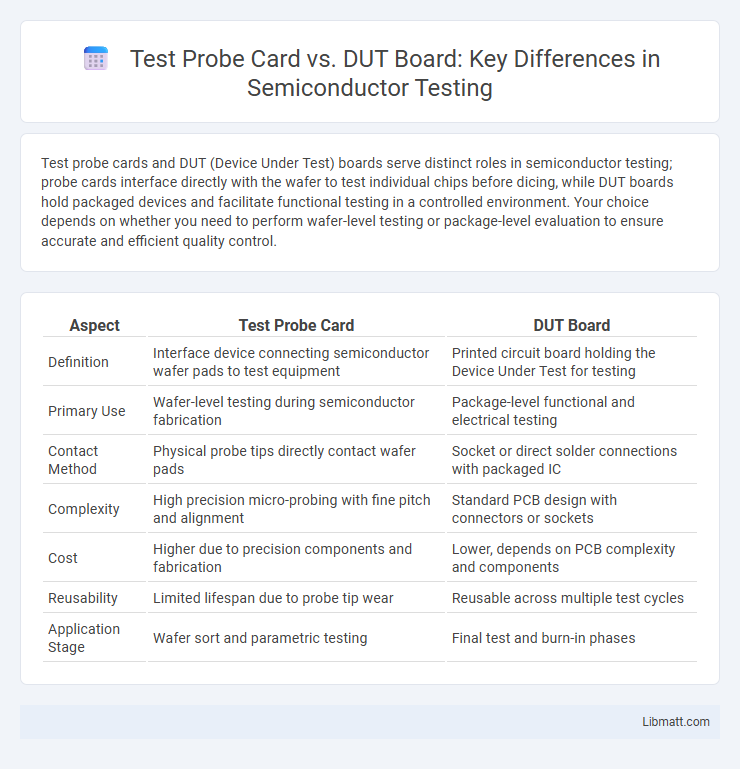
Test probe cards and DUT (Device Under Test) boards serve distinct roles in semiconductor testing; probe cards interface directly with the wafer to test individual chips before dicing, while DUT boards hold packaged devices and facilitate functional testing in a controlled environment. Your choice depends on whether you need to perform wafer-level testing or package-level evaluation to ensure accurate and efficient quality control.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Test Probe Card | DUT Board |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interface device connecting semiconductor wafer pads to test equipment | Printed circuit board holding the Device Under Test for testing |
| Primary Use | Wafer-level testing during semiconductor fabrication | Package-level functional and electrical testing |
| Contact Method | Physical probe tips directly contact wafer pads | Socket or direct solder connections with packaged IC |
| Complexity | High precision micro-probing with fine pitch and alignment | Standard PCB design with connectors or sockets |
| Cost | Higher due to precision components and fabrication | Lower, depends on PCB complexity and components |
| Reusability | Limited lifespan due to probe tip wear | Reusable across multiple test cycles |
| Application Stage | Wafer sort and parametric testing | Final test and burn-in phases |
Introduction to Test Probe Cards and DUT Boards
Test probe cards serve as critical interfaces connecting semiconductor wafers to automated test equipment, enabling precise electrical testing during the manufacturing process. DUT boards, or Device Under Test boards, are specially designed circuit boards that hold and support semiconductor devices during testing, ensuring signal integrity and accurate measurement. Both components play essential roles in semiconductor testing workflows, with probe cards facilitating wafer-level tests and DUT boards supporting packaged device evaluations.
Key Functions of Test Probe Cards
Test probe cards serve as essential interfaces that connect semiconductor wafers to test equipment, enabling precise electrical performance testing of integrated circuits before dicing. They provide critical functions such as delivering accurate probe contact to wafer pads, ensuring signal integrity, and supporting high-frequency signals during wafer sort testing. By facilitating rapid, reliable probing, test probe cards optimize yield analysis and quality control in semiconductor manufacturing.
