A sine bar provides precise angle measurement and layout by using known lengths and sine calculations, ideal for setting and inspecting angles with high accuracy. An angle plate secures workpieces at fixed right angles for machining or inspection, offering stability and repeatability without requiring trigonometric setup.
Table of Comparison
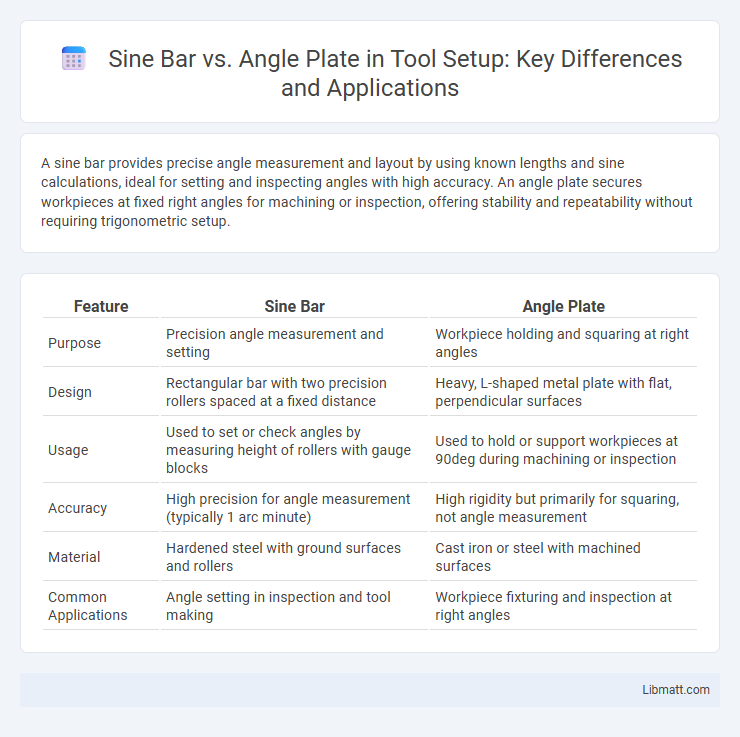
| Feature | Sine Bar | Angle Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Precision angle measurement and setting | Workpiece holding and squaring at right angles |
| Design | Rectangular bar with two precision rollers spaced at a fixed distance | Heavy, L-shaped metal plate with flat, perpendicular surfaces |
| Usage | Used to set or check angles by measuring height of rollers with gauge blocks | Used to hold or support workpieces at 90deg during machining or inspection |
| Accuracy | High precision for angle measurement (typically 1 arc minute) | High rigidity but primarily for squaring, not angle measurement |
| Material | Hardened steel with ground surfaces and rollers | Cast iron or steel with machined surfaces |
| Common Applications | Angle setting in inspection and tool making | Workpiece fixturing and inspection at right angles |
Introduction to Sine Bar and Angle Plate
A sine bar is a precision measuring tool used to measure angles accurately by leveraging the sine principle, often utilized in machining and metalworking for setting taper angles or checking angular components. An angle plate is a robust, L-shaped tool designed to firmly hold workpieces at fixed right angles during inspection or machining, ensuring precise alignment and stability. Both tools are essential in manufacturing environments for achieving high-accuracy angular measurements and setups.
What is a Sine Bar?
A sine bar is a precision measuring instrument used in metalworking and manufacturing to measure angles accurately by leveraging the sine trigonometric function. It consists of a hardened steel bar with two precision ground cylinders spaced a fixed distance apart, which allows the user to set and measure angles by raising one end and calculating the height using gauge blocks. Commonly used for layout, inspection, and setup tasks, sine bars are essential for ensuring angular accuracy in machining operations.
What is an Angle Plate?
An angle plate is a precision metal tool used to hold workpieces perpendicular to a surface, ensuring accurate machining or inspection. Made from cast iron or steel, angle plates feature flat surfaces and right-angle edges designed to support and secure components during manufacturing processes. Compared to a sine bar, which measures angles with high accuracy, an angle plate provides stable positioning for workpieces at fixed right angles.
Key Differences Between Sine Bar and Angle Plate
A sine bar is primarily designed for precise angle measurement and layout using trigonometric principles, while an angle plate provides a stable, fixed right-angle reference for workholding and inspection. Sine bars rely on rollers and gauge blocks to set exact angles, making them ideal for machining tasks requiring high accuracy in angular setups. Angle plates are typically rigid steel blocks with flat faces at 90 degrees, essential for supporting parts during milling or drilling operations that demand consistent perpendicularity.
Working Principle: Sine Bar vs Angle Plate
A sine bar operates on the principle of creating precise angles by using a calibrated bar and gauge blocks to set an exact sine value for the angle. Angle plates work by providing a rigid, perpendicular reference surface to support and align workpieces at fixed 90-degree or adjustable angles. The sine bar allows for accurate angle measurement and setup through trigonometric calculations, while angle plates primarily offer stable, fixed-angle positioning for machining or inspection.
Applications of Sine Bar
Sine bars are primarily used for precise angle measurement and inspection in machining and manufacturing processes, enabling accurate setup of workpieces for grinding, milling, and layout work. Their applications include setting and checking angles on machine tools, inspecting angular surfaces, and calibrating measuring instruments with exceptional accuracy. You can rely on sine bars for tasks requiring high precision in angular measurement beyond the capabilities of angle plates, which are more suited for holding workpieces at fixed right angles.
Applications of Angle Plate
Angle plates are precision tools widely used in metalworking and machining for holding workpieces square to the table during inspection and layout operations. They provide stable support for machining tasks such as drilling, milling, and grinding, ensuring accurate 90-degree angles. Your projects benefit from their ability to maintain perpendicularity and enhance the precision of assembly and fabrication processes.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Sine Bar vs Angle Plate
A sine bar offers high precision in measuring and setting angles due to its reliance on trigonometric calculations and gauge blocks, making it ideal for tasks requiring exact angular measurements. Angle plates provide stable and versatile support for workpieces during machining or inspection but may lack the fine measurement accuracy of a sine bar. Your choice depends on whether precise angle measurement (sine bar) or sturdy workpiece positioning (angle plate) is the priority.
How to Choose Between Sine Bar and Angle Plate
Choosing between a sine bar and an angle plate depends on the precision and type of angular measurement or machining you require. Sine bars offer highly accurate angle measurements by utilizing sine calculations and gauge blocks, making them ideal for setting or inspecting precise angles. Angle plates provide stable, rigid support for workpieces at fixed right angles, making them suitable for general fixturing and layout tasks in your machining processes.
Conclusion: Sine Bar or Angle Plate?
A sine bar offers precise angle measurement and is ideal for tasks requiring high accuracy in setting or inspecting angles, especially in machining operations. An angle plate provides stable support for holding workpieces at fixed right angles during drilling or inspection but lacks the fine angular adjustment capability of a sine bar. Choosing between a sine bar and an angle plate depends on whether precision angular measurement or rigid perpendicular positioning is the primary requirement in the application.
Sine bar vs angle plate Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com