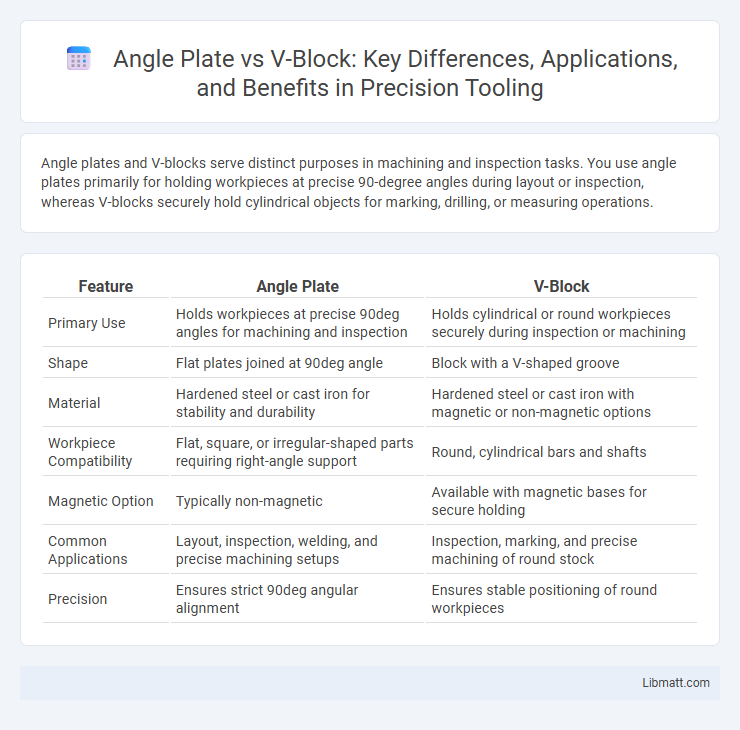
Angle plates and V-blocks serve distinct purposes in machining and inspection tasks. You use angle plates primarily for holding workpieces at precise 90-degree angles during layout or inspection, whereas V-blocks securely hold cylindrical objects for marking, drilling, or measuring operations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Angle Plate | V-Block |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Holds workpieces at precise 90deg angles for machining and inspection | Holds cylindrical or round workpieces securely during inspection or machining |
| Shape | Flat plates joined at 90deg angle | Block with a V-shaped groove |
| Material | Hardened steel or cast iron for stability and durability | Hardened steel or cast iron with magnetic or non-magnetic options |
| Workpiece Compatibility | Flat, square, or irregular-shaped parts requiring right-angle support | Round, cylindrical bars and shafts |
| Magnetic Option | Typically non-magnetic | Available with magnetic bases for secure holding |
| Common Applications | Layout, inspection, welding, and precise machining setups | Inspection, marking, and precise machining of round stock |
| Precision | Ensures strict 90deg angular alignment | Ensures stable positioning of round workpieces |
Introduction to Angle Plates and V-Blocks
Angle plates are precision metal tools used to hold workpieces at exact 90-degree angles during machining or inspection, ensuring accurate alignment and stability. V-blocks are specialized fixtures designed with a V-shaped groove to securely hold cylindrical or round objects for marking, drilling, or measuring tasks. Both tools are essential in manufacturing and metalworking for maintaining precision and repeatability in various applications.
Definition and Purpose of Angle Plates
Angle plates are precision metal tools used to hold workpieces at a fixed 90-degree angle for accurate machining and inspection, ensuring stability and alignment during metalworking tasks. Unlike V-blocks, which are designed primarily to secure cylindrical objects for drilling or measurement, angle plates provide a flat, perpendicular reference surface for squaring and supporting flat or irregularly shaped parts. Their robust construction and precise right angles make them essential for layout work, assembly, and inspection in manufacturing and machining environments.
Definition and Purpose of V-Blocks
V-blocks are precision metalworking tools designed to securely hold cylindrical or round objects during machining or inspection processes, ensuring accurate alignment and stability. Typically made from hardened steel, V-blocks feature a V-shaped groove that accommodates round workpieces, facilitating precise measurement or marking operations. Unlike angle plates, which primarily support flat or square components at specific angles, V-blocks excel in positioning and clamping curved or cylindrical parts for machining, grinding, or layout tasks.
Key Design Differences
Angle plates are precision tools with two flat surfaces set at a 90-degree angle, primarily designed for securing workpieces perpendicular to a base, while V-blocks feature a V-shaped groove to hold cylindrical objects firmly in place during machining. The angle plate's square design facilitates right-angle clamping for a variety of flat or irregular shapes, whereas the V-block's semi-cylindrical channel ensures stable alignment of round bars or pipes. Material composition typically includes hardened steel or cast iron for both, but the structural design differences cater to distinct machining setups and accuracy requirements.
Common Applications of Angle Plates
Angle plates are commonly used in machining and metalworking for precise right-angle positioning and workpiece support during inspection, layout, and assembly tasks. They provide stable mounting surfaces for holding parts perpendicular to the base, crucial in drilling, milling, and grinding operations where accurate angular alignment is required. Your workshop benefits from angle plates when securing workpieces for setup in jigs, fixtures, or inspection setups needing consistent 90-degree angles.
Common Applications of V-Blocks
V-blocks are primarily used for securely holding cylindrical workpieces during machining, inspection, and layout tasks, ensuring precise alignment along reference surfaces. Common applications include drilling, grinding, and milling round objects such as shafts, pipes, and rods, where stability and accuracy are critical. Their design allows for easy clamping and positioning, making them essential in quality control and fabrication environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Angle Plates
Angle plates provide precise right-angle support for workpieces during machining and inspection, ensuring accurate positioning and stability. They excel in versatility for holding parts vertically or horizontally but can be cumbersome due to their weight and bulk compared to V-blocks. Unlike V-blocks, which specialize in holding cylindrical objects, angle plates are less effective for round components but offer superior rigidity for square or rectangular parts.
Advantages and Disadvantages of V-Blocks
V-blocks provide exceptional support for clamping and machining cylindrical workpieces, offering a stable grip due to their V-shaped groove, which aligns round objects securely. They are highly versatile for precision marking, grinding, and inspection, but may lack the flat surface and angular measurement capabilities found in angle plates. Your choice depends on whether you require consistent angular positioning or enhanced round workpiece stability.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Angle Plate and V-Block
Precision requirements significantly influence choosing between an angle plate and a V-block, as angle plates provide stable right-angle support while V-blocks excel in securely holding cylindrical workpieces. Material compatibility and the shape of your workpiece determine the optimal tool, with V-blocks designed for round objects and angle plates better suited for flat or angular surfaces. Your machining setup and clamping needs also play a critical role, as angle plates can be bolted to machine tables, whereas V-blocks offer versatile clamping for inspection or marking tasks.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Tool for Your Machining Needs
Angle plates provide precise 90-degree reference surfaces essential for squaring workpieces, while V-blocks offer secure cylindrical workpiece holding and alignment during machining. Your choice depends on the shape and orientation of the material, with angle plates ideal for flat, perpendicular setups and V-blocks suited for round or irregular components. Selecting the right tool optimizes accuracy and efficiency in machining operations.
Angle plate vs V-block Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com