A plasma cutter delivers precise, high-speed cuts by using an electric arc to ionize gas, making it ideal for cutting various metals with minimal heat distortion. Your choice depends on the material thickness and portability needs, as oxy acetylene torches offer versatile heating and cutting capabilities but produce slower, less precise cuts with more thermal impact.
Table of Comparison
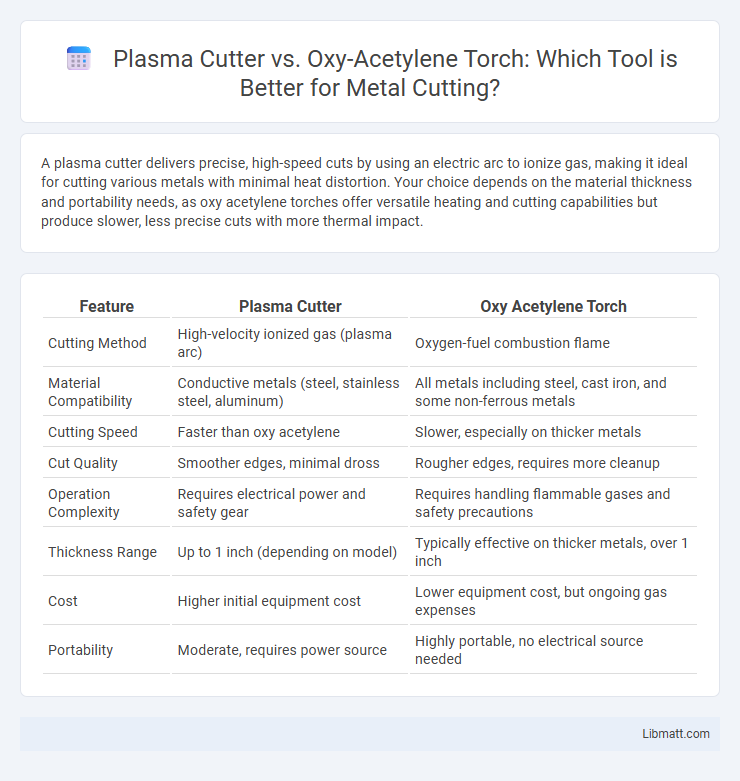
| Feature | Plasma Cutter | Oxy Acetylene Torch |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | High-velocity ionized gas (plasma arc) | Oxygen-fuel combustion flame |
| Material Compatibility | Conductive metals (steel, stainless steel, aluminum) | All metals including steel, cast iron, and some non-ferrous metals |
| Cutting Speed | Faster than oxy acetylene | Slower, especially on thicker metals |
| Cut Quality | Smoother edges, minimal dross | Rougher edges, requires more cleanup |
| Operation Complexity | Requires electrical power and safety gear | Requires handling flammable gases and safety precautions |
| Thickness Range | Up to 1 inch (depending on model) | Typically effective on thicker metals, over 1 inch |
| Cost | Higher initial equipment cost | Lower equipment cost, but ongoing gas expenses |
| Portability | Moderate, requires power source | Highly portable, no electrical source needed |
Introduction to Cutting Technologies
Plasma cutters use electrically ionized gas to generate a high-temperature plasma jet capable of cutting through various metals with precision and speed. Oxy acetylene torches combine oxygen and acetylene gases to produce a flame that melts metal, suitable for cutting and welding thicker materials. Your choice between these technologies depends on factors like material thickness, cutting speed, precision requirements, and cost efficiency.
How Plasma Cutters Work
Plasma cutters operate by generating an electrical arc through a high-velocity jet of ionized gas, which melts and expels metal from the cut area with precision. Unlike oxy-acetylene torches that rely on combustion to heat and burn metal, plasma cutters use plasma, a superheated, electrically conductive gas, enabling faster and cleaner cuts on various conductive metals. This technology provides enhanced control and accuracy, making plasma cutters ideal for detailed fabrication and industrial applications.
