OSD (On-Screen Display) enables dynamic interface control and customization directly on your device, while ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) offers highly efficient, purpose-built hardware designed for specific tasks, ensuring superior performance and power optimization. Choosing between OSD and ASIC depends on whether you prioritize flexibility and user interaction or dedicated processing power and efficiency.
Table of Comparison
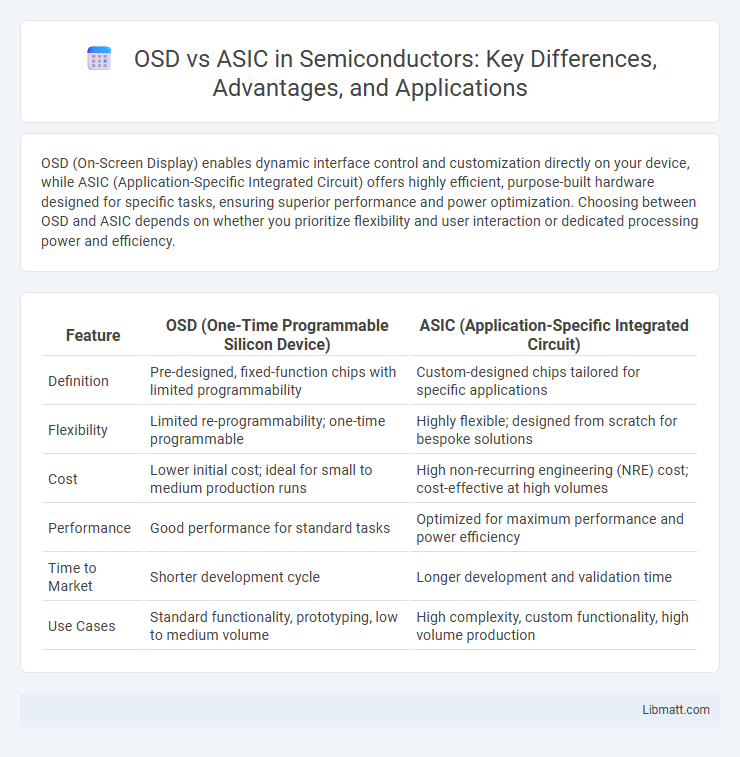
| Feature | OSD (One-Time Programmable Silicon Device) | ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-designed, fixed-function chips with limited programmability | Custom-designed chips tailored for specific applications |
| Flexibility | Limited re-programmability; one-time programmable | Highly flexible; designed from scratch for bespoke solutions |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; ideal for small to medium production runs | High non-recurring engineering (NRE) cost; cost-effective at high volumes |
| Performance | Good performance for standard tasks | Optimized for maximum performance and power efficiency |
| Time to Market | Shorter development cycle | Longer development and validation time |
| Use Cases | Standard functionality, prototyping, low to medium volume | High complexity, custom functionality, high volume production |
Introduction to OSD and ASIC
OSD (On-Screen Display) is a technology commonly used in monitors and televisions to overlay information, settings, or menus directly on the screen, enhancing user interaction without external controls. ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) refers to a customized chip designed for a particular application, offering optimized performance and efficiency in various electronic devices. Understanding the roles of OSD and ASIC is crucial for selecting technology solutions tailored to your specific display and processing needs.
Defining OSD (Open-Source Design)
Open-Source Design (OSD) refers to a collaborative approach in hardware development where design files, specifications, and documentation are freely shared and accessible for modification and redistribution. Unlike Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), which are proprietary and custom-built for specific functions, OSD promotes transparency, innovation, and community-driven improvements. OSD enables faster prototyping, cost-effective iterations, and broad adaptability across various applications in electronics engineering.
What is an ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit)?
An ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) is a customized semiconductor chip designed for a particular use or application, enhancing performance and efficiency compared to general-purpose hardware. Unlike OSD (On-Screen Display) that serves as a graphical interface, ASICs are engineered to execute specific functions at high speed and low power consumption. Your choice between ASIC and OSD depends on whether you need specialized hardware acceleration or flexible display capabilities.
Key Differences Between OSD and ASIC
OSD (On-Screen Display) and ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) differ primarily in function and design; OSD is a user interface feature that overlays information on video displays, while ASIC is a custom-designed chip tailored for specific applications. OSD operates at the software or firmware level, enabling real-time adjustments of display settings without modifying hardware, whereas ASIC provides dedicated hardware acceleration for optimized performance and efficiency in targeted tasks. The key distinction lies in OSD's versatility for user interaction versus ASIC's specialized processing capabilities, impacting their usage across industries like consumer electronics and telecommunications.
Performance Comparison: OSD vs ASIC
ASICs deliver superior performance compared to OSDs due to their custom design tailored for specific applications, resulting in higher processing speeds and lower latency. OSDs, or Off-the-Shelf Devices, offer flexibility and easier integration but typically suffer from slower execution and higher power consumption. Performance benchmarks show ASICs achieving up to 10x faster throughput in critical tasks than equivalent OSD solutions.
Cost Considerations: OSD versus ASIC
OSD (Optical Signal Detection) systems generally offer lower upfront costs compared to ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) development, which involves significant non-recurring engineering expenses. While ASICs provide cost efficiency in large-volume production due to lower per-unit costs, OSD solutions are more economical for small to medium production runs and offer faster time-to-market. The total cost of ownership for OSD versus ASIC depends on volume, development complexity, and lifecycle requirements.
Flexibility and Customization
OSD (Off-the-Shelf Devices) offer greater flexibility and customization options compared to ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits), allowing rapid adaptation to changing requirements and easier integration with various systems. ASICs provide optimized performance for specific tasks but lack the adaptability of OSDs, resulting in limited customization once fabricated. Enterprises prioritizing scalability and dynamic updates often prefer OSD solutions to leverage modular design and frequent firmware upgrades.
Security Implications
ASICs offer enhanced security by incorporating dedicated cryptographic modules and tamper-resistant features that reduce vulnerability to hacking compared to OSDs. OSDs often rely on general-purpose microcontrollers, which can be more susceptible to firmware attacks and reverse engineering. Your choice between OSD and ASIC should consider the specific security requirements, as ASICs provide more robust protection against physical and logical attacks in sensitive applications.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
OSD (On-Screen Display) technology is widely used in consumer electronics such as monitors, TVs, and cameras to provide user-friendly interfaces for settings adjustment. ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) is designed for specialized applications in industries like telecommunications, automotive, and medical devices, where high performance and efficiency are critical. Your choice between OSD and ASIC depends on whether you need customizable display controls or dedicated hardware optimized for specific industrial tasks.
Future Trends in OSD and ASIC Development
Future trends in On-Screen Display (OSD) technology emphasize enhanced integration with AI-driven interfaces and higher resolution support for ultra-high-definition displays, improving user interaction and visual clarity. ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) development is moving toward greater customization and energy efficiency, leveraging advanced semiconductor processes like 3nm technology to enable faster, low-power performance tailored for specific applications such as 5G networking and AI workloads. The convergence of OSD and ASIC advancements is driving smarter, more efficient consumer electronics and embedded systems with seamless multimedia processing capabilities.
OSD vs ASIC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com