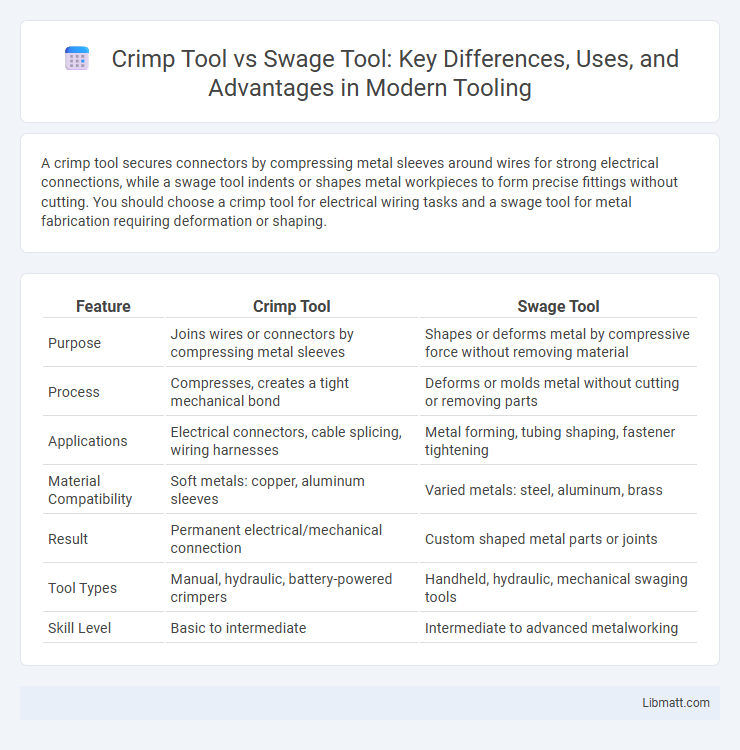
A crimp tool secures connectors by compressing metal sleeves around wires for strong electrical connections, while a swage tool indents or shapes metal workpieces to form precise fittings without cutting. You should choose a crimp tool for electrical wiring tasks and a swage tool for metal fabrication requiring deformation or shaping.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Crimp Tool | Swage Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Joins wires or connectors by compressing metal sleeves | Shapes or deforms metal by compressive force without removing material |
| Process | Compresses, creates a tight mechanical bond | Deforms or molds metal without cutting or removing parts |
| Applications | Electrical connectors, cable splicing, wiring harnesses | Metal forming, tubing shaping, fastener tightening |
| Material Compatibility | Soft metals: copper, aluminum sleeves | Varied metals: steel, aluminum, brass |
| Result | Permanent electrical/mechanical connection | Custom shaped metal parts or joints |
| Tool Types | Manual, hydraulic, battery-powered crimpers | Handheld, hydraulic, mechanical swaging tools |
| Skill Level | Basic to intermediate | Intermediate to advanced metalworking |
Introduction to Crimp Tools and Swage Tools
Crimp tools are specialized hand tools designed to join metal connectors to wires by compressing and deforming the connector, ensuring a secure mechanical and electrical connection. Swage tools operate by reshaping or compressing metal parts, often used to form strong, permanent connections or customize metal fittings without cutting or adding extra components. Both tools are essential in electrical, automotive, and metalworking industries for creating reliable joints, but crimp tools focus on fastening connectors while swage tools primarily reshape metal components.
Key Differences Between Crimping and Swaging
Crimp tools compress a connector onto a cable by deforming the connector material, creating a secure mechanical and electrical connection primarily for electrical wires and coaxial cables. Swage tools reshape metal without cutting or removing material, often used for forming permanent joints in metal tubes or cables by applying controlled pressure. Key differences lie in their applications--crimping is typically used for joining wires and connectors, while swaging is preferred for reinforcing or resizing metal parts without compromising material integrity.
How Crimp Tools Work: Mechanism and Applications
Crimp tools operate by compressing a metal sleeve or connector onto a cable or wire, creating a secure and reliable electrical or mechanical connection through deformation. This mechanism ensures strong conductivity and resistance to vibration, commonly applied in electrical wiring, coaxial cables, and automotive repairs. Your choice between crimp and swage tools depends on the specific application, as crimp tools are ideal for quick, consistent wire termination and signal integrity.
Understanding Swage Tools: Function and Uses
Swage tools are designed to reshape or compress metal by applying controlled pressure, often used in metalworking to form or join pieces without cutting or removing material. Unlike crimp tools that mainly secure connectors onto wires by deforming the connector, swage tools enable precise shaping of metal components, such as creating flares or reinforcing tubes. Understanding your swage tool's function helps ensure proper application in processes like fitting aviation tubing or assembling cable assemblies.
Materials and Connectors: Compatibility for Each Tool
Crimp tools are compatible with a variety of soft metals such as copper and aluminum, commonly used in electrical connectors, terminals, and coaxial cable fittings. Swage tools are designed to shape and join harder materials like steel or stainless steel, frequently applied in mechanical fittings and high-strength wire rope assemblies. Choosing the right tool depends on the connector type and material hardness to ensure a secure and reliable connection.
Pros and Cons of Using Crimp Tools
Crimp tools offer efficient and reliable connections by compressing connectors onto cables, ensuring strong electrical continuity and minimized signal loss. They are easy to use, require minimal training, and provide consistent results for a variety of wire gauges and connector types. However, crimp tools can cause damage if improper force is applied or if the wrong die is used, potentially leading to weak or unreliable connections.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Swage Tools
Swage tools provide a stronger, more permanent connection by deforming metal components without cutting, which enhances durability and reliability in heavy-duty applications. They offer precise, clean joints ideal for high-stress environments but require specialized equipment and greater skill compared to crimp tools. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize ease of use and speed (crimp tools) or maximum strength and longevity (swage tools).
Performance and Reliability Comparison
Crimp tools deliver consistent, high-pressure compression essential for reliable electrical connections in wire terminals, ensuring minimal signal loss and strong mechanical bonds. Swage tools provide precise deformation by cold-forming metal fittings, enhancing durability and resistance to mechanical stress in structural applications. Performance reliability of crimp tools excels in electrical and electronic industries, while swage tools are preferred for heavy-duty, industrial settings requiring long-lasting, corrosion-resistant assemblies.
Cost Considerations: Tool Price and Maintenance
Crimp tools typically offer a lower initial purchase price compared to swage tools, making them more cost-effective for small-scale or occasional projects. Swage tools, often designed for heavy-duty or precision applications, tend to have higher upfront costs but provide greater durability, reducing long-term maintenance expenses. Maintenance requirements for crimp tools are generally minimal, while swage tools may require periodic calibration and part replacements to maintain optimal performance, impacting overall cost considerations.
Choosing the Right Tool: Crimp or Swage?
Selecting the right tool depends on the application: crimp tools compress connectors onto cables for electrical and network installations, ensuring secure mechanical and electrical connections. Swage tools reshape or deform metal fittings, commonly used in rigging or jewelry, to create strong, permanent joints without adding material. Understanding the specific material and connection requirements drives the choice between crimping for quick, reliable electrical contacts and swaging for durable, high-strength mechanical bonds.
Crimp tool vs swage tool Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com