Open-top container vessels provide flexibility for transporting oversized or heavy cargo that cannot fit into standard containers, while fully enclosed vessels offer better protection from weather and theft, ensuring your goods remain secure and dry during transit. Choosing between them depends on the nature of your cargo and specific shipping requirements.
Table of Comparison
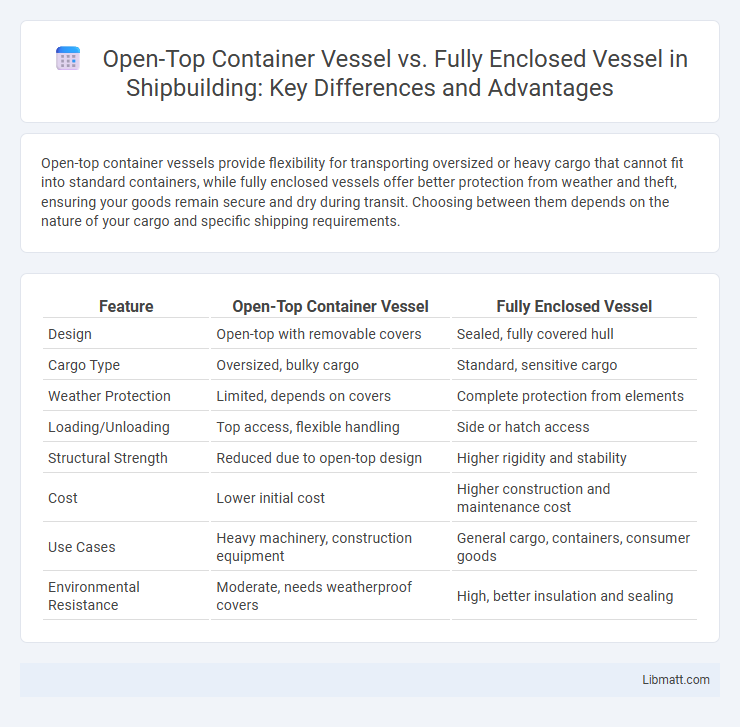
| Feature | Open-Top Container Vessel | Fully Enclosed Vessel |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Open-top with removable covers | Sealed, fully covered hull |
| Cargo Type | Oversized, bulky cargo | Standard, sensitive cargo |
| Weather Protection | Limited, depends on covers | Complete protection from elements |
| Loading/Unloading | Top access, flexible handling | Side or hatch access |
| Structural Strength | Reduced due to open-top design | Higher rigidity and stability |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher construction and maintenance cost |
| Use Cases | Heavy machinery, construction equipment | General cargo, containers, consumer goods |
| Environmental Resistance | Moderate, needs weatherproof covers | High, better insulation and sealing |
Overview: Open-Top Container Vessels vs Fully Enclosed Vessels
Open-top container vessels feature an open cargo hold covered by removable tarpaulins, allowing easy transport of oversized or bulky items such as machinery and timber that cannot fit in standard containers. Fully enclosed vessels provide complete protection from weather and external elements, enhancing cargo security and suitability for sensitive goods like electronics and pharmaceuticals. Choosing the right vessel depends on your cargo type, with open-top vessels offering flexibility for oversized loads and fully enclosed vessels ensuring maximum protection.
Structural Design Differences
Open-top container vessels feature a structural design with an open cargo hold covered by a tarpaulin, allowing the transport of oversized or tall cargo that cannot fit under fixed decks, while fully enclosed vessels have a sealed hold with weatherproof steel decks and hatch covers ensuring protection from environmental elements. The open-top design requires reinforced sidewalls and hatch coamings to maintain hull integrity despite the lack of a rigid deck, contrasting with fully enclosed vessels where the deck and hatch covers contribute significantly to the overall structural strength and torsional rigidity. Open-top containers demand specialized structural reinforcements to prevent deformation during heavy sea conditions, whereas fully enclosed vessels benefit from a continuous hull structure that provides enhanced structural uniformity and stability.
