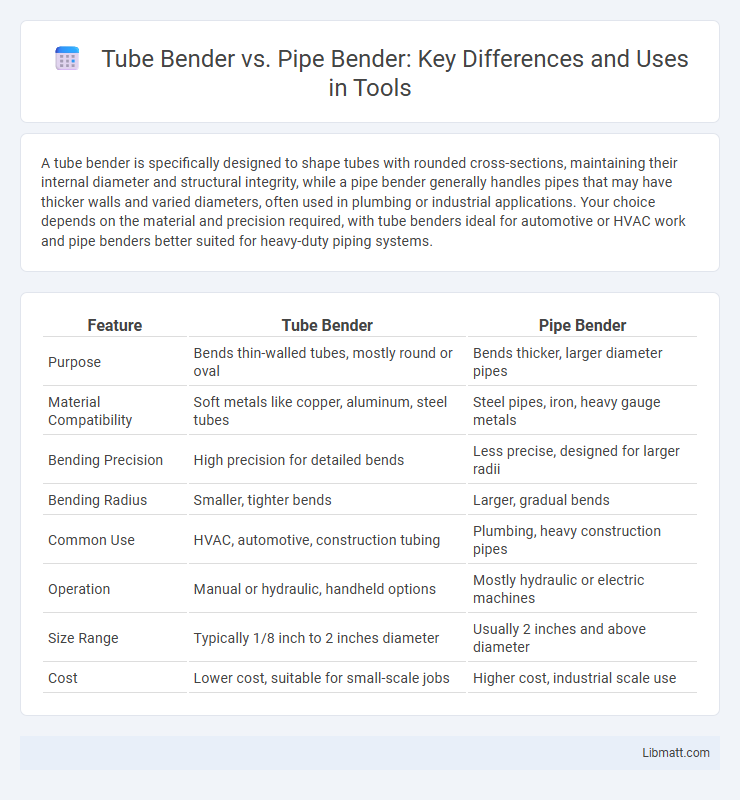
A tube bender is specifically designed to shape tubes with rounded cross-sections, maintaining their internal diameter and structural integrity, while a pipe bender generally handles pipes that may have thicker walls and varied diameters, often used in plumbing or industrial applications. Your choice depends on the material and precision required, with tube benders ideal for automotive or HVAC work and pipe benders better suited for heavy-duty piping systems.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tube Bender | Pipe Bender |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Bends thin-walled tubes, mostly round or oval | Bends thicker, larger diameter pipes |
| Material Compatibility | Soft metals like copper, aluminum, steel tubes | Steel pipes, iron, heavy gauge metals |
| Bending Precision | High precision for detailed bends | Less precise, designed for larger radii |
| Bending Radius | Smaller, tighter bends | Larger, gradual bends |
| Common Use | HVAC, automotive, construction tubing | Plumbing, heavy construction pipes |
| Operation | Manual or hydraulic, handheld options | Mostly hydraulic or electric machines |
| Size Range | Typically 1/8 inch to 2 inches diameter | Usually 2 inches and above diameter |
| Cost | Lower cost, suitable for small-scale jobs | Higher cost, industrial scale use |
Introduction to Tube Benders and Pipe Benders
Tube benders and pipe benders are essential tools used to create precise bends in metal tubing and piping, respectively, with tube benders typically designed for thin-walled tubes and pipe benders for thicker-walled pipes. Tube benders often feature mandrels and flexible dies to prevent deformation of delicate tube walls, while pipe benders use more robust mechanisms to handle larger diameters and heavier materials. Understanding the specific applications and structural differences helps in selecting the right bending equipment for industries such as automotive, plumbing, and construction.
Key Differences Between Tube Benders and Pipe Benders
Tube benders are designed to shape thin-walled tubes with precise control over the bend radius, minimizing deformation and maintaining the tube's structural integrity. Pipe benders handle thicker-walled pipes, often requiring greater force to bend without compromising the pipe's diameter or causing internal collapse. These key differences highlight the suitability of tube benders for automotive and aerospace applications, while pipe benders are essential in plumbing and industrial piping systems.
