MQTT excels in lightweight, low-bandwidth messaging suited for IoT devices, while OPC UA offers a robust, secure, and platform-independent architecture with complex data modeling tailored for industrial automation. Choosing between MQTT and OPC UA depends on Your priority for simplicity and scalability versus comprehensive interoperability and security in your communication protocols.
Table of Comparison
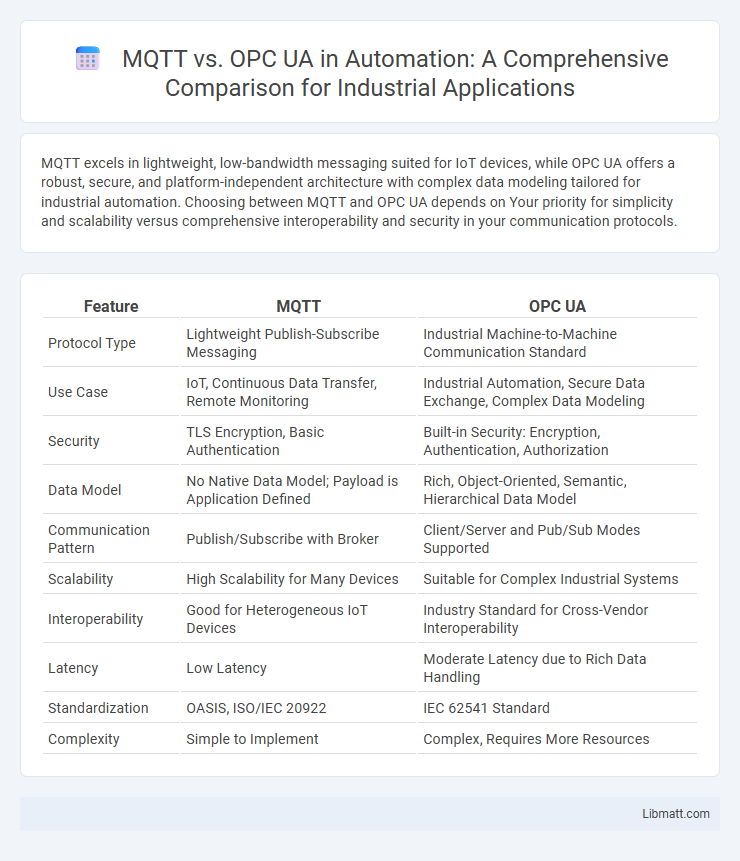
| Feature | MQTT | OPC UA |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Lightweight Publish-Subscribe Messaging | Industrial Machine-to-Machine Communication Standard |
| Use Case | IoT, Continuous Data Transfer, Remote Monitoring | Industrial Automation, Secure Data Exchange, Complex Data Modeling |
| Security | TLS Encryption, Basic Authentication | Built-in Security: Encryption, Authentication, Authorization |
| Data Model | No Native Data Model; Payload is Application Defined | Rich, Object-Oriented, Semantic, Hierarchical Data Model |
| Communication Pattern | Publish/Subscribe with Broker | Client/Server and Pub/Sub Modes Supported |
| Scalability | High Scalability for Many Devices | Suitable for Complex Industrial Systems |
| Interoperability | Good for Heterogeneous IoT Devices | Industry Standard for Cross-Vendor Interoperability |
| Latency | Low Latency | Moderate Latency due to Rich Data Handling |
| Standardization | OASIS, ISO/IEC 20922 | IEC 62541 Standard |
| Complexity | Simple to Implement | Complex, Requires More Resources |
Introduction to MQTT and OPC UA
MQTT is a lightweight, publish-subscribe messaging protocol designed for efficient communication in resource-constrained IoT environments, emphasizing low bandwidth and minimal power usage. OPC UA is a platform-independent, service-oriented architecture that provides secure and reliable data exchange in industrial automation with rich semantic modeling capabilities. Both protocols serve distinct roles in industrial IoT, with MQTT optimizing real-time telemetry and OPC UA enabling complex interoperability and standardized information models.
