A laser engraver precisely etches designs onto surfaces without cutting through the material, making it ideal for detailed artwork and personalization. Your choice depends on whether you need to create intricate patterns or completely cut shapes from materials.
Table of Comparison
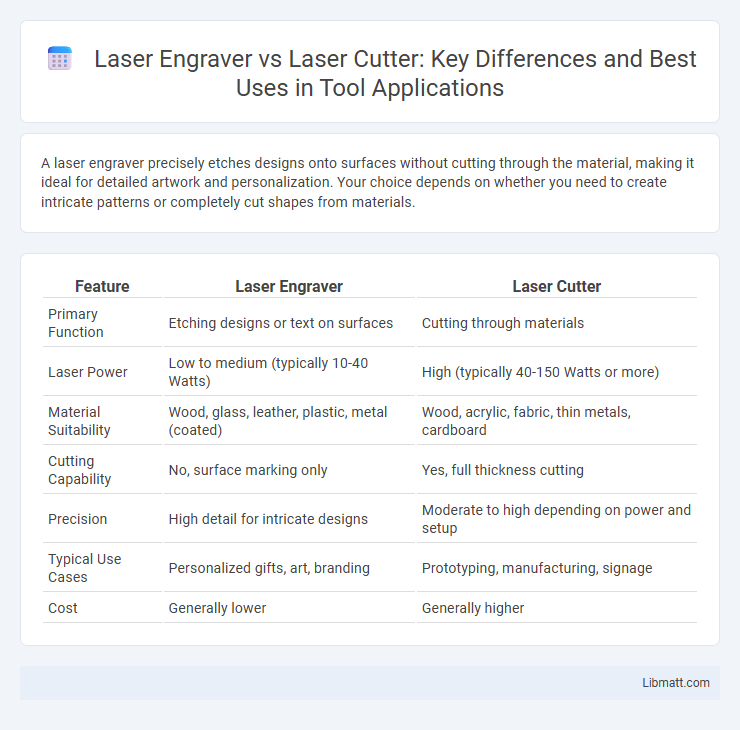
| Feature | Laser Engraver | Laser Cutter |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Etching designs or text on surfaces | Cutting through materials |
| Laser Power | Low to medium (typically 10-40 Watts) | High (typically 40-150 Watts or more) |
| Material Suitability | Wood, glass, leather, plastic, metal (coated) | Wood, acrylic, fabric, thin metals, cardboard |
| Cutting Capability | No, surface marking only | Yes, full thickness cutting |
| Precision | High detail for intricate designs | Moderate to high depending on power and setup |
| Typical Use Cases | Personalized gifts, art, branding | Prototyping, manufacturing, signage |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Introduction to Laser Engraving and Cutting
Laser engraving uses focused laser beams to etch detailed designs onto surfaces without cutting through the material, ideal for personalization and intricate patterns on wood, metal, and acrylic. Laser cutting, conversely, employs higher power lasers to precisely slice through materials such as fabric, leather, and thin metals for manufacturing and prototyping. Both technologies leverage computer-controlled precision to create high-quality, customizable products but differ fundamentally in their interaction depth and application scope.
What is a Laser Engraver?
A laser engraver uses focused laser beams to etch detailed designs, patterns, or text onto the surface of materials like wood, acrylic, leather, and metal without cutting through them. It operates by vaporizing or oxidizing the surface layer, creating precise, permanent marks with high resolution and fine detail. Laser engravers are ideal for customization, branding, and decorative applications where surface marking is required without material separation.
What is a Laser Cutter?
A laser cutter is a precision machine that uses a focused laser beam to slice through materials such as wood, acrylic, metal, and fabric by vaporizing or melting the target area. Laser cutters excel at producing intricate cuts with high accuracy, making them ideal for industrial manufacturing, prototyping, and custom fabrication. Unlike laser engravers, which primarily mark the surface of materials, laser cutters fully penetrate and separate the material along the cut path.
Core Differences Between Laser Engravers and Laser Cutters
Laser engravers primarily remove a thin layer on the material's surface to create detailed designs or markings without cutting through, while laser cutters use higher power to slice entirely through materials like wood, acrylic, or metal. Engraving focuses on precision and intricate detailing on surfaces, whereas cutting emphasizes complete separation along specified paths, which is critical for creating physical parts or shapes. Your choice depends on whether you need detailed surface decoration or full material separation, as each tool excels in these distinct tasks.
Materials Supported by Each Machine
Laser engravers are ideal for detailed etching on materials such as wood, acrylic, glass, leather, and certain metals, enabling precise surface marking without cutting through the substrate. Laser cutters excel at slicing through thicker materials like plywood, MDF, acrylic sheets, cardboard, and fabrics, providing clean edges and intricate cut patterns. Both machines support a range of materials but differ in processing depth and application scope based on laser power and focus type.
Precision and Detail: Engraving vs Cutting
Laser engravers offer superior precision and intricate detail by removing surface material without cutting through, ideal for creating fine patterns and textures on various materials. Laser cutters deliver precise, clean cuts through materials, optimized for contouring and separating shapes with consistent accuracy. The choice hinges on application needs: engraving excels in detailed surface designs, while cutting prioritizes material separation and edge quality.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Laser engravers typically operate at slower speeds than laser cutters due to the precision required for detailed engraving, but they offer higher accuracy for intricate designs. Laser cutters excel in speed and efficiency when cutting through materials like wood, acrylic, or metal sheets, making them ideal for high-volume production. Your choice should depend on whether your project demands detailed surface etching (laser engraver) or fast, clean cuts (laser cutter).
Typical Applications for Engravers and Cutters
Laser engravers excel in creating detailed designs on materials like wood, glass, and metal, often used for personalized gifts, intricate artwork, and branding on promotional products. Laser cutters primarily serve in fabrication tasks, efficiently slicing through materials such as acrylic, leather, and fabric to produce parts for signage, packaging, and product prototypes. Both technologies find critical roles in industries like manufacturing, arts and crafts, and custom manufacturing, with engravers focusing on surface decoration and cutters on precise material separation.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Laser engravers typically incur lower initial costs than laser cutters due to less powerful lasers and simpler mechanisms, making them more accessible for hobbyists and small businesses. Maintenance expenses vary, with laser cutters often requiring more frequent servicing and part replacements because of their higher power output and more complex systems. Both devices need regular cleaning of lenses and mirrors, but the intensity and frequency of maintenance depend largely on usage intensity and material types processed.
How to Choose: Engraver or Cutter for Your Needs
Choosing between a laser engraver and a laser cutter depends on the precision and depth required for your projects, as engravers excel in detailed surface etching while cutters efficiently slice through materials. Consider the material type, thickness, and project complexity; engravers work best on wood, glass, and leather for fine designs, whereas cutters handle thicker materials like acrylic, fabric, and wood sheets with clean edges. Your decision should focus on whether your primary goal is marking intricate patterns or producing fully separated components.
Laser engraver vs laser cutter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com