How Oxy Acetylene Torches Operate
Oxy acetylene torches operate by mixing oxygen and acetylene gases in precise proportions to create a high-temperature flame exceeding 3,200degC, which melts metal for cutting, welding, or brazing. This process relies on a chemical reaction between the gases that produces intense heat, enabling you to cut through thick metal with controlled flame adjustments. Unlike plasma cutters, oxy acetylene torches use combustion rather than electricity, making them versatile for various metalworking applications but less suitable for precise or high-speed cuts.
Key Differences Between Plasma Cutters and Oxy Acetylene Torches
Plasma cutters use an electrically ionized gas to cut through conductive metals with high precision and speed, ideal for clean, intricate designs on steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. Oxy acetylene torches rely on a chemical combustion process combining oxygen and acetylene gas to generate a flame capable of melting and cutting metal, suitable for thicker materials and welding applications. Plasma cutters offer superior cut quality and ease of use, while oxy acetylene torches provide versatility in repair, heating, and cutting tasks on a wider range of metal thicknesses.
Cutting Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Plasma cutters deliver significantly faster cutting speeds, often up to 10 times quicker than oxy-acetylene torches, especially on thinner metals like steel and aluminum. The efficiency of plasma cutters is enhanced by their ability to produce clean, precise cuts with minimal heat distortion, reducing the need for secondary finishing. In contrast, oxy-acetylene torches are slower due to their reliance on chemical combustion, making them less efficient for repetitive or high-volume metal cutting tasks.
Material Compatibility and Thickness Capabilities
Plasma cutters excel at cutting a wide range of electrically conductive metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and copper, with precise cuts on materials up to 1 inch thick or more depending on the cutter's power. Oxy-acetylene torches are versatile for cutting and welding ferrous metals, particularly steel, with the ability to cut through thicker materials, often exceeding 6 inches, but with less precision and slower speeds. Material compatibility for plasma cutters is limited to conductive metals, while oxy-acetylene torches can work on any metal that oxidizes, giving them an advantage in heavy-duty applications.
Precision and Cut Quality Analysis
Plasma cutters provide superior precision and cut quality compared to oxy acetylene torches, delivering cleaner, more accurate cuts with minimal heat-affected zones. The high-temperature ionized gas in plasma cutters enables precise cuts on various metal thicknesses, while oxy acetylene torches often leave wider kerfs and rougher edges due to flame-based cutting. Choosing a plasma cutter enhances your project's accuracy and finish, especially for detailed metalwork requiring consistent, high-quality results.
Safety Considerations for Each Method
Plasma cutters require proper protective gear such as gloves, face shields, and flame-resistant clothing to guard against intense UV radiation, sparks, and molten metal splatter. Oxy acetylene torches pose risks including fire hazards, gas leaks, and explosions, necessitating strict adherence to ventilation regulations and regular equipment inspections. Understanding your workspace environment and following recommended safety protocols ensures safe operation regardless of the cutting method you choose.
Cost Factors: Equipment and Operation
Plasma cutters generally have higher upfront equipment costs, ranging from $300 to $3,000 depending on power and features, while oxy acetylene torches are cheaper initially, often costing between $150 and $500. Operational expenses for plasma cutters include electricity and consumable electrodes, which can be more economical in high-precision and high-volume cutting scenarios compared to the continuous fuel consumption of oxy acetylene torches, which use oxygen and acetylene gases. Over time, plasma cutters tend to offer greater efficiency and lower operating costs for metal cutting tasks, especially for thicker materials, whereas oxy acetylene torches may be more cost-effective for occasional, lower-precision cutting jobs.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Application
A plasma cutter delivers precise, clean cuts on various metals with high speed and minimal heat distortion, making it ideal for detailed fabrication and industrial projects. An oxy acetylene torch excels in cutting thicker metals and is versatile for welding, brazing, and heating tasks, suitable for heavy-duty construction and repair work. Evaluating the metal thickness, cut quality requirements, and portability will help you choose the right tool for your application efficiently.
Plasma cutter vs oxy acetylene torch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com