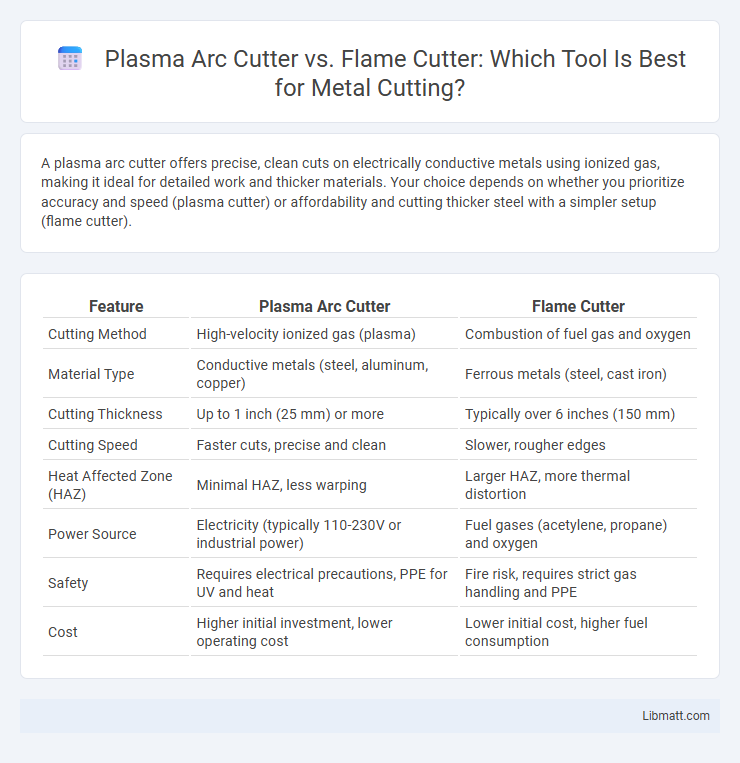
A plasma arc cutter offers precise, clean cuts on electrically conductive metals using ionized gas, making it ideal for detailed work and thicker materials. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize accuracy and speed (plasma cutter) or affordability and cutting thicker steel with a simpler setup (flame cutter).
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plasma Arc Cutter | Flame Cutter |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | High-velocity ionized gas (plasma) | Combustion of fuel gas and oxygen |
| Material Type | Conductive metals (steel, aluminum, copper) | Ferrous metals (steel, cast iron) |
| Cutting Thickness | Up to 1 inch (25 mm) or more | Typically over 6 inches (150 mm) |
| Cutting Speed | Faster cuts, precise and clean | Slower, rougher edges |
| Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) | Minimal HAZ, less warping | Larger HAZ, more thermal distortion |
| Power Source | Electricity (typically 110-230V or industrial power) | Fuel gases (acetylene, propane) and oxygen |
| Safety | Requires electrical precautions, PPE for UV and heat | Fire risk, requires strict gas handling and PPE |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower operating cost | Lower initial cost, higher fuel consumption |
Introduction to Plasma Arc Cutters and Flame Cutters
Plasma arc cutters utilize ionized gas at extremely high temperatures to efficiently cut through electrically conductive metals, offering precision and speed unmatched by traditional methods. Flame cutters, also known as oxy-fuel cutters, rely on a chemical reaction between oxygen and fuel gas to produce a high-temperature flame capable of cutting thick steel and iron. Both technologies serve critical roles in metal fabrication, with plasma cutters excelling in fine, detailed work and flame cutters preferred for heavy-duty, thick materials.
How Plasma Arc Cutting Works
Plasma arc cutting operates by generating an electric arc through a constricted plasma gas jet, which melts and blows away metal to create precise cuts. The plasma gas, often compressed air or inert gases like nitrogen or argon, is ionized to reach temperatures exceeding 20,000degC, enabling rapid, clean cuts on conductive metals. This process offers superior speed and accuracy compared to flame cutting, which relies on oxidizing the metal with a fuel gas flame.
How Flame Cutting Works
Flame cutting works by using a high-temperature oxy-fuel flame to heat metal to its ignition temperature, then a stream of pure oxygen is directed onto the heated metal, causing it to oxidize and blow away the molten material. This process is primarily effective on ferrous metals due to their ability to oxidize easily, making it less suitable for non-ferrous metals. Your choice between plasma arc cutter and flame cutter depends on the specific material and precision requirements of your cutting tasks.
Material Compatibility: Plasma vs. Flame
Plasma arc cutters excel in cutting electrically conductive metals such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper with high precision and minimal heat distortion. Flame cutters are better suited for cutting ferrous metals like mild and carbon steel, especially thicker materials, relying on oxidation rather than electrical conductivity. Your choice depends on the material type and thickness, as plasma offers versatility for various metals while flame cutting remains preferred for heavy steel applications.
Cutting Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Plasma arc cutters offer significantly faster cutting speeds compared to flame cutters, especially on thin to medium-thickness metals, due to their high-temperature ionized gas jet that melts and expels material efficiently. Flame cutters are more efficient for thicker steel and metals as they utilize a controlled oxidation process, but their slower cutting rates can reduce overall productivity. Your choice of cutter should consider material thickness and desired cutting speed to optimize efficiency and project timelines.
Precision and Cut Quality Analysis
Plasma arc cutters deliver superior precision and cleaner cut quality compared to flame cutters, achieving narrow kerf widths and minimal heat-affected zones ideal for detailed metalwork. Flame cutters are less precise due to a broader heat application, resulting in rougher edges and increased post-cut cleanup, particularly on thinner materials. Your choice of cutter should consider the required cut accuracy and finish quality, with plasma arc cutters excelling in tasks demanding high precision and smooth cuts.
Safety Considerations for Both Methods
Plasma arc cutters offer enhanced safety through reduced risk of harmful gas exposure and minimal flame hazards compared to flame cutters, which produce intense heat and open flames prone to causing burns and fires. Both methods require proper personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, face shields, and fire-resistant clothing to protect against sparks, UV radiation, and molten metal splatter. Effective ventilation and fire suppression systems are essential in work environments to mitigate inhalation of fumes and reduce fire risks associated with both plasma arc and flame cutting operations.
Cost Comparison: Initial and Operational
Plasma arc cutters generally have a higher initial cost compared to flame cutters, but their operational expenses are often lower due to faster cutting speeds and reduced gas consumption. Flame cutters require continuous fuel gas supply, increasing long-term costs, especially for thicker materials. Your choice depends on balancing upfront investment with efficiency and ongoing fuel expenditures.
Typical Applications and Industries
Plasma arc cutters excel in industries requiring precise, high-speed cutting of electrically conductive metals, such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and shipbuilding. Flame cutters remain widely used in heavy steel fabrication, construction, and maintenance work for cutting thick, carbon steel plates. Each technology suits specific applications: plasma arc cutters for clean, accurate cuts on thin to medium metals, while flame cutters handle robust, thicker steel materials efficiently.
Choosing the Right Cutter for Your Needs
Plasma arc cutters offer precise, high-speed cutting with minimal heat distortion, making them ideal for intricate metalwork and various conductive materials. Flame cutters excel in cutting thicker steel plates and are more cost-effective for heavy-duty, slower jobs requiring deeper penetration. Choosing the right cutter depends on your material thickness, desired cut quality, and budget constraints.
Plasma arc cutter vs flame cutter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com