SOG (Structured Output Generation) and SOD (Segmentation Object Detection) represent distinct approaches in computer vision and AI tasks, with SOG focusing on generating organized, meaningful outputs from input data, while SOD emphasizes detecting and segmenting objects within images or scenes. Your choice between SOG and SOD depends on whether you need to produce structured information or accurately locate and identify objects in visual content.
Table of Comparison
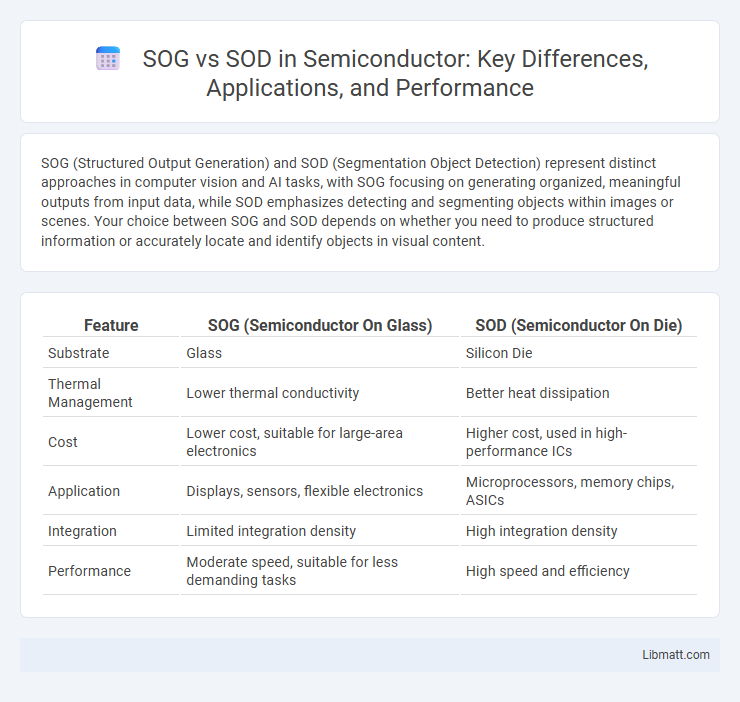
| Feature | SOG (Semiconductor On Glass) | SOD (Semiconductor On Die) |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate | Glass | Silicon Die |
| Thermal Management | Lower thermal conductivity | Better heat dissipation |
| Cost | Lower cost, suitable for large-area electronics | Higher cost, used in high-performance ICs |
| Application | Displays, sensors, flexible electronics | Microprocessors, memory chips, ASICs |
| Integration | Limited integration density | High integration density |
| Performance | Moderate speed, suitable for less demanding tasks | High speed and efficiency |
Understanding SOG and SOD: Definitions
SOG (Speed Over Ground) measures a vessel's actual speed relative to the earth's surface, calculated using GPS data to account for currents and wind effects. SOD (Speed on Device) refers to the speed indicated by onboard instruments such as logs or Doppler sensors, which measure water flow past the hull. Understanding the distinction between SOG and SOD is essential for accurate navigation and performance assessment in maritime operations.
Key Differences Between SOG and SOD
SOG (Start of Green) and SOD (Start of Day) are crucial metrics in crop phenology monitoring, where SOG marks the onset of the green-up phase signaling active vegetation growth, while SOD indicates the calendar date when measurements begin. SOG is derived from vegetation indices like NDVI, capturing biological changes, whereas SOD is a fixed temporal reference point independent of vegetation status. Understanding these distinctions helps you accurately interpret crop development stages for optimized agricultural management.
Advantages of Using SOG
SOG (Start of Gate) testing offers faster time-to-market advantages by identifying product issues early in the manufacturing process, reducing costly rework and delays often encountered with SOD (Start of Delivery) testing. You benefit from improved product quality and reliability as defects are detected before shipping, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing warranty claims. Implementing SOG testing optimizes production efficiency and lowers overall operational costs by minimizing disruptions in supply chain and delivery schedules.
Benefits of Implementing SOD
Segregation of Duties (SOD) enhances internal controls by distributing responsibilities to prevent fraud and errors, ensuring no single individual has control over all critical aspects of a financial transaction. Implementing SOD reduces risks associated with unauthorized activities and improves auditability, providing greater transparency and accountability within your organization. This framework supports compliance with regulatory requirements and strengthens overall operational security.
Common Applications of SOG and SOD
SOG (Start of Generation) is commonly applied in audio and video production to mark the exact beginning of content segments, facilitating synchronization and editing precision. SOD (Start of Day) is widely used in broadcasting and scheduling systems to denote the initiation of daily programming or operational cycles, helping to organize workflow and manage time slots effectively. Both SOG and SOD are essential in media and broadcasting environments for streamlining content management and ensuring seamless transmission.
Challenges Associated with SOG
Challenges associated with Start of Gantry (SOG) include complex machinery alignment and increased risk of operational delays due to equipment malfunctions or improper calibration. Precise synchronization with other processes is critical, making error detection and maintenance more demanding compared to Start of Delivery (SOD). Your projects may face higher costs and reduced efficiency when SOG issues disrupt workflow continuity in automated systems.
Limitations of SOD in Practice
SOD (Separation of Duties) faces practical limitations such as increased complexity in small organizations where roles overlap, making strict enforcement challenging. It can also lead to operational inefficiencies due to the need for multiple approvals or checks, slowing down workflows. Furthermore, without adequate technological support, maintaining and monitoring SOD controls often results in gaps that could expose organizations to internal fraud or errors.
SOG vs SOD: Performance Comparison
SOG (Sense of Gaming) and SOD (Sense of Direction) differ significantly in performance metrics, with SOG excelling in immersive user engagement and responsiveness in gaming environments, while SOD demonstrates superior accuracy in spatial navigation and environmental awareness tasks. Your choice between SOG and SOD should depend on whether the priority lies in interactive entertainment or precise directional guidance. Benchmark tests reveal that SOG consistently achieves lower latency and higher frame rates, whereas SOD offers enhanced location precision and real-time pathfinding capabilities.
Industry Trends: SOG vs SOD
In the finance and credit industry, SOG (Statement of Goods) and SOD (Start of Day) are evolving with a growing emphasis on automation and real-time data integration. Industry trends highlight a shift towards digital SOG systems enabling seamless product tracking and inventory management, while advanced SOD solutions focus on optimizing transaction workflows and daily operational efficiency. Market demand increasingly favors cloud-based platforms for both SOG and SOD, driving enhanced accuracy and faster decision-making in supply chain and financial operations.
Choosing Between SOG and SOD: Factors to Consider
Choosing between SOG (Substrate-Oriented Growth) and SOD (Substrate-Oriented Development) depends on your project's specific needs, such as the desired material properties, scalability, and application environment. Consider factors like the compatibility of the substrate with the active layer, the required structural integrity, and process complexity to optimize performance. Evaluating these parameters ensures that your decision aligns with technical requirements and cost efficiency.
SOG vs SOD Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com