RF welders use high-frequency electromagnetic energy to generate heat and bond materials, making them ideal for plastics with polar molecules like PVC and polyurethane. Ultrasonic welders rely on high-frequency mechanical vibrations to create heat through friction, offering precise, fast, and clean welding for thermoplastics and delicate components in industries such as electronics and medical devices.
Table of Comparison
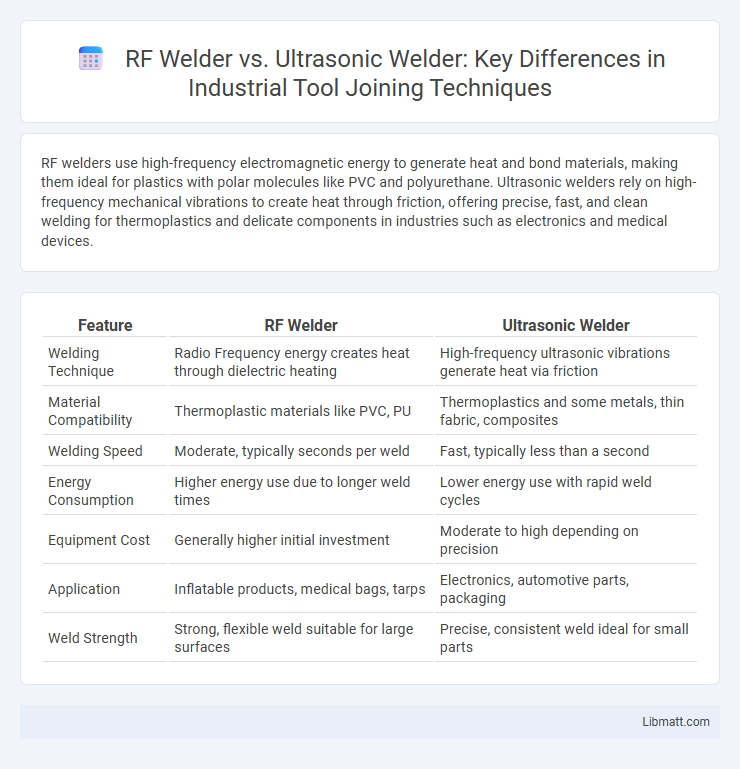
| Feature | RF Welder | Ultrasonic Welder |
|---|---|---|
| Welding Technique | Radio Frequency energy creates heat through dielectric heating | High-frequency ultrasonic vibrations generate heat via friction |
| Material Compatibility | Thermoplastic materials like PVC, PU | Thermoplastics and some metals, thin fabric, composites |
| Welding Speed | Moderate, typically seconds per weld | Fast, typically less than a second |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy use due to longer weld times | Lower energy use with rapid weld cycles |
| Equipment Cost | Generally higher initial investment | Moderate to high depending on precision |
| Application | Inflatable products, medical bags, tarps | Electronics, automotive parts, packaging |
| Weld Strength | Strong, flexible weld suitable for large surfaces | Precise, consistent weld ideal for small parts |
Introduction to RF and Ultrasonic Welding
RF welding uses high-frequency electromagnetic fields to generate heat within dielectric materials, causing them to bond at the molecular level. Ultrasonic welding employs high-frequency mechanical vibrations to create frictional heat, enabling thermoplastics to fuse quickly without external heat sources. Both methods are widely applied in industries requiring strong, precise sealing of plastic components, but differ fundamentally in their heat generation and material compatibility.
How RF Welding Works
RF welding works by using high-frequency electromagnetic waves, typically between 13.56 MHz and 40.68 MHz, to generate heat within dielectric materials, causing them to fuse together. This method specifically targets polymers containing polar molecules, such as PVC and polyurethane, allowing for precise and strong seams without melting the entire material. Your choice between RF and ultrasonic welding depends on the material properties and the desired weld quality, as RF is ideal for moisture-resistant, airtight seals in flexible materials.
How Ultrasonic Welding Works
Ultrasonic welding uses high-frequency ultrasonic vibrations to create a solid-state bond between materials by generating localized heat through friction at the interface. This process is ideal for joining thermoplastics and thin metals without the need for adhesives or external heat sources. You can achieve precise, fast, and clean welds with ultrasonic welding, making it highly efficient for delicate or intricate components.
Key Differences Between RF and Ultrasonic Welders
RF welders use high-frequency electromagnetic waves to heat and join plastic materials, while ultrasonic welders rely on high-frequency mechanical vibrations to create frictional heat for bonding. RF welding is ideal for materials with polar molecules like PVC, whereas ultrasonic welding works best with non-polar thermoplastics such as polypropylene. Your choice depends on the material type, thickness, and production speed requirements for optimal welding performance.
Material Compatibility Comparison
RF welders excel in joining thermoplastic materials such as PVC and polyurethane, offering strong, durable bonds ideal for flexible, single-layer fabrics. Ultrasonic welders are more versatile with a broader range of materials, including nonwoven fabrics, nylon, polyester, and certain composites, making them suitable for delicate or multilayer applications. Your choice depends on the specific polymers and thicknesses involved, as RF welding performs best with polar plastics while ultrasonic welding handles non-polar and thin materials efficiently.
Precision and Strength of Welds
RF welders create strong, consistent bonds by using high-frequency electromagnetic energy to heat materials uniformly, resulting in precise welds ideal for synthetic fabrics and plastics. Ultrasonic welders use high-frequency mechanical vibrations to generate localized heat, producing precise welds with minimal distortion, especially effective for small, intricate components. Your choice depends on the material type and required weld strength, with RF welders typically offering superior bond strength for thicker or multi-layered materials.
Equipment Costs and Operational Efficiency
RF welders generally have higher initial equipment costs compared to ultrasonic welders, but they offer greater efficiency for bonding specific materials like PVC and polyurethane. Ultrasonic welders operate at lower power consumption, reducing operational expenses and maintenance needs, making them cost-effective for high-volume production of thermoplastics. Your choice depends on balancing upfront investment with long-term energy savings and material compatibility.
Typical Applications for RF and Ultrasonic Welding
RF welding excels in joining flexible materials like PVC and polyurethane, commonly used in medical bags, inflatable products, and automotive interiors where airtight and watertight seals are crucial. Ultrasonic welding is ideal for thermoplastics and delicate components, frequently applied in electronics, packaging, and medical device manufacturing to create precise, clean seals without adhesives. Your choice depends on material compatibility and the specific requirements of strength, speed, and detail in your application.
Safety Considerations in Each Method
RF welders use high-frequency electromagnetic waves to heat materials, requiring strict shielding and grounding protocols to prevent electrical hazards and operator exposure. Ultrasonic welders generate heat through high-frequency mechanical vibrations, posing risks of noise-induced hearing damage and potential burns if not properly shielded. Your safety depends on proper training, use of personal protective equipment, and adherence to equipment-specific safety guidelines for both methods.
Choosing the Right Welding Technology
Choosing the right welding technology depends on the material type and application requirements, with RF welders excelling in sealing synthetic textiles like PVC and polyurethane due to their radio frequency energy. Ultrasonic welders provide precise, fast bonding for thermoplastics and thin materials by using high-frequency ultrasonic acoustic vibrations, making them ideal for delicate components and non-ferrous materials. Evaluating factors such as material compatibility, weld strength, speed, and production volume ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency in manufacturing processes.
RF welder vs ultrasonic welder Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com