Wired networks provide faster, more stable connections with enhanced security due to physical cables, ideal for environments requiring high bandwidth and minimal interference. Wireless networks offer greater flexibility and mobility, allowing your devices to connect without physical constraints, though they may be more susceptible to signal interference and security risks.
Table of Comparison
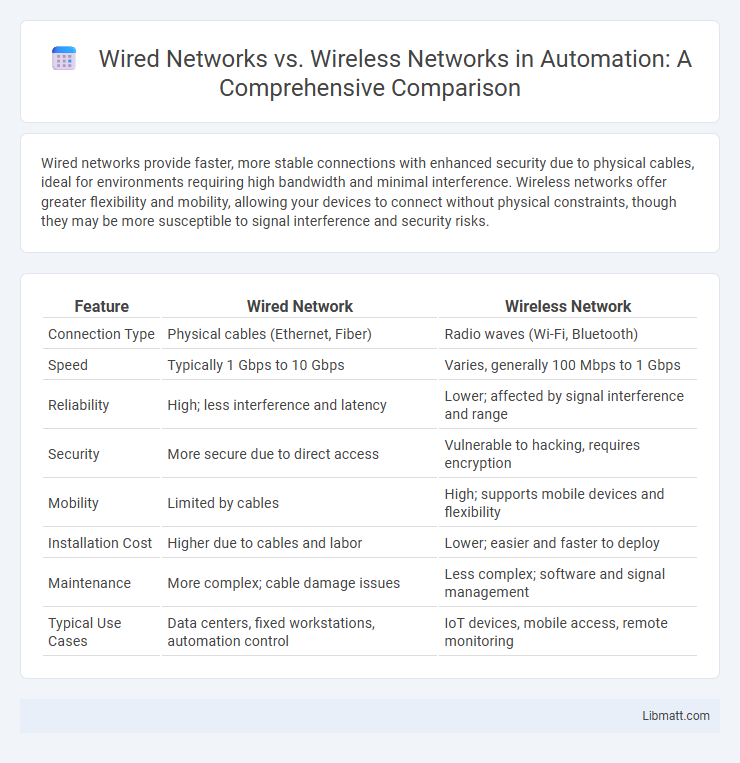
| Feature | Wired Network | Wireless Network |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Physical cables (Ethernet, Fiber) | Radio waves (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth) |
| Speed | Typically 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps | Varies, generally 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps |
| Reliability | High; less interference and latency | Lower; affected by signal interference and range |
| Security | More secure due to direct access | Vulnerable to hacking, requires encryption |
| Mobility | Limited by cables | High; supports mobile devices and flexibility |
| Installation Cost | Higher due to cables and labor | Lower; easier and faster to deploy |
| Maintenance | More complex; cable damage issues | Less complex; software and signal management |
| Typical Use Cases | Data centers, fixed workstations, automation control | IoT devices, mobile access, remote monitoring |
Introduction to Wired and Wireless Networks
Wired networks use physical cables such as Ethernet to connect devices, providing stable and high-speed data transmission ideal for environments requiring consistent performance. Wireless networks rely on radio waves or Wi-Fi signals to enable device connectivity without physical cables, offering greater flexibility and mobility for users. Understanding the strengths and limitations of your wired or wireless network helps optimize connectivity based on your specific needs.
Key Differences Between Wired and Wireless Networks
Wired networks use physical cables like Ethernet to connect devices, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and more reliable connections compared to wireless networks, which rely on radio waves for device communication. Wireless networks provide greater mobility and ease of installation but are more prone to interference, security vulnerabilities, and signal degradation over distance. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the network type best suited for your specific performance needs and environmental conditions.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Latency
Wired networks generally provide faster speeds and lower latency compared to wireless networks due to direct physical connections that reduce signal interference. Your online experience benefits from stable throughput and minimal delay, essential for activities like gaming and video conferencing. Wireless networks offer convenience but typically experience variable speeds and higher latency influenced by distance, obstacles, and network traffic.
Security Considerations in Wired vs Wireless Networks
Wired networks offer enhanced security by providing physical control over data transmission, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and external interference. Wireless networks are more vulnerable to security threats such as eavesdropping, signal interception, and unauthorized access due to their reliance on radio frequencies, requiring robust encryption protocols like WPA3. You should implement strong authentication and encryption measures to mitigate risks and protect sensitive information in both network types.
Installation and Setup Complexity
Wired networks require physical cabling, which involves higher installation complexity due to cable management, drilling, and infrastructure modifications. Wireless networks offer easier setup with minimal hardware, relying on access points and wireless adapters that reduce physical constraints. Organizations often choose wireless for rapid deployment, while wired networks demand more planning and expert installation for stable connections.
Cost Analysis: Wired vs Wireless Solutions
Wired network solutions typically involve higher initial costs due to expenses for cables, switches, and installation labor, but often provide lower ongoing maintenance costs and more stable connectivity. Wireless network setups generally have lower upfront expenses since they reduce the need for extensive cabling infrastructure, though they may incur higher long-term costs from regular equipment upgrades and potential signal interference mitigation. Companies must evaluate total cost of ownership (TCO) including installation, maintenance, scalability, and performance requirements when comparing wired versus wireless network investments.
Scalability and Flexibility
Wired networks offer limited scalability due to physical cable requirements and fixed infrastructure, making expansion costly and time-consuming. Wireless networks provide greater flexibility and scalability by enabling easy addition of new devices without extensive hardware changes or downtime. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize stable, high-speed connections or adaptable, rapidly deployable network solutions.
Reliability and Stability
Wired networks provide superior reliability and stability due to direct physical connections that minimize interference and signal loss, ensuring consistent data transmission speeds. Wireless networks, while offering greater flexibility and mobility, often face variable performance caused by environmental factors, signal interference, and network congestion. Enterprises requiring mission-critical applications typically prefer wired connections to maintain uninterrupted service and secure data integrity.
Use Cases: When to Choose Wired or Wireless
Wired networks offer enhanced security and stable connections, making them ideal for environments requiring high data transfer rates and minimal latency, such as data centers, corporate offices, and gaming setups. Wireless networks provide flexibility and mobility, supporting devices in dynamic environments like cafes, airports, and smart homes where convenience and ease of installation are priorities. Your choice depends on specific use cases: opt for wired networks when reliability and speed are critical, and choose wireless for mobility and quick access on the go.
Future Trends in Networking Technologies
Future trends in networking technologies emphasize the growth of wireless networks driven by 5G, Wi-Fi 6E, and emerging 6G standards, offering higher speeds, lower latency, and enhanced device connectivity. Wired networks continue to evolve with advancements in fiber-optic technology, including 400G and beyond, to support massive data transfer demands and ultra-reliable connections in data centers and enterprises. Hybrid network architectures integrating wired backbone and wireless access are becoming standard, optimizing performance, security, and scalability for next-generation applications like IoT, AI, and smart cities.
Wired Network vs Wireless Network Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com