Materials Handled: Tubes vs. Pipes
Tube benders specialize in shaping hollow, structural materials such as square, rectangular, and round tubes made from metals like steel, aluminum, and copper, offering precise control for thin-walled tubing. Pipe benders are designed to handle thicker, often cylindrical pipes used in plumbing, gas, and fluid transportation systems, accommodating materials such as steel, iron, and PVC with a focus on maintaining flow integrity. The distinction in materials handled influences the bending technique, with tube benders emphasizing minimal distortion on delicate tubing surfaces and pipe benders prioritizing the structural integrity of larger, high-pressure pipes.
Types of Bending Techniques
Tube benders and pipe benders utilize various bending techniques such as rotary draw bending, compression bending, mandrel bending, and roll bending to shape materials accurately. Rotary draw bending offers precise control for tight-radius bends in both tubes and pipes, while mandrel bending prevents wrinkling and collapse in thin-walled materials. Roll bending is more suitable for large-radius curves and is commonly used for both tubes and pipes across structural and automotive applications.
Applications: Where to Use Each Bender
Tube benders are ideal for forming complex shapes in round, square, or rectangular tubing commonly used in automotive frames, furniture, and HVAC systems, offering precise bends without compromising the integrity of the tube. Pipe benders excel in plumbing, gas lines, and structural projects where thicker, heavier-walled pipes require controlled, consistent bending to maintain flow and structural strength. Selecting the right bender depends on the material thickness, shape, and the specific requirements of industries like construction, manufacturing, or custom fabrication.
Pros and Cons of Tube Benders
Tube benders excel at creating precise, smooth bends in metal tubes without kinking or collapsing, making them ideal for automotive, construction, and HVAC applications. Their main advantages include maintaining the tube's internal diameter and structural integrity, but they can be limited by the tube material's thickness and the bender's size capacity. However, tube benders typically require specialized dies and can be more expensive and less versatile than pipe benders for larger diameter applications.
Pros and Cons of Pipe Benders
Pipe benders offer precise control and durability for shaping thicker-walled pipes, making them ideal for plumbing and industrial applications requiring strong, leak-proof bends. Their main advantage lies in maintaining the pipe's structural integrity without kinking, but they tend to be heavier and less portable compared to tube benders. However, pipe benders are less versatile with square or oval tubing, limiting their use primarily to round, hollow pipes.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Tube and Pipe Benders
When choosing between tube benders and pipe benders, consider the material type and wall thickness, as tube benders accommodate thin-walled and smaller diameter tubes while pipe benders suit thicker, larger-diameter pipes. Your project's required bend radius and angle precision are essential factors, with tube benders offering tighter radii and pipe benders providing stronger, gradual bends. Evaluate compatibility with the specific metal type--such as steel, copper, or aluminum--and the desired bending method, including manual, hydraulic, or electric, to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Maintenance and Durability Comparison
Tube benders typically require more frequent maintenance due to their precision components and complex mechanisms, which ensures consistent bending accuracy over time. Pipe benders, designed for heavier, more robust materials, often feature simpler construction that enhances overall durability and reduces maintenance needs. The choice between the two tools depends on the balance between precision requirements and long-term operational resilience in various industrial applications.
Which Bender is Best for Your Project?
Tube benders are ideal for projects requiring precision and smooth bends in hollow, thin-walled tubes commonly used in automotive and furniture applications, while pipe benders excel in shaping thicker, heavy-duty pipes often found in plumbing and construction. Choosing the best bender depends on the material thickness, bend radius, and project complexity, with tube benders offering cleaner, wrinkle-free bends and pipe benders providing strength for structural uses. Evaluating project specifications ensures selecting the right tool for optimal performance and durability.
Tube bender vs pipe bender Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com