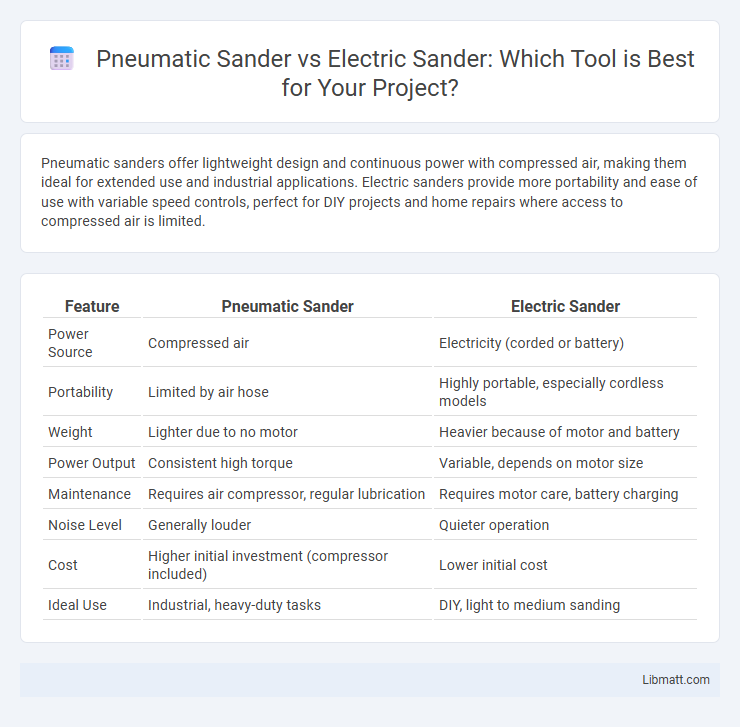
Pneumatic sanders offer lightweight design and continuous power with compressed air, making them ideal for extended use and industrial applications. Electric sanders provide more portability and ease of use with variable speed controls, perfect for DIY projects and home repairs where access to compressed air is limited.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pneumatic Sander | Electric Sander |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Compressed air | Electricity (corded or battery) |
| Portability | Limited by air hose | Highly portable, especially cordless models |
| Weight | Lighter due to no motor | Heavier because of motor and battery |
| Power Output | Consistent high torque | Variable, depends on motor size |
| Maintenance | Requires air compressor, regular lubrication | Requires motor care, battery charging |
| Noise Level | Generally louder | Quieter operation |
| Cost | Higher initial investment (compressor included) | Lower initial cost |
| Ideal Use | Industrial, heavy-duty tasks | DIY, light to medium sanding |
Introduction to Pneumatic and Electric Sanders
Pneumatic sanders operate using compressed air, delivering high power-to-weight ratios ideal for industrial and automotive applications where continuous heavy-duty use is required. Electric sanders rely on an electric motor to drive the sanding motion, offering more portability and ease of use for hobbyists and small-scale projects. Both types provide distinct advantages in performance, power source, and suitability depending on the sanding task and environment.
How Pneumatic Sanders Work
Pneumatic sanders operate using compressed air to power a motor that drives the sanding pad or disc, delivering consistent and high-speed abrasive action. This air-powered mechanism allows for efficient dust removal and less heat generation compared to electric sanders, enhancing performance during extended use. Your choice of pneumatic sander ensures a lightweight, durable tool ideal for industrial and automotive applications requiring precision and reliability.
How Electric Sanders Work
Electric sanders operate by converting electrical energy into mechanical motion through an electric motor that powers the sanding pad in various patterns such as orbital, belt, or random orbit. These tools provide consistent speed and torque, ensuring smooth sanding performance on wood, metal, and plastic surfaces. Your choice of electric sander can improve efficiency and precision in finishing tasks by adapting to specific sanding needs.
Key Differences Between Pneumatic and Electric Sanders
Pneumatic sanders operate using compressed air, offering lightweight design and superior durability, making them ideal for industrial use and continuous heavy-duty applications. Electric sanders rely on electric motors, providing greater portability, ease of use, and suitability for smaller projects or home use. Key differences include power source, noise level--pneumatic models are typically quieter--and maintenance requirements, with pneumatic sanders needing an air compressor while electric versions require regular motor care.
Performance Comparison: Power and Speed
Pneumatic sanders deliver consistent power through compressed air, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring high-speed operation and continuous use without overheating. Electric sanders offer variable speed control and higher torque, providing versatility for detailed finishing tasks and extended runtime with less maintenance. The choice between the two depends on the need for portability, power consistency, and speed precision in specific sanding projects.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Maintenance
Pneumatic sanders typically have a lower initial purchase price but require an air compressor, increasing setup costs and ongoing maintenance expenses. Electric sanders often involve a higher upfront investment but benefit from lower maintenance requirements and no need for additional equipment, making them cost-effective long-term. Your choice should weigh the initial setup against ongoing maintenance to optimize budget efficiency.
Ergonomics and User Comfort
Pneumatic sanders offer lightweight designs and reduced vibration, enhancing ergonomics and minimizing user fatigue during extended use. Electric sanders provide consistent power with adjustable speed settings, allowing users to control intensity for improved comfort and precision. Both types feature ergonomic handles, but pneumatic models often excel in weight distribution, benefiting users in repetitive sanding tasks.
Application Suitability: Ideal Use Cases
Pneumatic sanders are ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications where continuous use and consistent power are required, such as automotive bodywork and metal fabrication. Electric sanders are better suited for lighter tasks and home use, offering portability and ease of use for woodworking, furniture refinishing, and small DIY projects. Your choice depends on the specific demands of your project, with pneumatic models excelling in durability and electric models providing convenience.
Durability and Longevity
Pneumatic sanders typically offer superior durability and longevity due to fewer moving parts and a reliance on compressed air, reducing the risk of motor burnouts common in electric sanders. Your choice of a pneumatic sander can lead to extended tool life, especially in heavy-duty or continuous-use environments. Electric sanders may require more frequent maintenance and replacement parts, impacting overall durability.
Which Sander is Right for You?
Choosing between a pneumatic sander and an electric sander depends on your specific project needs and workspace setup. Pneumatic sanders offer higher torque and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial tasks and continuous operation without overheating. Electric sanders provide portability and ease of use, perfect for DIY enthusiasts and small to medium projects where convenience and lower maintenance are priorities.
Pneumatic sander vs electric sander Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com