspections enhance customer satisfaction by guaranteeing that only compliant and defect-free items reach your market, reducing returns and warranty claims. The approach also streamlines final product verification, allowing for efficient batch acceptance and regulatory compliance documentation.
Limitations and Challenges of Inline Inspection
Inline inspection faces limitations such as difficulty in detecting complex defects due to limited sensing angles and real-time processing constraints. Challenges include high costs associated with integrating advanced sensors into production lines and potential disruptions to workflow caused by inspection equipment. Moreover, maintaining accuracy in varying environmental conditions and managing large data volumes for immediate analysis remain significant hurdles.
Drawbacks and Issues with End-of-Line Inspection
End-of-Line Inspection often faces drawbacks such as delayed defect detection, leading to higher rework costs and increased waste. This method limits real-time quality control, which can result in undetected issues reaching the final product stage. Your manufacturing efficiency improves by integrating Inline Inspection, as it enables continuous monitoring and immediate corrective actions.
Choosing the Right Inspection Method for Your Operation
Choosing the right inspection method depends on production speed, product complexity, and quality requirements. Inline inspection integrates seamlessly within the production process, enabling real-time defect detection and reducing downtime. End-of-line inspection offers comprehensive quality assurance by thoroughly evaluating finished products but may delay feedback and corrective actions.
Future Trends in Industrial Inspection Technologies
Future trends in industrial inspection technologies emphasize increased automation and real-time data analysis through inline inspection systems, enabling continuous monitoring of production processes for enhanced quality control. End-of-line inspection remains crucial for final product verification but is increasingly integrated with advanced machine learning algorithms and AI-driven defect detection to improve accuracy and speed. Your manufacturing operations benefit from combining both methods to achieve comprehensive inspection coverage and optimize overall efficiency.
Inline Inspection vs End-of-Line Inspection Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com