Essential Roles of DUT Boards
DUT boards play a crucial role in semiconductor testing by providing a reliable interface between the device under test (DUT) and the test system, ensuring accurate signal transmission and minimizing noise interference. Unlike test probe cards, which physically contact the chip for each test, DUT boards facilitate stable connections and support complex testing scenarios by integrating necessary components such as sockets, connectors, and signal conditioning circuits. Their reliability and adaptability significantly enhance test efficiency, yield analysis, and functional verification in chip manufacturing processes.
Structural Differences Between Probe Cards and DUT Boards
Probe cards feature an array of precisely aligned micro-needles or contact pins designed for making temporary electrical connections to semiconductor wafers during testing, emphasizing fine pitch and high-density interconnects. DUT (Device Under Test) boards, in contrast, are rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs) structured to securely hold the packaged device and provide stable, durable connections to test equipment, prioritizing mechanical support and signal integrity. Structural distinctions revolve around the probe card's flexible, delicate needle arrangement for wafer-level probing versus the DUT board's robust PCB layout optimized for packaged device evaluation.
Applications in Semiconductor Testing
Test probe cards enable high-precision contact with semiconductor wafers during wafer-level testing, ensuring functionality and parametric validation before die separation. DUT boards serve as the interface for packaged devices, facilitating system-level performance evaluation and functional testing under real-world operating conditions. Your choice between a test probe card and a DUT board depends on the specific stage of semiconductor testing, from wafer probe to final device verification.
Performance Metrics: Accuracy and Reliability
Test probe cards are critical for ensuring high accuracy in semiconductor wafer testing by providing precise electrical contact with minimal signal distortion, whereas DUT (Device Under Test) boards focus on overall system reliability by facilitating stable connections during device evaluation. Probe cards achieve superior accuracy metrics through advanced contact technology and fine pitch alignment, while DUT boards emphasize reliability metrics such as durability under repeated test cycles and signal integrity in diverse testing conditions. Both components are essential for optimizing yield and quality assurance in semiconductor manufacturing, but probe cards predominantly impact measurement precision, and DUT boards primarily affect test consistency and robustness.
Cost Considerations and ROI Comparison
Test probe cards typically involve higher upfront costs due to intricate design and precision manufacturing, impacting initial investment significantly. In contrast, DUT boards are generally more affordable but may require frequent replacements or modifications, influencing long-term expenses. Your choice should balance the higher durability and potential ROI of probe cards against the lower immediate cost but possibly increased maintenance of DUT boards.
Compatibility with Automated Test Equipment (ATE)
Test Probe Cards are specifically designed to interface directly with semiconductor wafers and are highly compatible with Automated Test Equipment (ATE), ensuring precise electrical contact and efficient signal transmission. DUT Boards, or Device Under Test Boards, serve as adaptable platforms to mount packaged devices and connect them to ATE, providing flexibility for various test scenarios but potentially introducing additional signal integrity challenges. Understanding the distinct compatibility features of both Test Probe Cards and DUT Boards allows you to optimize test setups for accuracy and efficiency in semiconductor testing environments.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Management
Test probe cards require frequent maintenance to ensure optimal contact quality and prevent signal degradation, with regular cleaning and pin replacement essential for extending their lifespan. DUT boards generally experience lower maintenance demands but must be managed carefully to avoid damage from repeated test cycles, which can shorten their effective lifecycle. Implementing predictive maintenance techniques and detailed lifecycle tracking significantly improves the reliability and longevity of both test probe cards and DUT boards in semiconductor testing environments.
Choosing Between Probe Cards and DUT Boards
Choosing between test probe cards and DUT boards depends on your testing needs and device complexity. Probe cards offer precise contact for wafer-level testing, enabling high-throughput analysis of semiconductor wafers before packaging, while DUT boards provide a more flexible solution for testing packaged devices with customizable interfaces. Your selection should consider production volume, test accuracy requirements, and the physical form of the device under test.
Test Probe Card vs DUT Board Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com