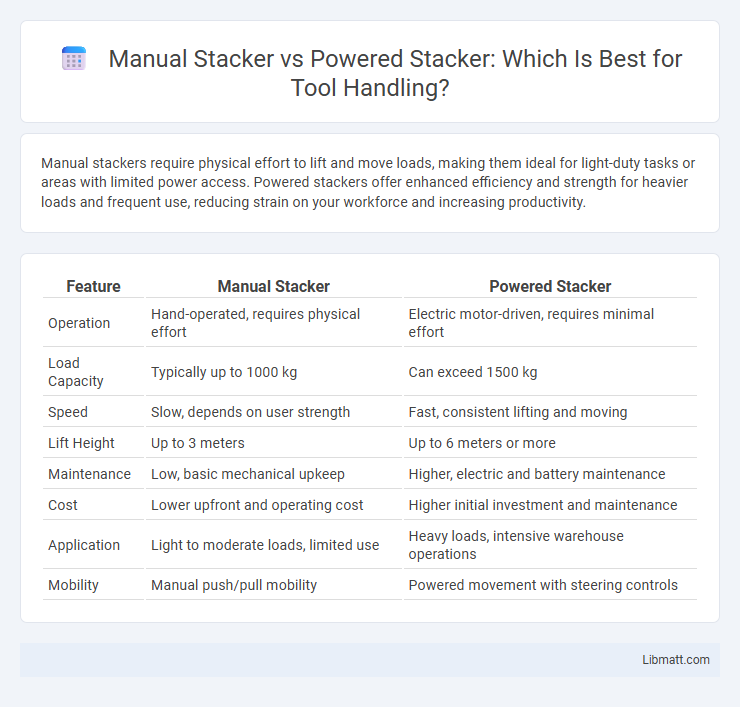
Manual stackers require physical effort to lift and move loads, making them ideal for light-duty tasks or areas with limited power access. Powered stackers offer enhanced efficiency and strength for heavier loads and frequent use, reducing strain on your workforce and increasing productivity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Manual Stacker | Powered Stacker |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Hand-operated, requires physical effort | Electric motor-driven, requires minimal effort |
| Load Capacity | Typically up to 1000 kg | Can exceed 1500 kg |
| Speed | Slow, depends on user strength | Fast, consistent lifting and moving |
| Lift Height | Up to 3 meters | Up to 6 meters or more |
| Maintenance | Low, basic mechanical upkeep | Higher, electric and battery maintenance |
| Cost | Lower upfront and operating cost | Higher initial investment and maintenance |
| Application | Light to moderate loads, limited use | Heavy loads, intensive warehouse operations |
| Mobility | Manual push/pull mobility | Powered movement with steering controls |
Introduction to Manual and Powered Stackers
Manual stackers rely on human effort to lift and move loads, making them ideal for lighter tasks and environments where power sources are unavailable. Powered stackers use electric motors to handle heavier weights and increase operational efficiency, often found in busy warehouses requiring frequent stacking and unstacking. Your choice depends on factors like load capacity, frequency of use, and workspace conditions.
Key Differences Between Manual and Powered Stackers
Manual stackers rely on human effort for lifting and moving loads, making them ideal for lighter weight applications and low-frequency use. Powered stackers utilize electric motors to lift and transport heavier loads more efficiently, increasing productivity in warehouses with high-volume handling requirements. The key differences include operational effort, load capacity, speed, and suitability for varying work environments.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Each Type
Manual stackers are ideal for lighter loads and short-distance stacking or retrieval in small warehouses or retail shops where maneuverability and cost-efficiency are priorities. Powered stackers excel in busy distribution centers or large warehouses, handling heavier loads and frequent lifting with greater speed and reduced operator fatigue. You should select a manual stacker for infrequent, light tasks and a powered stacker for high-volume, heavy-duty material handling applications.
Cost Comparison: Manual vs Powered Stackers
Manual stackers generally have a lower initial purchase cost compared to powered stackers, making them an economical choice for small-scale or occasional lifting tasks. Powered stackers, while more expensive upfront, offer increased efficiency and reduced operator fatigue, potentially lowering labor costs and increasing productivity over time. Your decision between manual and powered stackers should consider not only the purchase price but also long-term operational expenses and maintenance requirements.
Efficiency and Productivity Considerations
Manual stackers offer lower upfront costs and greater control for precise handling but require more physical effort, limiting efficiency during high-volume tasks. Powered stackers increase productivity by automating lifting and transport, allowing faster load movement and reducing operator fatigue. Your choice between manual and powered stackers should reflect the scale of operations and prioritization of efficiency in material handling workflows.
Safety Features and Operator Requirements
Manual stackers prioritize simplicity and low risk, featuring basic safety mechanisms like emergency brakes and overload protection, making them suitable for operators with minimal training. Powered stackers incorporate advanced safety features such as automatic speed control, anti-slip platforms, and operator presence sensors, which require specialized training to ensure proper handling and reduce accident risks. Your choice depends on balancing operational complexity with safety standards tailored to the specific warehouse environment.
Maintenance and Longevity
Manual stackers require minimal maintenance due to their simple mechanical design, resulting in lower overall upkeep costs and fewer breakdowns. Powered stackers, while offering increased efficiency and lifting capacity, demand regular maintenance on electrical components and batteries to ensure longevity and prevent costly repairs. Choosing the right stacker for Your operation involves balancing maintenance needs against usage intensity and expected equipment lifespan.
Space and Mobility Constraints
Manual stackers excel in tight spaces due to their compact design and ease of maneuverability, making them ideal for narrow aisles and limited floor areas. Powered stackers offer enhanced lifting capabilities but require more space to operate efficiently, often limiting their use in confined environments. Choosing between the two depends on balancing operational space constraints with load handling requirements.
Environmental Impact and Energy Consumption
Manual stackers produce zero emissions and rely solely on human power, making them environmentally friendly and ideal for reducing energy consumption in warehouse operations. Powered stackers consume electricity or fuel, resulting in higher energy use and potential carbon emissions, but they offer increased efficiency and load capacity. Your choice impacts both sustainability goals and operational energy demands, with manual stackers favoring minimal environmental impact and powered stackers prioritizing productivity.
Choosing the Right Stacker for Your Needs
Manual stackers offer cost-effective, low-maintenance solutions ideal for light to medium lifting tasks and environments with limited power access, while powered stackers provide enhanced lifting capacity, speed, and operator ease for frequent, heavy-duty operations. Evaluating factors such as load weight, usage frequency, workspace constraints, and budget helps determine the optimal choice for efficient material handling. Industrial applications demanding higher productivity typically benefit from powered stackers, whereas small-scale or occasional lifting tasks suit manual stackers.
Manual stacker vs powered stacker Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com