Hand taps provide precise threading control for small or delicate jobs, while power taps offer faster and more efficient thread cutting for larger or repetitive tasks. Choose the right tap based on your project's scale and accuracy requirements to optimize your threading process.
Table of Comparison
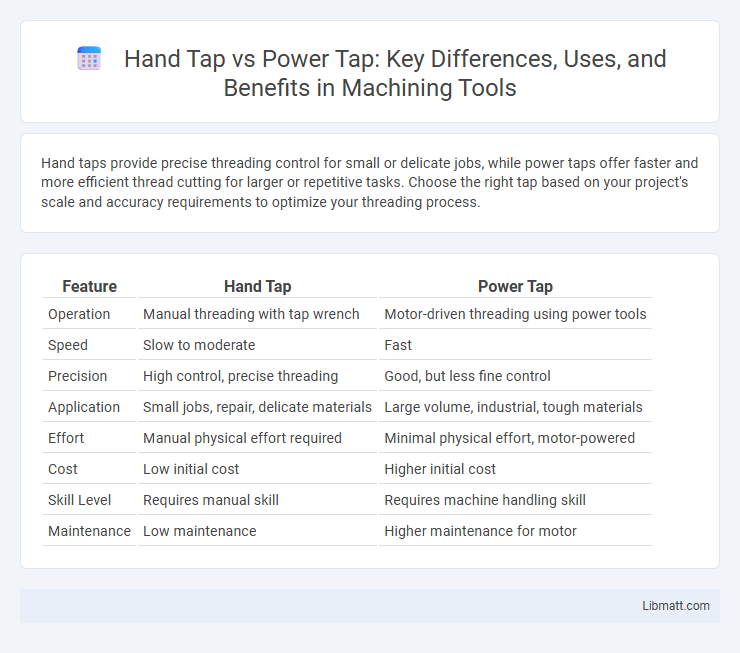
| Feature | Hand Tap | Power Tap |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Manual threading with tap wrench | Motor-driven threading using power tools |
| Speed | Slow to moderate | Fast |
| Precision | High control, precise threading | Good, but less fine control |
| Application | Small jobs, repair, delicate materials | Large volume, industrial, tough materials |
| Effort | Manual physical effort required | Minimal physical effort, motor-powered |
| Cost | Low initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Skill Level | Requires manual skill | Requires machine handling skill |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Higher maintenance for motor |
Introduction to Tapping Methods
Hand taps rely on manual force for threading holes, offering precise control and reduced risk of over-tapping in delicate materials. Power taps, driven by machines or drills, enable faster threading and are ideal for high-volume or tougher materials but require careful speed and torque management to prevent tool breakage. Your choice between hand tap and power tap depends on material type, required accuracy, and production efficiency.
What is a Hand Tap?
A hand tap is a cutting tool used to create internal threads in pre-drilled holes manually, ensuring precision and control during threading processes. Commonly made from high-speed steel or carbon steel, hand taps come in various types such as taper, plug, and bottoming taps, each designed for different threading stages. Unlike power taps, hand taps require manual turning, providing greater accuracy and reduced risk of thread damage in delicate or small-scale applications.
What is a Power Tap?
A Power Tap is a type of tap used in threading that is driven by a power tool or machine rather than manually by hand. It offers faster and more consistent thread cutting, especially in high-production environments, by utilizing rotary motion to cut internal threads efficiently. Power taps are designed to withstand higher torque and reduce operator fatigue compared to hand taps, making them ideal for industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Hand Tap and Power Tap
Hand taps require manual operation and are ideal for precision threading in softer materials or small-diameter holes, offering greater control and accuracy. Power taps are designed for use with machines, enabling faster threading in harder materials and larger holes but typically with less tactile feedback. The key differences lie in their operational method, speed, required force, and suitability for specific material hardness and hole sizes.
Applications of Hand Tapping
Hand tapping is widely used in precision applications where operator control and tactile feedback are crucial, such as in delicate machinery assembly and small-scale manufacturing. It is ideal for threading materials like aluminum, brass, and softer metals where minimizing tool breakage is important. Hand tapping enables fine adjustments during repair work and prototyping, allowing for accurate and consistent thread creation in confined or hard-to-reach spaces.
Applications of Power Tapping
Power tapping is ideal for high-volume manufacturing environments where speed and efficiency are critical, enabling rapid thread creation in metal or plastic components. This method excels in automated assembly lines, robotics, and CNC machining centers, significantly reducing cycle times compared to manual hand tapping. Power tapping is especially suitable for materials like aluminum, mild steel, and cast iron, ensuring precise and consistent threading in industrial production settings.
Advantages of Hand Taps
Hand taps provide superior control and precision when cutting threads, minimizing the risk of damaging delicate materials. They are ideal for small or intricate jobs where accuracy is critical, allowing for tactile feedback that prevents over-torquing and thread distortion. Hand taps are also cost-effective and require no power source, making them accessible and versatile for diverse machining environments.
Advantages of Power Taps
Power taps offer significant advantages over hand taps by providing faster and more consistent threading, which enhances productivity and reduces operator fatigue. Their ability to handle tougher materials and maintain precise thread quality in high-volume manufacturing settings ensures greater efficiency and durability. Choosing a power tap benefits your workflow by minimizing manual effort while delivering accurate, repeatable results.
Choosing the Right Tap for Your Project
Selecting the right tap for your project hinges on material hardness and production volume; hand taps are ideal for low-volume, precise threading in softer materials, while power taps excel in high-volume, efficient operations with harder metals. Hand taps provide greater control and reduce the risk of breaking in delicate tasks, whereas power taps require compatible machinery but offer speed and uniformity. Understanding these factors ensures optimal thread quality, tool longevity, and project success.
Safety Tips and Best Practices
Hand taps require careful control and steady pressure to avoid breakage, while power taps should be operated at manufacturer-recommended speeds with appropriate cutting fluids to prevent overheating. Always wear safety glasses and use the correct size tap wrench or machine attachment to ensure stability and reduce the risk of injury. Proper lubrication and regular inspection of taps for wear significantly enhance precision and extend tool life in both manual and powered tapping operations.
Hand tap vs power tap Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com