Manual valves require physical operation to control fluid flow, making them suitable for simple, low-frequency adjustments, while automated valves use actuators for remote or automated control, offering precision and efficiency for complex or high-demand systems. Your choice depends on the application's need for control accuracy, speed, and integration with automated systems.
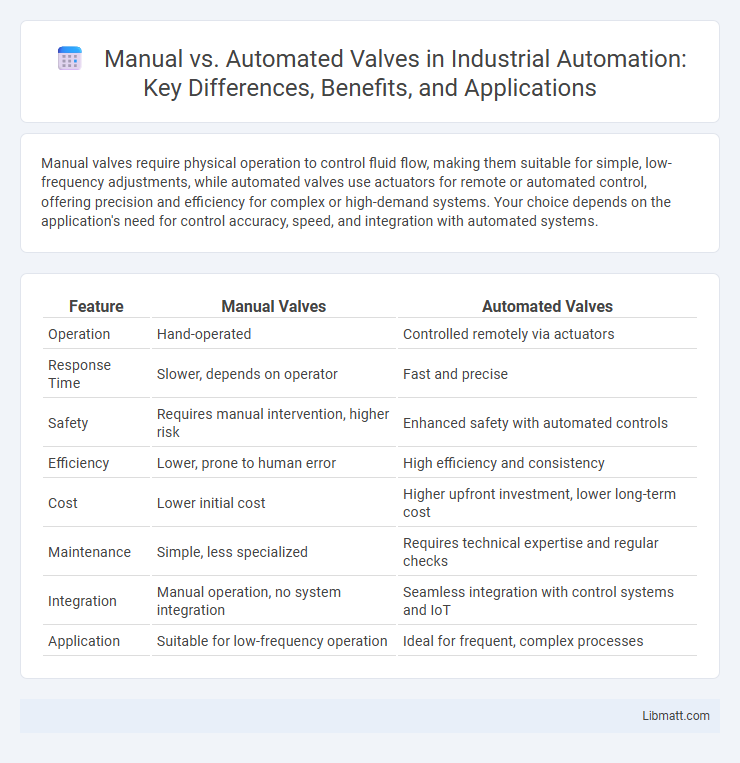
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Manual Valves | Automated Valves |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Hand-operated | Controlled remotely via actuators |
| Response Time | Slower, depends on operator | Fast and precise |
| Safety | Requires manual intervention, higher risk | Enhanced safety with automated controls |
| Efficiency | Lower, prone to human error | High efficiency and consistency |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment, lower long-term cost |
| Maintenance | Simple, less specialized | Requires technical expertise and regular checks |
| Integration | Manual operation, no system integration | Seamless integration with control systems and IoT |
| Application | Suitable for low-frequency operation | Ideal for frequent, complex processes |
Introduction to Manual and Automated Valves
Manual valves are operated by hand, providing direct control over fluid flow in various systems, making them ideal for simple operations or low-frequency adjustments. Automated valves use actuators powered by electricity, pneumatic, or hydraulic systems to remotely control flow with precision, enhancing efficiency and reducing human intervention. Your choice between manual and automated valves depends on factors like application complexity, operational frequency, and control requirements.
Key Differences Between Manual and Automated Valves
Manual valves require human intervention to operate, relying on physical effort to open or close the flow, while automated valves use actuators powered by electric, hydraulic, or pneumatic sources for remote and precise control. Automated valves offer faster response times, higher accuracy, and integration with control systems, which is essential in complex or hazardous environments. Manual valves provide simplicity, lower cost, and reliability when automation is unnecessary or impractical.
Operational Mechanisms Explained
Manual valves operate through direct physical interaction, typically using handwheels, levers, or knobs to control fluid flow by opening or closing the valve. Automated valves rely on actuators powered by electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic systems to remotely regulate flow, allowing for precise and rapid adjustments without human intervention. The choice between manual and automated valves depends on factors such as system complexity, required response time, and the need for remote operation or automation integration.
Application Areas for Each Valve Type
Manual valves are commonly used in low-pressure systems, residential plumbing, and applications where precise control or infrequent operation is required, such as irrigation systems and small industrial plants. Automated valves find widespread application in complex industrial processes, including oil and gas pipelines, chemical manufacturing, and HVAC systems, where remote operation, high reliability, and rapid response are critical. Selection between manual and automated valves depends heavily on system complexity, operating conditions, and the need for real-time control or automation integration.
Advantages of Manual Valves
Manual valves offer precise control, making them ideal for applications requiring fine adjustments in fluid flow. They are cost-effective, easy to install, and require minimal maintenance compared to automated valves, reducing operational expenses. Your choice of manual valves ensures reliable operation in environments where automation may be impractical or unnecessary.
Benefits of Automated Valves
Automated valves offer precise control and faster response times, significantly improving process efficiency and safety in industrial applications. Your operations benefit from reduced manual intervention, minimizing human error and lowering maintenance costs through real-time monitoring and remote operation capabilities. This enhances overall system reliability and ensures consistent performance in complex fluid control systems.
Limitations and Drawbacks
Manual valves require constant human intervention, leading to slower response times and potential for operational errors. Automated valves rely on complex electronic components that can fail due to power outages or software malfunctions, causing unexpected downtime. Both types present challenges in maintenance: manual valves need regular physical checks, while automated valves demand specialized technical expertise for troubleshooting and repairs.
Cost Comparison: Manual vs Automated Valves
Manual valves typically have a lower initial cost compared to automated valves due to simpler design and fewer components. Automated valves, while more expensive upfront, can reduce long-term operational costs through increased efficiency, precision, and reduced labor requirements. Your choice should consider both the immediate budget constraints and potential savings from automation over the valve's lifecycle.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
Manual valves require regular inspection and lubrication to prevent wear and ensure smooth operation, while automated valves depend heavily on sensors and actuators that need periodic calibration and software updates to maintain reliability. Automated valves often offer enhanced reliability through precise control and remote monitoring but can be more complex and costly to maintain compared to the simpler mechanical parts of manual valves. Your choice should consider the maintenance resources available and the criticality of process control accuracy to optimize system reliability.
Choosing the Right Valve for Your Application
Choosing the right valve for your application requires assessing factors such as flow control precision, operational frequency, and maintenance capabilities. Manual valves offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness for low-frequency adjustments, while automated valves provide enhanced accuracy and remote control suited for complex or high-demand systems. Evaluating system requirements and long-term operational goals ensures optimal valve selection for performance and reliability.
Manual vs Automated Valves Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com