Core Principles and Protocol Architecture
MQTT operates on a lightweight publish-subscribe model designed for efficient, low-bandwidth communication ideal for IoT devices, using a broker-based architecture to manage message distribution. OPC UA employs a more complex, service-oriented architecture enabling secure, reliable, and platform-independent data exchange with built-in support for rich data modeling and semantics. Your choice between these protocols depends on the need for simplicity and scalability in MQTT versus the extensive interoperability and information modeling capabilities of OPC UA.
Communication Models: Publish/Subscribe vs Client/Server
MQTT employs a publish/subscribe communication model where devices act as publishers or subscribers, enabling efficient, scalable, and decoupled message exchange through a central broker. OPC UA uses a client/server communication model, allowing clients to directly request data or services from the server, providing flexible interaction and robust security features. The publish/subscribe model in MQTT excels in lightweight, event-driven IoT scenarios, while OPC UA's client/server architecture supports complex industrial automation with structured data access and interoperability.
Data Handling and Serialization
MQTT uses a lightweight publish-subscribe model with simple message payloads, primarily in JSON or binary formats, enabling efficient data handling for real-time IoT communication. OPC UA employs a complex data modeling approach with built-in serialization standards like binary encoding and XML, supporting rich data types and hierarchical structures for industrial automation. Your choice depends on whether you need MQTT's speed and simplicity or OPC UA's comprehensive data representation and interoperability.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
MQTT offers lightweight messaging optimized for high-throughput, low-latency environments, making it ideal for scalable IoT deployments with resource-constrained devices. OPC UA provides robust data modeling and built-in security suitable for complex industrial systems, but its heavier protocol stack may impact performance in large-scale, high-frequency messaging scenarios. For your applications requiring rapid data exchange across numerous endpoints, MQTT delivers superior scalability, while OPC UA ensures comprehensive interoperability and data integrity in demanding industrial contexts.
Security Features and Approaches
MQTT employs username/password authentication, TLS encryption, and access control lists to secure message transmission, though it relies heavily on external brokers for comprehensive security management. OPC UA integrates robust security features including built-in encryption, authentication, authorization, and data integrity measures, leveraging X.509 certificates and role-based access control for end-to-end secure communication. The protocol's ability to provide session encryption, message signing, and secure user authentication positions OPC UA as a more inherently secure solution for industrial automation compared to MQTT.
Use Cases in Industrial Automation
MQTT excels in lightweight telemetry and remote monitoring scenarios, making it ideal for IIoT devices with constrained bandwidth in industrial automation. OPC UA offers robust, secure, and complex data modeling suited for factory floor systems requiring interoperability and real-time control. Both protocols enable seamless data exchange, but OPC UA's extensive metadata and address space make it preferable for advanced process automation and asset management.
Integration and Interoperability
MQTT offers lightweight publish-subscribe communication ideal for resource-constrained IoT devices but lacks standardized data modeling, which can limit seamless integration across diverse industrial systems. OPC UA provides a comprehensive, platform-independent framework with robust data modeling, security features, and standardized information models, enabling superior interoperability among heterogeneous automation equipment and enterprise applications. Combining MQTT's efficient messaging with OPC UA's rich semantic context enhances integration flexibility in Industry 4.0 environments.
Implementation Complexity and Cost
MQTT offers a lightweight protocol with straightforward implementation suitable for low-cost IoT deployments, minimizing infrastructure expenses and development time. OPC UA, while more complex due to its extensive security features and rich data modeling capabilities, demands higher initial investment and specialized expertise. For Your project, choosing MQTT reduces cost and complexity, whereas OPC UA provides robust scalability and interoperability at increased implementation effort.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Application
Selecting the right protocol between MQTT and OPC UA depends on the specific requirements of your industrial or IoT application. MQTT excels in lightweight, low-bandwidth environments with simple publish-subscribe messaging, ideal for sensor data and remote monitoring. OPC UA offers robust security, complex data modeling, and interoperability for industrial automation systems requiring real-time control and detailed information exchange.
MQTT vs OPC UA Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com