Cargo Flexibility and Capacity
Open-top container vessels offer increased cargo flexibility by accommodating oversized or awkwardly shaped goods that cannot fit into standard containers, enhancing your options for transporting heavy machinery or bulky items. Fully enclosed vessels provide superior protection for sensitive cargo from weather and environmental damage, ensuring secure transport but limiting the ability to carry oversized loads. Choosing between these vessel types depends on balancing the need for cargo capacity with the specific requirements of your freight.
Weather Protection and Risk Management
Open-top container vessels provide limited weather protection, exposing cargo to elements such as rain and saltwater, increasing the risk of damage, while fully enclosed vessels offer comprehensive shielding from harsh weather conditions, significantly reducing potential cargo loss. The risk management strategies for open-top vessels often involve specialized tarpaulins and rigorous cargo securing methods, whereas fully enclosed vessels minimize these concerns with solid structures that prevent ingress of moisture and contaminants. Choosing fully enclosed vessels enhances cargo safety during adverse weather, lowering insurance costs and improving overall risk mitigation.
Loading and Unloading Operations
Open-top container vessels streamline the loading and unloading of oversized cargo by allowing cranes to place goods directly into the open hold without height restrictions, increasing operational efficiency for bulky items. Fully enclosed vessels require cargo to be carefully maneuvered through limited hatch openings, often necessitating additional handling equipment and time, which can slow down operations. This makes open-top vessels preferable for irregular or tall cargo, while fully enclosed ships offer better protection but demand more complex loading strategies.
Cost Implications: Construction and Operation
Open-top container vessels generally incur lower construction costs due to their simpler design, whereas fully enclosed vessels require more extensive materials and structural reinforcements, increasing initial expenses. Operational costs for open-top vessels can be higher because of increased maintenance from exposure to weather and cargo protection needs, while fully enclosed vessels offer better cargo security and reduced weather-related damage, potentially lowering insurance and repair costs. The choice between these vessel types depends on balancing upfront construction investments against long-term operational efficiencies and cargo safety requirements.
Common Use Cases and Industry Applications
Open-top container vessels are primarily used for transporting oversized cargo such as machinery, construction materials, and bulk goods that cannot fit into standard containers, making them ideal for industries like construction, mining, and heavy manufacturing. Fully enclosed vessels offer enhanced protection against weather and contamination, making them suitable for shipping sensitive goods, electronics, and consumer products across sectors like retail, pharmaceuticals, and food distribution. Choosing between these vessel types depends on your cargo's size, fragility, and protection requirements to ensure efficient and safe delivery.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Open-top container vessels require stringent safety measures to prevent cargo exposure to environmental hazards and ensure seaworthiness under adverse conditions, adhering to International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations for cargo securing and vessel stability. Fully enclosed vessels offer enhanced protection against weather and theft, meeting comprehensive safety standards such as SOLAS (Safety of Life at Sea) and MARPOL for pollution prevention. Regulatory compliance for both vessel types involves rigorous inspections, certification processes, and adherence to international codes to mitigate risks and ensure crew and cargo safety.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Open-top container vessels often have lower energy efficiency due to increased air resistance and require additional protective measures that can generate waste, impacting environmental sustainability negatively. Fully enclosed vessels enhance fuel efficiency by improving aerodynamics and providing better protection against weather-related cargo damage, reducing the need for repackaging or disposal. The choice between these vessel types affects carbon emissions, operational waste, and lifecycle environmental impacts, making fully enclosed vessels generally more sustainable for long-term shipping operations.
Choosing the Right Vessel for Your Shipping Needs
Open-top container vessels offer flexibility for oversized and heavy cargo that cannot fit into standard containers, providing easy loading and unloading through the open roof. Fully enclosed vessels ensure maximum protection against weather and environmental damage, ideal for delicate, high-value, or moisture-sensitive goods. Selecting the right vessel depends on factors such as cargo dimensions, vulnerability to weather, and port infrastructure compatibility.
Open-top container vessel vs fully enclosed vessel Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com