A punch press uses a die to cut or shape metal by applying pressure to create precise holes or forms, while a shear press cuts metal by applying a straight blade to slice through material without forming or shaping. Your choice depends on whether you need detailed cutting and shaping (punch press) or straightforward metal cutting (shear press).
Table of Comparison
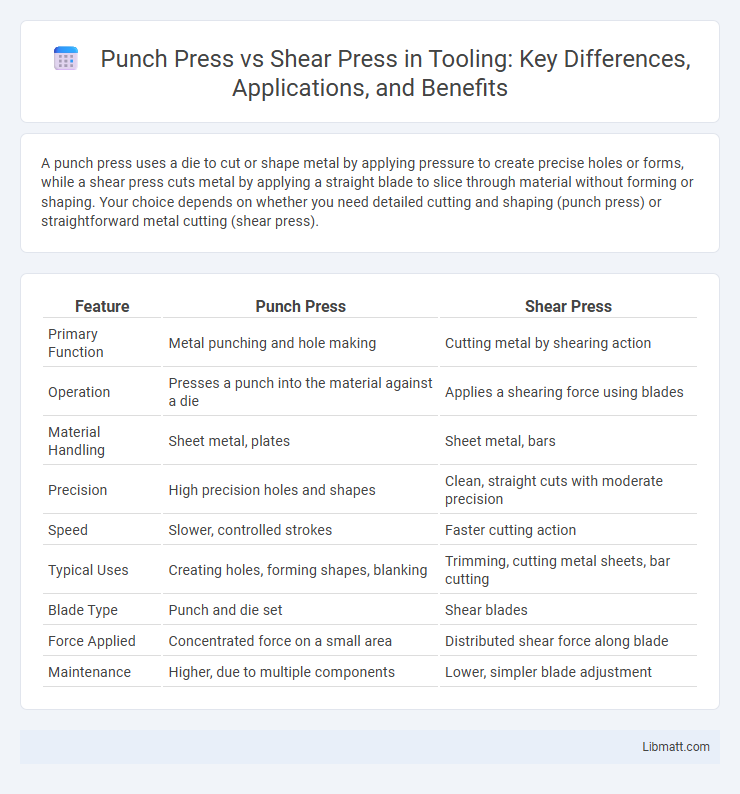
| Feature | Punch Press | Shear Press |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Metal punching and hole making | Cutting metal by shearing action |
| Operation | Presses a punch into the material against a die | Applies a shearing force using blades |
| Material Handling | Sheet metal, plates | Sheet metal, bars |
| Precision | High precision holes and shapes | Clean, straight cuts with moderate precision |
| Speed | Slower, controlled strokes | Faster cutting action |
| Typical Uses | Creating holes, forming shapes, blanking | Trimming, cutting metal sheets, bar cutting |
| Blade Type | Punch and die set | Shear blades |
| Force Applied | Concentrated force on a small area | Distributed shear force along blade |
| Maintenance | Higher, due to multiple components | Lower, simpler blade adjustment |
Introduction to Punch Press and Shear Press
Punch presses and shear presses are essential machinery in metal fabrication, each serving distinct functions tailored to specific manufacturing needs. Punch presses utilize a die to cut or shape metal by applying a precise, controlled force, ideal for creating holes or intricate patterns. Shear presses operate by applying a linear force to cut metal sheets into straight sections, offering efficient, clean cuts for material preparation.
Key Differences Between Punch Press and Shear Press
Punch presses are primarily designed for cutting, shaping, or forming metal by applying a direct punching force using a die, ideal for creating holes or specific shapes in sheet metal. Shear presses function by applying a clean slicing action to cut straight lines or shapes from metal sheets, emphasizing precision in lengthwise or crosswise cuts. The key differences lie in their operational mechanisms: punch presses use dies for deformation and hole creation, while shear presses rely on sharp blades for straight cutting without deformation.
Working Principles of Punch Press
The punch press operates by using a ram to apply downward force, driving a punch through a sheet metal positioned on a die, effectively creating precise holes or shapes. Hydraulic or mechanical systems power the ram's movement, ensuring accurate, repeatable cuts with controlled force and speed. This process relies on the alignment of the punch and die to shear material cleanly without excessive distortion or deformation.
Working Principles of Shear Press
A shear press operates by applying a linear force to cut or shear materials, using a stationary blade opposite a moving blade to create precise cuts. Unlike punch presses that create holes by pressing a punch through the material, shear presses slice through the workpiece along a straight line. Understanding the working principles of a shear press helps you choose the right machine for applications requiring clean, straight-edge cuts in metal or other materials.
Types of Materials Processed
Punch presses efficiently process sheet metals like steel, aluminum, and copper by cutting or shaping through shearing and bending forces, making them ideal for detailed component manufacturing. Shear presses specialize in cutting straight lines through tougher, thicker materials such as heavy steel plates or metal bars, offering clean, precise cuts for large-scale industrial applications. Selection depends on material thickness and desired precision, with punch presses suited for intricate patterns and shear presses for bulk material separation.
Applications in Modern Manufacturing
Punch presses excel in producing precise holes and shapes in sheet metal, making them ideal for automotive, aerospace, and appliance manufacturing. Shear presses are primarily used for cutting large metal sheets into manageable sizes or specific shapes, essential in heavy machinery and construction component fabrication. Your choice between the two depends on whether detailed shaping or bulk cutting better suits your production needs.
Advantages of Punch Press
Punch presses offer precise and versatile metal shaping capabilities, making them ideal for creating complex shapes and detailed cutouts with minimal material waste. Their ability to handle various metal thicknesses and automated operation increases production efficiency and consistency in high-volume manufacturing. You benefit from reduced setup times and enhanced accuracy, resulting in lower costs and faster turnaround for custom metal fabrication projects.
Advantages of Shear Press
Shear presses offer significant advantages in cutting and shaping metal sheets with high precision and minimal material distortion, resulting in cleaner edges and reduced waste. Their ability to handle thicker materials efficiently makes them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications, ensuring consistent performance and durability. You benefit from enhanced productivity and lower maintenance costs compared to punch presses in operations requiring repetitive cutting tasks.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Punch and Shear Press
Choosing between a punch press and a shear press depends on material thickness, desired precision, and production volume. Punch presses excel in creating detailed, complex shapes with high accuracy, ideal for sheet metal fabrication requiring multiple cutouts or holes. Shear presses are more efficient for straight cuts and high-speed cutting of thicker materials, offering durability and faster cycle times for simpler shapes.
Conclusion: Which Press is Right for Your Needs?
Choosing between a punch press and a shear press depends on your specific metalworking requirements; punch presses excel in creating precise holes and shapes with high repeatability, ideal for fabrication and custom parts. Shear presses are better suited for cutting large metal sheets into straight sections quickly and efficiently, making them a top choice for volume production and rough cutting tasks. Evaluate project complexity, material type, and production volume to determine the best press for your manufacturing needs.
Punch press vs shear press Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com