An end mill features multiple cutting edges on its sides and tip, making it ideal for creating complex shapes, pockets, and contours in machining processes. Slot drills have fewer flutes and are specifically designed to cut slots or grooves with precision, offering better chip clearance and reduced cutting forces during slotting operations.
Table of Comparison
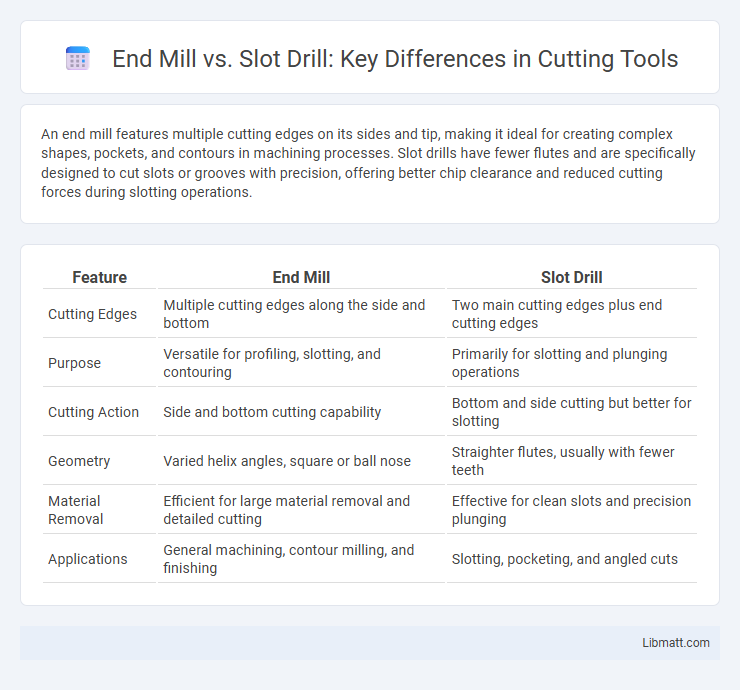
| Feature | End Mill | Slot Drill |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Edges | Multiple cutting edges along the side and bottom | Two main cutting edges plus end cutting edges |
| Purpose | Versatile for profiling, slotting, and contouring | Primarily for slotting and plunging operations |
| Cutting Action | Side and bottom cutting capability | Bottom and side cutting but better for slotting |
| Geometry | Varied helix angles, square or ball nose | Straighter flutes, usually with fewer teeth |
| Material Removal | Efficient for large material removal and detailed cutting | Effective for clean slots and precision plunging |
| Applications | General machining, contour milling, and finishing | Slotting, pocketing, and angled cuts |
Introduction to End Mills and Slot Drills
End mills are versatile cutting tools used primarily for milling applications, featuring multiple flutes and designed for side milling, slotting, and contouring on various materials. Slot drills, a subset of end mills, are specifically engineered for cutting slots and grooves with their center-cutting capability, allowing plunge cuts and efficient material removal. Understanding the distinction between end mills and slot drills enhances precision in machining processes by selecting the appropriate tool for specific milling tasks.
Key Differences Between End Mills and Slot Drills
End mills feature multiple cutting edges on the periphery and are primarily used for side milling, profiling, and contouring, offering high precision and surface finish. Slot drills, typically having two cutting edges, excel in cutting slots and plunge cutting due to their robust design and better chip evacuation in confined spaces. The key differences lie in their geometry, cutting edge count, and typical applications, with end mills suited for versatile milling tasks and slot drills optimized for slotting operations.
Design and Geometry Comparison
End mills feature a cylindrical shape with cutting edges on both the periphery and the tip, allowing for versatile milling operations including side milling and slotting. Slot drills have two or three flutes and a pointed tip designed primarily for creating slots and pockets with precision and less vibration. Your selection depends on the complexity of the cut and the surface finish required, with end mills providing smoother finishes and slot drills enabling precise slot widths.
Material Compatibility
End mills are highly versatile and compatible with a wide range of materials including steel, aluminum, brass, plastics, and composites due to their diverse flute configurations and cutting geometries. Slot drills, designed primarily for slotting and milling operations, excel in softer materials like aluminum and plastics, offering precise slotting with minimal tool deflection. Choosing between end mills and slot drills depends on material hardness and machining requirements, as end mills typically handle tougher materials better while slot drills provide accurate slot cuts in lighter metals.
Cutting Performance and Efficiency
End mills offer superior cutting performance with their versatile flute designs, allowing efficient material removal and smooth finishes in diverse milling applications. Slot drills, equipped with two cutting edges, excel in precision slotting and plunge cutting but may lag behind end mills in chip evacuation and surface quality on complex contours. Choosing the right tool depends on the required efficiency, material type, and specific cutting task to maximize productivity and tool life.
Applications and Use Cases
End mills are primarily used for profiling, contouring, and slotting in materials like metals, plastics, and composites, making them ideal for complex shapes and surface finishes. Slot drills excel at creating precise slots and grooves due to their two-flute design, providing better chip clearance and reduced cutting forces. Choosing the right tool depends on your specific machining needs, such as whether you require intricate detail work or efficient slot creation.
Pros and Cons of End Mills
End mills offer versatile cutting options for milling operations, excelling in contouring, profiling, and slotting with their multi-flute design that provides superior surface finish and faster material removal. However, they can be more expensive and less rigid than slot drills, which may lead to tool deflection in deep or narrow slots. Your choice depends on balancing precision and tool durability against cost and specific machining requirements.
Pros and Cons of Slot Drills
Slot drills offer superior precision and efficient chip removal due to their two-flute design, making them ideal for shallow slotting and contouring tasks. Their versatility allows for plunge cutting and side milling, but they may not perform well in deep slotting compared to specialized end mills. You should consider that slot drills can generate higher cutting forces, which might impact tool life and surface finish in harder materials.
Selection Tips: Choosing the Right Tool
Selecting the right tool between an end mill and a slot drill depends on your machining needs and material type. End mills are best for precision finishing and complex contours, while slot drills excel in creating slots and pockets with efficient chip evacuation. Consider your cutting depth, feed rates, and required surface finish to optimize your tool choice for enhanced performance and tool life.
Conclusion and Recommendations
End mills offer superior versatility and precision for a wide range of milling operations, making them ideal for complex profiles and contouring. Slot drills excel in producing accurate slots and slots with sharp corners, especially in applications requiring rigid tool engagement and reduced tool deflection. Select end mills for multi-axis machining and detailed 3D work, while slot drills are recommended for slotting and plunge cutting to maximize cutting efficiency and tool life.
End mill vs slot drill Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com